Ning Bian
Rule or Story, Which is a Better Commonsense Expression for Talking with Large Language Models?
Feb 22, 2024Abstract:Building machines with commonsense has been a longstanding challenge in NLP due to the reporting bias of commonsense rules and the exposure bias of rule-based commonsense reasoning. In contrast, humans convey and pass down commonsense implicitly through stories. This paper investigates the inherent commonsense ability of large language models (LLMs) expressed through storytelling. We systematically investigate and compare stories and rules for retrieving and leveraging commonsense in LLMs. Experimental results on 28 commonsense QA datasets show that stories outperform rules as the expression for retrieving commonsense from LLMs, exhibiting higher generation confidence and commonsense accuracy. Moreover, stories are the more effective commonsense expression for answering questions regarding daily events, while rules are more effective for scientific questions. This aligns with the reporting bias of commonsense in text corpora. We further show that the correctness and relevance of commonsense stories can be further improved via iterative self-supervised fine-tuning. These findings emphasize the importance of using appropriate language to express, retrieve, and leverage commonsense for LLMs, highlighting a promising direction for better exploiting their commonsense abilities.
A Drop of Ink may Make a Million Think: The Spread of False Information in Large Language Models
May 08, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT have gained increasing prominence in artificial intelligence, making a profound impact on society and various industries like business and science. However, the presence of false information on the internet and in text corpus poses a significant risk to the reliability and safety of LLMs, underscoring the urgent need to understand the mechanisms of how false information impacts and spreads in LLMs. In this paper, we investigate how false information spreads in LLMs and affects related responses by conducting a series of experiments on the effects of source authority, injection paradigm, and information relevance. Specifically, we compare four authority levels of information sources (Twitter, web blogs, news reports, and research papers), two common knowledge injection paradigms (in-context injection and learning-based injection), and three degrees of information relevance (direct, indirect, and peripheral). The experimental results show that (1) False information will spread and contaminate related memories in LLMs via a semantic diffusion process, i.e., false information has global detrimental effects beyond its direct impact. (2) Current LLMs are susceptible to authority bias, i.e., LLMs are more likely to follow false information presented in a trustworthy style like news or research papers, which usually causes deeper and wider pollution of information. (3) Current LLMs are more sensitive to false information through in-context injection than through learning-based injection, which severely challenges the reliability and safety of LLMs even if all training data are trusty and correct. The above findings raise the need for new false information defense algorithms to address the global impact of false information, and new alignment algorithms to unbiasedly lead LLMs to follow internal human values rather than superficial patterns.
ChatGPT is a Knowledgeable but Inexperienced Solver: An Investigation of Commonsense Problem in Large Language Models
Mar 29, 2023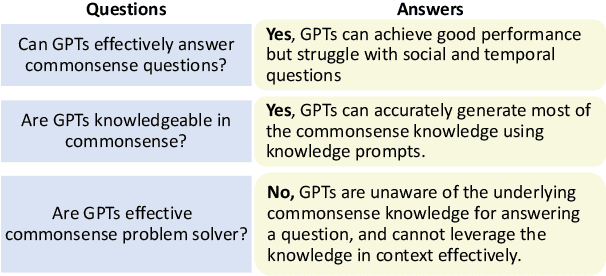

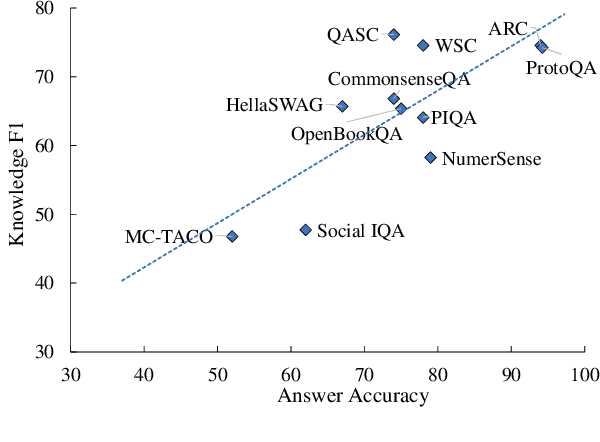
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 have made significant progress in NLP. However, their ability to memorize, represent, and leverage commonsense knowledge has been a well-known pain point for LLMs. It remains unclear that: (1) Can GPTs effectively answer commonsense questions? (2) Are GPTs knowledgeable in commonsense? (3) Are GPTs aware of the underlying commonsense knowledge for answering a specific question? (4) Can GPTs effectively leverage commonsense for answering questions? To evaluate the above commonsense problems, we conduct a series of experiments to evaluate ChatGPT's commonsense abilities, and the experimental results show that: (1) GPTs can achieve good QA accuracy in commonsense tasks, while they still struggle with certain types of knowledge. (2) ChatGPT is knowledgeable, and can accurately generate most of the commonsense knowledge using knowledge prompts. (3) Despite its knowledge, ChatGPT is an inexperienced commonsense problem solver, which cannot precisely identify the needed commonsense knowledge for answering a specific question, i.e., ChatGPT does not precisely know what commonsense knowledge is required to answer a question. The above findings raise the need to investigate better mechanisms for utilizing commonsense knowledge in LLMs, such as instruction following, better commonsense guidance, etc.
Bridging the Gap between Language Model and Reading Comprehension: Unsupervised MRC via Self-Supervision
Jul 19, 2021



Abstract:Despite recent success in machine reading comprehension (MRC), learning high-quality MRC models still requires large-scale labeled training data, even using strong pre-trained language models (PLMs). The pre-training tasks for PLMs are not question-answering or MRC-based tasks, making existing PLMs unable to be directly used for unsupervised MRC. Specifically, MRC aims to spot an accurate answer span from the given document, but PLMs focus on token filling in sentences. In this paper, we propose a new framework for unsupervised MRC. Firstly, we propose to learn to spot answer spans in documents via self-supervised learning, by designing a self-supervision pretext task for MRC - Spotting-MLM. Solving this task requires capturing deep interactions between sentences in documents. Secondly, we apply a simple sentence rewriting strategy in the inference stage to alleviate the expression mismatch between questions and documents. Experiments show that our method achieves a new state-of-the-art performance for unsupervised MRC.
Benchmarking Knowledge-Enhanced Commonsense Question Answering via Knowledge-to-Text Transformation
Jan 05, 2021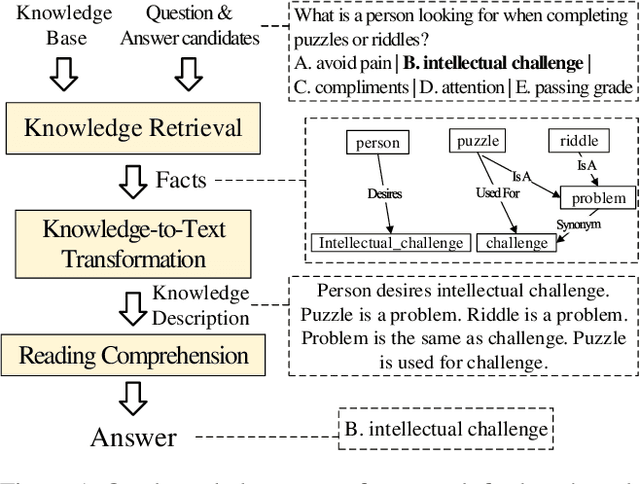
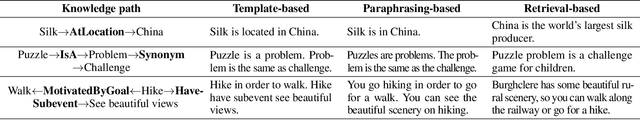
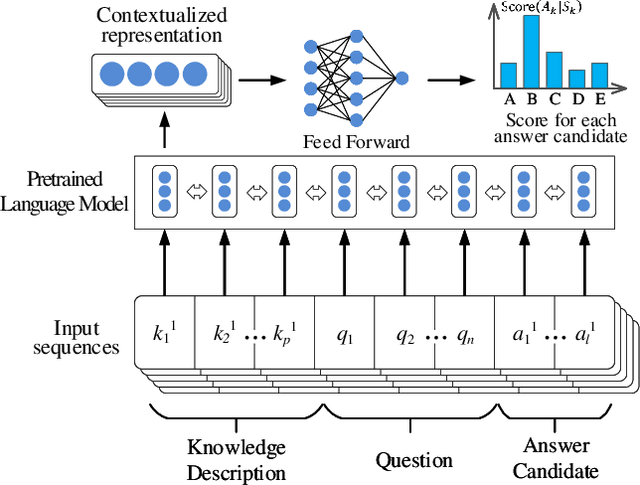
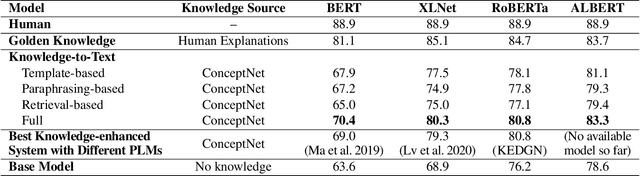
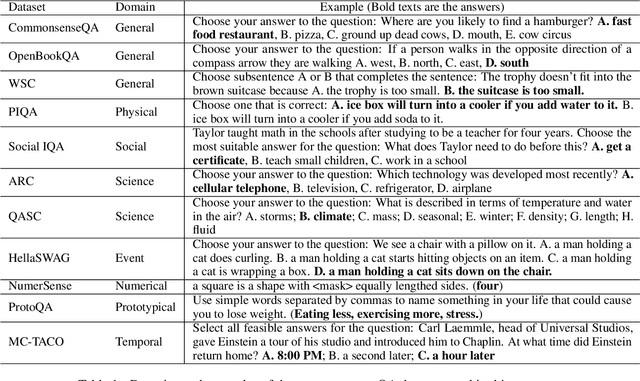
Abstract:A fundamental ability of humans is to utilize commonsense knowledge in language understanding and question answering. In recent years, many knowledge-enhanced Commonsense Question Answering (CQA) approaches have been proposed. However, it remains unclear: (1) How far can we get by exploiting external knowledge for CQA? (2) How much potential of knowledge has been exploited in current CQA models? (3) Which are the most promising directions for future CQA? To answer these questions, we benchmark knowledge-enhanced CQA by conducting extensive experiments on multiple standard CQA datasets using a simple and effective knowledge-to-text transformation framework. Experiments show that: (1) Our knowledge-to-text framework is effective and achieves state-of-the-art performance on CommonsenseQA dataset, providing a simple and strong knowledge-enhanced baseline for CQA; (2) The potential of knowledge is still far from being fully exploited in CQA -- there is a significant performance gap from current models to our models with golden knowledge; and (3) Context-sensitive knowledge selection, heterogeneous knowledge exploitation, and commonsense-rich language models are promising CQA directions.
From Bag of Sentences to Document: Distantly Supervised Relation Extraction via Machine Reading Comprehension
Dec 09, 2020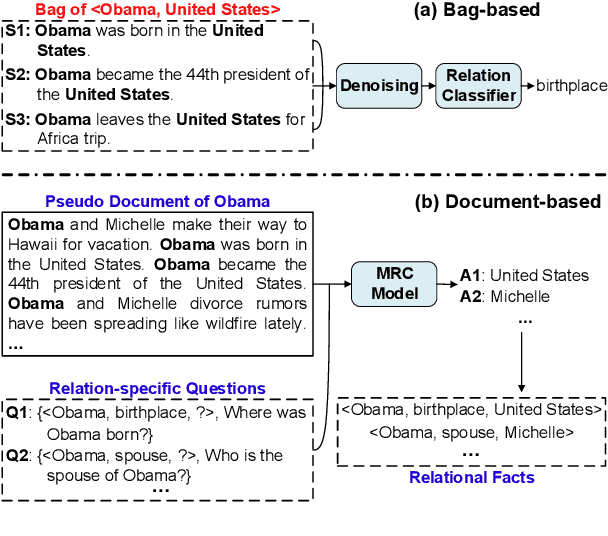

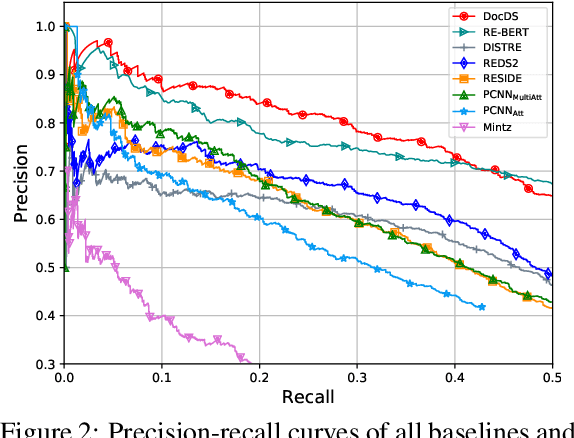
Abstract:Distant supervision (DS) is a promising approach for relation extraction but often suffers from the noisy label problem. Traditional DS methods usually represent an entity pair as a bag of sentences and denoise labels using multi-instance learning techniques. The bag-based paradigm, however, fails to leverage the inter-sentence-level and the entity-level evidence for relation extraction, and their denoising algorithms are often specialized and complicated. In this paper, we propose a new DS paradigm--document-based distant supervision, which models relation extraction as a document-based machine reading comprehension (MRC) task. By re-organizing all sentences about an entity as a document and extracting relations via querying the document with relation-specific questions, the document-based DS paradigm can simultaneously encode and exploit all sentence-level, inter-sentence-level, and entity-level evidence. Furthermore, we design a new loss function--DSLoss (distant supervision loss), which can effectively train MRC models using only $\langle$document, question, answer$\rangle$ tuples, therefore noisy label problem can be inherently resolved. Experiments show that our method achieves new state-of-the-art DS performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge