Or Hirschorn
Multi-View Foundation Models
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models are vital tools in various Computer Vision applications. They take as input a single RGB image and output a deep feature representation that is useful for various applications. However, in case we have multiple views of the same 3D scene, they operate on each image independently and do not always produce consistent features for the same 3D point. We propose a way to convert a Foundation Model into a Multi-View Foundation Model. Such a model takes as input a set of images and outputs a feature map for each image such that the features of corresponding points are as consistent as possible. This approach bypasses the need to build a consistent 3D model of the features and allows direct manipulation in the image space. Specifically, we show how to augment Transformers-based foundation models (i.e., DINO, SAM, CLIP) with intermediate 3D-aware attention layers that help match features across different views. As leading examples, we show surface normal estimation and multi-view segmentation tasks. Quantitative experiments show that our method improves feature matching considerably compared to current foundation models.
Splatent: Splatting Diffusion Latents for Novel View Synthesis
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Radiance field representations have recently been explored in the latent space of VAEs that are commonly used by diffusion models. This direction offers efficient rendering and seamless integration with diffusion-based pipelines. However, these methods face a fundamental limitation: The VAE latent space lacks multi-view consistency, leading to blurred textures and missing details during 3D reconstruction. Existing approaches attempt to address this by fine-tuning the VAE, at the cost of reconstruction quality, or by relying on pre-trained diffusion models to recover fine-grained details, at the risk of some hallucinations. We present Splatent, a diffusion-based enhancement framework designed to operate on top of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in the latent space of VAEs. Our key insight departs from the conventional 3D-centric view: rather than reconstructing fine-grained details in 3D space, we recover them in 2D from input views through multi-view attention mechanisms. This approach preserves the reconstruction quality of pretrained VAEs while achieving faithful detail recovery. Evaluated across multiple benchmarks, Splatent establishes a new state-of-the-art for VAE latent radiance field reconstruction. We further demonstrate that integrating our method with existing feed-forward frameworks, consistently improves detail preservation, opening new possibilities for high-quality sparse-view 3D reconstruction.
Sifting through the haystack -- efficiently finding rare animal behaviors in large-scale datasets
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:In the study of animal behavior, researchers often record long continuous videos, accumulating into large-scale datasets. However, the behaviors of interest are often rare compared to routine behaviors. This incurs a heavy cost on manual annotation, forcing users to sift through many samples before finding their needles. We propose a pipeline to efficiently sample rare behaviors from large datasets, enabling the creation of training datasets for rare behavior classifiers. Our method only needs an unlabeled animal pose or acceleration dataset as input and makes no assumptions regarding the type, number, or characteristics of the rare behaviors. Our pipeline is based on a recent graph-based anomaly detection model for human behavior, which we apply to this new data domain. It leverages anomaly scores to automatically label normal samples while directing human annotation efforts toward anomalies. In research data, anomalies may come from many different sources (e.g., signal noise versus true rare instances). Hence, the entire labeling budget is focused on the abnormal classes, letting the user review and label samples according to their needs. We tested our approach on three datasets of freely-moving animals, acquired in the laboratory and the field. We found that graph-based models are particularly useful when studying motion-based behaviors in animals, yielding good results while using a small labeling budget. Our method consistently outperformed traditional random sampling, offering an average improvement of 70% in performance and creating datasets even when the behavior of interest was only 0.02% of the data. Even when the performance gain was minor (e.g., when the behavior is not rare), our method still reduced the annotation effort by half
Edge Weight Prediction For Category-Agnostic Pose Estimation
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Category-Agnostic Pose Estimation (CAPE) localizes keypoints across diverse object categories with a single model, using one or a few annotated support images. Recent works have shown that using a pose graph (i.e., treating keypoints as nodes in a graph rather than isolated points) helps handle occlusions and break symmetry. However, these methods assume a static pose graph with equal-weight edges, leading to suboptimal results. We introduce EdgeCape, a novel framework that overcomes these limitations by predicting the graph's edge weights which optimizes localization. To further leverage structural priors, we propose integrating Markovian Structural Bias, which modulates the self-attention interaction between nodes based on the number of hops between them. We show that this improves the model's ability to capture global spatial dependencies. Evaluated on the MP-100 benchmark, which includes 100 categories and over 20K images, EdgeCape achieves state-of-the-art results in the 1-shot setting and leads among similar-sized methods in the 5-shot setting, significantly improving keypoint localization accuracy. Our code is publicly available.
CapeX: Category-Agnostic Pose Estimation from Textual Point Explanation
Jun 01, 2024



Abstract:Conventional 2D pose estimation models are constrained by their design to specific object categories. This limits their applicability to predefined objects. To overcome these limitations, category-agnostic pose estimation (CAPE) emerged as a solution. CAPE aims to facilitate keypoint localization for diverse object categories using a unified model, which can generalize from minimal annotated support images. Recent CAPE works have produced object poses based on arbitrary keypoint definitions annotated on a user-provided support image. Our work departs from conventional CAPE methods, which require a support image, by adopting a text-based approach instead of the support image. Specifically, we use a pose-graph, where nodes represent keypoints that are described with text. This representation takes advantage of the abstraction of text descriptions and the structure imposed by the graph. Our approach effectively breaks symmetry, preserves structure, and improves occlusion handling. We validate our novel approach using the MP-100 benchmark, a comprehensive dataset spanning over 100 categories and 18,000 images. Under a 1-shot setting, our solution achieves a notable performance boost of 1.07\%, establishing a new state-of-the-art for CAPE. Additionally, we enrich the dataset by providing text description annotations, further enhancing its utility for future research.
Optimize and Reduce: A Top-Down Approach for Image Vectorization
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:Vector image representation is a popular choice when editability and flexibility in resolution are desired. However, most images are only available in raster form, making raster-to-vector image conversion (vectorization) an important task. Classical methods for vectorization are either domain-specific or yield an abundance of shapes which limits editability and interpretability. Learning-based methods, that use differentiable rendering, have revolutionized vectorization, at the cost of poor generalization to out-of-training distribution domains, and optimization-based counterparts are either slow or produce non-editable and redundant shapes. In this work, we propose Optimize & Reduce (O&R), a top-down approach to vectorization that is both fast and domain-agnostic. O&R aims to attain a compact representation of input images by iteratively optimizing B\'ezier curve parameters and significantly reducing the number of shapes, using a devised importance measure. We contribute a benchmark of five datasets comprising images from a broad spectrum of image complexities - from emojis to natural-like images. Through extensive experiments on hundreds of images, we demonstrate that our method is domain agnostic and outperforms existing works in both reconstruction and perceptual quality for a fixed number of shapes. Moreover, we show that our algorithm is $\times 10$ faster than the state-of-the-art optimization-based method.
Pose Anything: A Graph-Based Approach for Category-Agnostic Pose Estimation
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:Traditional 2D pose estimation models are limited by their category-specific design, making them suitable only for predefined object categories. This restriction becomes particularly challenging when dealing with novel objects due to the lack of relevant training data. To address this limitation, category-agnostic pose estimation (CAPE) was introduced. CAPE aims to enable keypoint localization for arbitrary object categories using a single model, requiring minimal support images with annotated keypoints. This approach not only enables object pose generation based on arbitrary keypoint definitions but also significantly reduces the associated costs, paving the way for versatile and adaptable pose estimation applications. We present a novel approach to CAPE that leverages the inherent geometrical relations between keypoints through a newly designed Graph Transformer Decoder. By capturing and incorporating this crucial structural information, our method enhances the accuracy of keypoint localization, marking a significant departure from conventional CAPE techniques that treat keypoints as isolated entities. We validate our approach on the MP-100 benchmark, a comprehensive dataset comprising over 20,000 images spanning more than 100 categories. Our method outperforms the prior state-of-the-art by substantial margins, achieving remarkable improvements of 2.16% and 1.82% under 1-shot and 5-shot settings, respectively. Furthermore, our method's end-to-end training demonstrates both scalability and efficiency compared to previous CAPE approaches.
Normalizing Flows for Human Pose Anomaly Detection
Nov 20, 2022



Abstract:Video anomaly detection is an ill-posed problem because it relies on many parameters such as appearance, pose, camera angle, background, and more. We distill the problem to anomaly detection of human pose, thus reducing the risk of nuisance parameters such as appearance affecting the result. Focusing on pose alone also has the side benefit of reducing bias against distinct minority groups. Our model works directly on human pose graph sequences and is exceptionally lightweight ($\sim1K$ parameters), capable of running on any machine able to run the pose estimation with negligible additional resources. We leverage the highly compact pose representation in a normalizing flows framework, which we extend to tackle the unique characteristics of spatio-temporal pose data and show its advantages in this use case. Our algorithm uses normalizing flows to learn a bijective mapping between the pose data distribution and a Gaussian distribution, using spatio-temporal graph convolution blocks. The algorithm is quite general and can handle training data of only normal examples, as well as a supervised dataset that consists of labeled normal and abnormal examples. We report state-of-the-art results on two anomaly detection benchmarks - the unsupervised ShanghaiTech dataset and the recent supervised UBnormal dataset.
Shape-consistent Generative Adversarial Networks for multi-modal Medical segmentation maps
Feb 04, 2022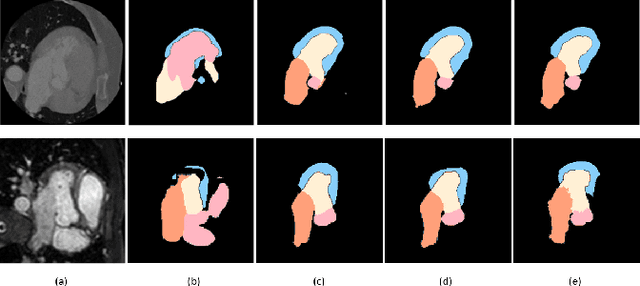
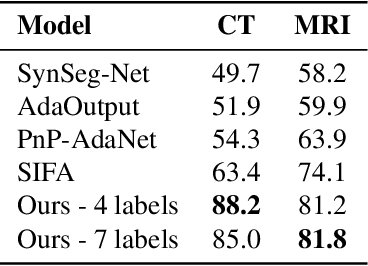
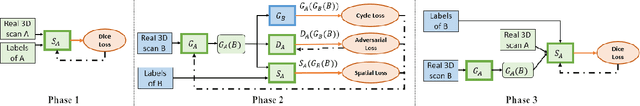

Abstract:Image translation across domains for unpaired datasets has gained interest and great improvement lately. In medical imaging, there are multiple imaging modalities, with very different characteristics. Our goal is to use cross-modality adaptation between CT and MRI whole cardiac scans for semantic segmentation. We present a segmentation network using synthesised cardiac volumes for extremely limited datasets. Our solution is based on a 3D cross-modality generative adversarial network to share information between modalities and generate synthesized data using unpaired datasets. Our network utilizes semantic segmentation to improve generator shape consistency, thus creating more realistic synthesised volumes to be used when re-training the segmentation network. We show that improved segmentation can be achieved on small datasets when using spatial augmentations to improve a generative adversarial network. These augmentations improve the generator capabilities, thus enhancing the performance of the Segmentor. Using only 16 CT and 16 MRI cardiovascular volumes, improved results are shown over other segmentation methods while using the suggested architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge