Onur Gungor
TurkBench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Turkish Large Language Models
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:With the recent surge in the development of large language models, the need for comprehensive and language-specific evaluation benchmarks has become critical. While significant progress has been made in evaluating English language models, benchmarks for other languages, particularly those with unique linguistic characteristics such as Turkish, remain less developed. Our study introduces TurkBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to assess the capabilities of generative large language models in the Turkish language. TurkBench involves 8,151 data samples across 21 distinct subtasks. These are organized under six main categories of evaluation: Knowledge, Language Understanding, Reasoning, Content Moderation, Turkish Grammar and Vocabulary, and Instruction Following. The diverse range of tasks and the culturally relevant data would provide researchers and developers with a valuable tool for evaluating their models and identifying areas for improvement. We further publish our benchmark for online submissions at https://huggingface.co/turkbench
Improving Pinterest Search Relevance Using Large Language Models
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:To improve relevance scoring on Pinterest Search, we integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) into our search relevance model, leveraging carefully designed text representations to predict the relevance of Pins effectively. Our approach uses search queries alongside content representations that include captions extracted from a generative visual language model. These are further enriched with link-based text data, historically high-quality engaged queries, user-curated boards, Pin titles and Pin descriptions, creating robust models for predicting search relevance. We use a semi-supervised learning approach to efficiently scale up the amount of training data, expanding beyond the expensive human labeled data available. By utilizing multilingual LLMs, our system extends training data to include unseen languages and domains, despite initial data and annotator expertise being confined to English. Furthermore, we distill from the LLM-based model into real-time servable model architectures and features. We provide comprehensive offline experimental validation for our proposed techniques and demonstrate the gains achieved through the final deployed system at scale.
Morphological Embeddings for Named Entity Recognition in Morphologically Rich Languages
Jun 01, 2017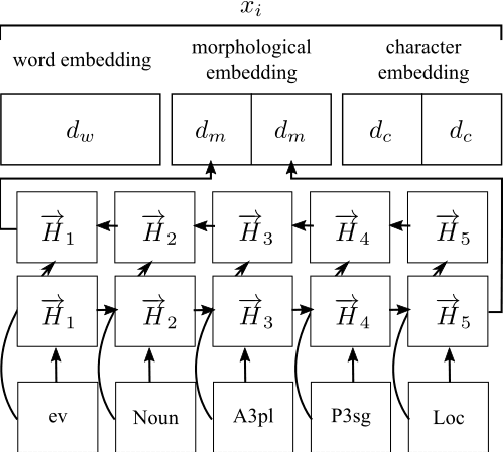

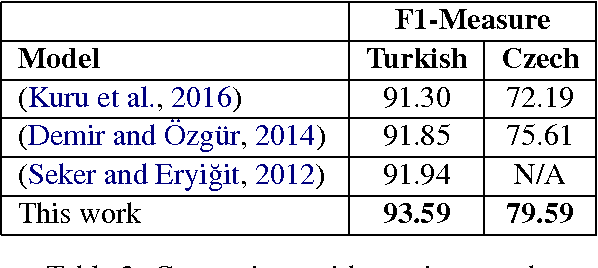
Abstract:In this work, we present new state-of-the-art results of 93.59,% and 79.59,% for Turkish and Czech named entity recognition based on the model of (Lample et al., 2016). We contribute by proposing several schemes for representing the morphological analysis of a word in the context of named entity recognition. We show that a concatenation of this representation with the word and character embeddings improves the performance. The effect of these representation schemes on the tagging performance is also investigated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge