Ozlem Garibay
Monkey Jump : MoE-Style PEFT for Efficient Multi-Task Learning
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Mixture-of-experts variants of parameter-efficient fine-tuning enable per-token specialization, but they introduce additional trainable routers and expert parameters, increasing memory usage and training cost. This undermines the core goal of parameter-efficient fine-tuning. We propose Monkey Jump, a method that brings mixture-of-experts-style specialization to parameter-efficient fine-tuning without introducing extra trainable parameters for experts or routers. Instead of adding new adapters as experts, Monkey Jump treats the adapters already present in each Transformer block (such as query, key, value, up, and down projections) as implicit experts and routes tokens among them. Routing is performed using k-means clustering with exponentially moving averaged cluster centers, requiring no gradients and no learned parameters. We theoretically show that token-wise routing increases expressivity and can outperform shared adapters by avoiding cancellation effects. Across multi-task experiments covering 14 text, 14 image, and 19 video benchmarks, Monkey Jump achieves competitive performance with mixture-of-experts-based parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods while using 7 to 29 times fewer trainable parameters, up to 48 percent lower memory consumption, and 1.5 to 2 times faster training. Monkey Jump is architecture-agnostic and can be applied to any adapter-based parameter-efficient fine-tuning method.
Predicting Through Generation: Why Generation Is Better for Prediction
Feb 25, 2025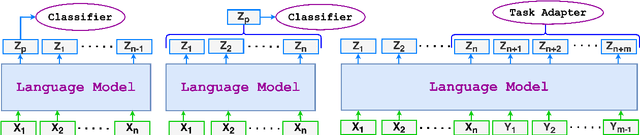
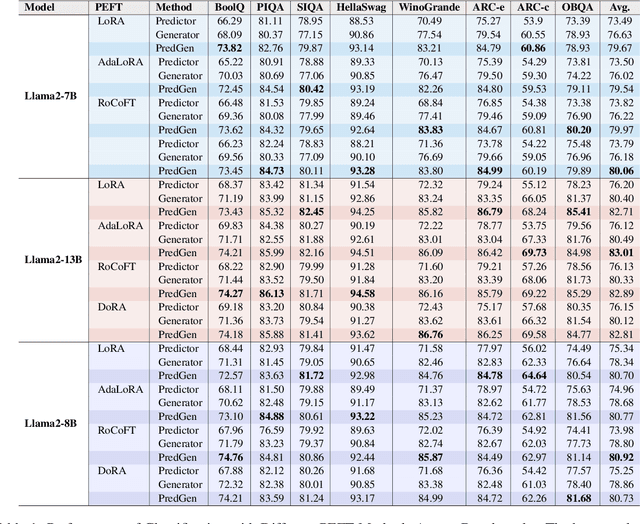
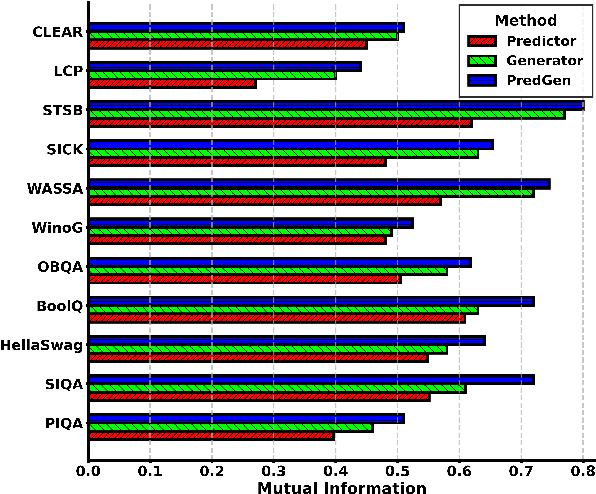
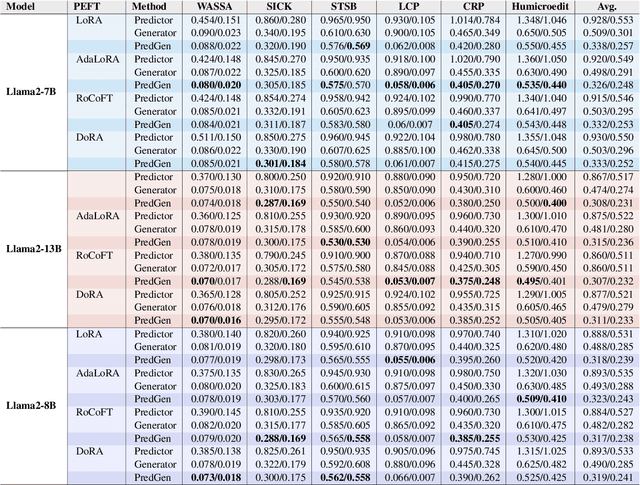
Abstract:This paper argues that generating output tokens is more effective than using pooled representations for prediction tasks because token-level generation retains more mutual information. Since LLMs are trained on massive text corpora using next-token prediction, generation aligns naturally with their learned behavior. Using the Data Processing Inequality (DPI), we provide both theoretical and empirical evidence supporting this claim. However, autoregressive models face two key challenges when used for prediction: (1) exposure bias, where the model sees ground truth tokens during training but relies on its own predictions during inference, leading to errors, and (2) format mismatch, where discrete tokens do not always align with the tasks required output structure. To address these challenges, we introduce PredGen(Predicting Through Generating), an end to end framework that (i) uses scheduled sampling to reduce exposure bias, and (ii) introduces a task adapter to convert the generated tokens into structured outputs. Additionally, we introduce Writer-Director Alignment Loss (WDAL), which ensures consistency between token generation and final task predictions, improving both text coherence and numerical accuracy. We evaluate PredGen on multiple classification and regression benchmarks. Our results show that PredGen consistently outperforms standard baselines, demonstrating its effectiveness in structured prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge