Oisín Boydell
Deep learning at the shallow end: Malware classification for non-domain experts
Jul 22, 2018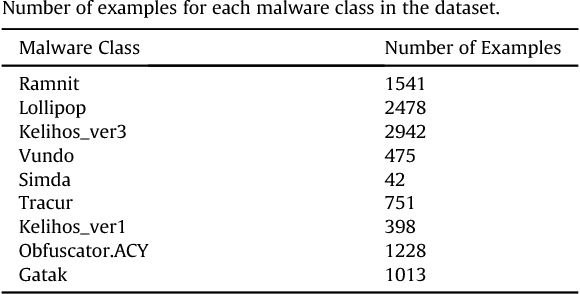
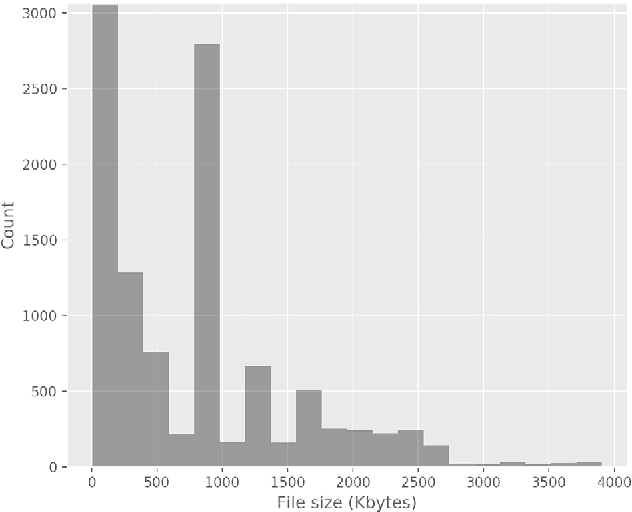

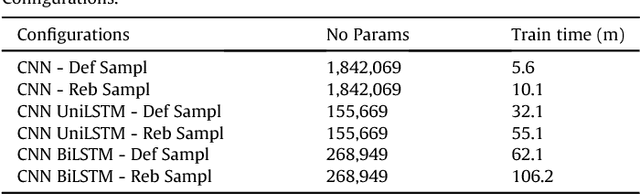
Abstract:Current malware detection and classification approaches generally rely on time consuming and knowledge intensive processes to extract patterns (signatures) and behaviors from malware, which are then used for identification. Moreover, these signatures are often limited to local, contiguous sequences within the data whilst ignoring their context in relation to each other and throughout the malware file as a whole. We present a Deep Learning based malware classification approach that requires no expert domain knowledge and is based on a purely data driven approach for complex pattern and feature identification.
Topic Stability over Noisy Sources
Aug 05, 2015



Abstract:Topic modelling techniques such as LDA have recently been applied to speech transcripts and OCR output. These corpora may contain noisy or erroneous texts which may undermine topic stability. Therefore, it is important to know how well a topic modelling algorithm will perform when applied to noisy data. In this paper we show that different types of textual noise will have diverse effects on the stability of different topic models. From these observations, we propose guidelines for text corpus generation, with a focus on automatic speech transcription. We also suggest topic model selection methods for noisy corpora.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge