Nima Akhlaghi
Sparsity Analysis of a Sonomyographic Muscle-Computer Interface
Sep 06, 2018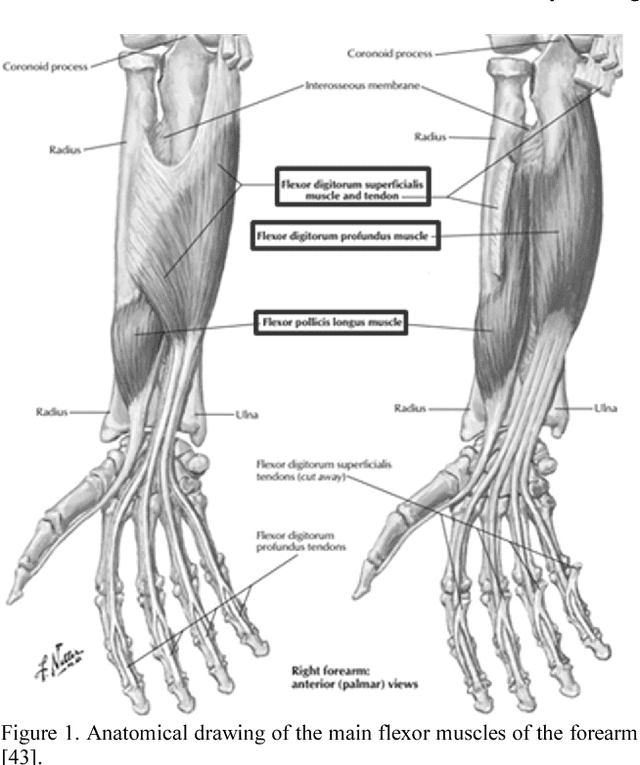
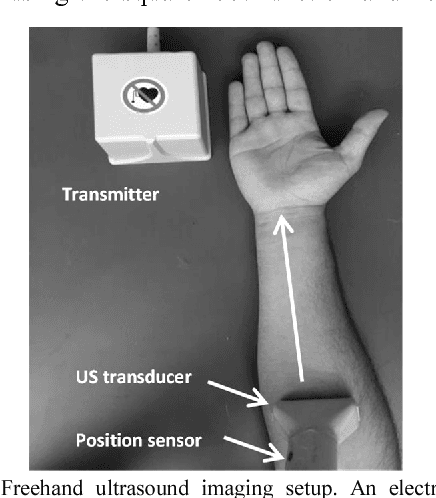
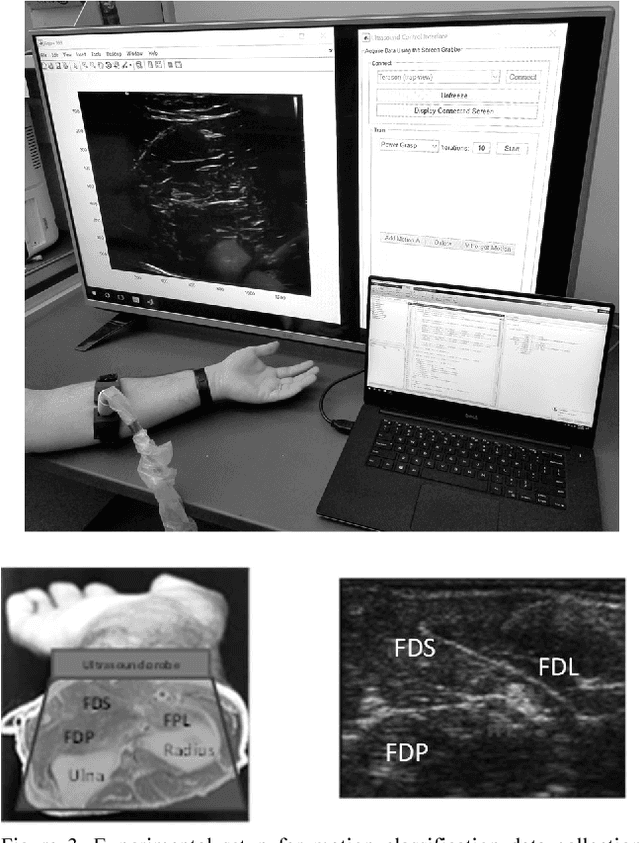
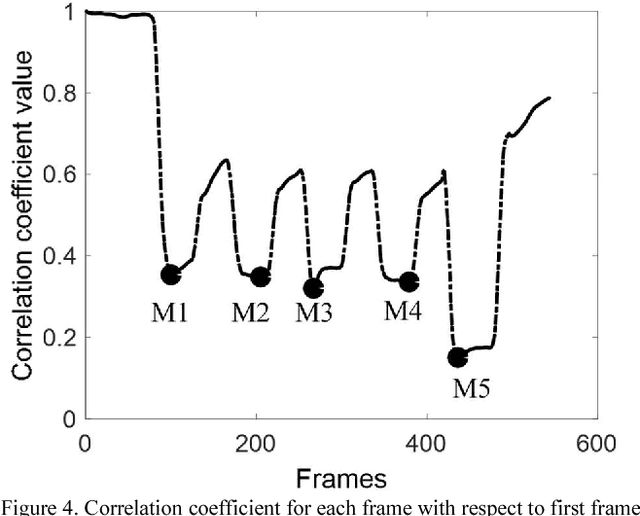
Abstract:Objective: The objectives of this paper are to determine the optimal location for ultrasound transducer placement on the anterior forearm for imaging maximum muscle deformations during different hand motions and to investigate the effect of using a sparse set of ultrasound scanlines for motion classification for ultrasound-based muscle computer interfaces (MCIs). Methods: The optimal placement of the ultrasound transducer along the forearm is identified using freehand 3D reconstructions of the muscle thickness during rest and motion completion. From the ultrasound images acquired from the optimally placed transducer, we determine classification accuracy with equally spaced scanlines across the cross-sectional field-of-view (FOV). Furthermore, we investigated the unique contribution of each scanline to class discrimination using Fisher criteria (FC) and mutual information (MI) with respect to motion discriminability. Results: Experiments with 5 able-bodied subjects show that the maximum muscle deformation occurred between 30-50% of the forearm length for multiple degrees-of-freedom. The average classification accuracy was 94.6% with the entire 128 scanline image and 94.5% with 4 equally-spaced scanlines. However, no significant improvement in classification accuracy was observed with optimal scanline selection using FC and MI. Conclusion: For an optimally placed transducer, a small subset of ultrasound scanlines can be used instead of a full imaging array without sacrificing performance in terms of classification accuracy for multiple degrees-of-freedom. Significance: The selection of a small subset of transducer elements can enable the reduction of computation, and simplification of the instrumentation and power consumption of wearable sonomyographic MCIs particularly for rehabilitation and gesture recognition applications.
Proprioceptive Sonomyographic Control: A novel method of intuitive proportional control of multiple degrees of freedom for upper-extremity amputees
Aug 20, 2018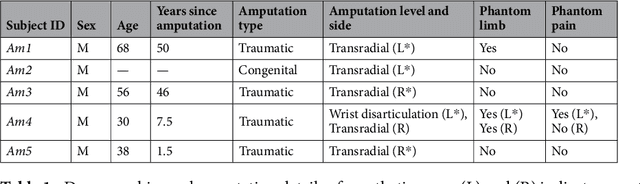
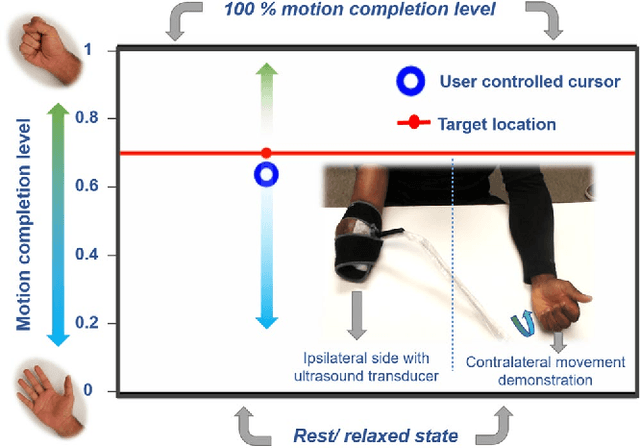
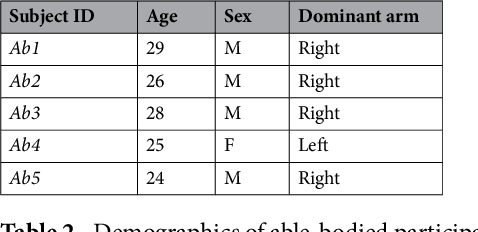
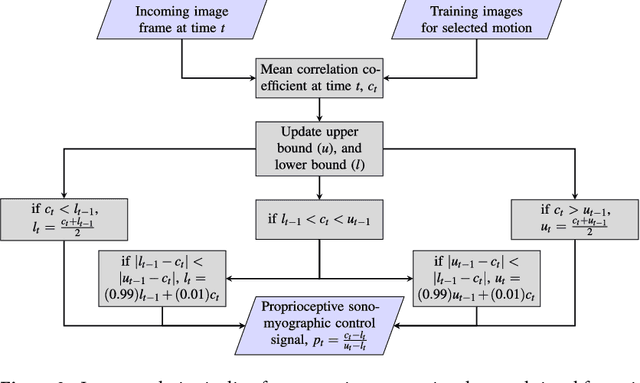
Abstract:Technological advances in multi-articulated prosthetic hands have outpaced the methods available to amputees to intuitively control these devices. Amputees often cite difficulty of use as a key contributing factor for abandoning their prosthesis, creating a pressing need for improved control technology. A major challenge of traditional myoelectric control strategies using surface electromyography electrodes has been the difficulty in achieving intuitive and robust proportional control of multiple degrees of freedom. In this paper, we describe a new control method, proprioceptive sonomyographic control that overcomes several limitations of myoelectric control. In sonomyography, muscle mechanical deformation is sensed using ultrasound, as compared to electrical activation, and therefore the resulting control signals can directly control the position of the end effector. Compared to myoelectric control which controls the velocity of the end-effector device, sonomyographic control is more congruent with residual proprioception in the residual limb. We tested our approach with 5 upper-extremity amputees and able-bodied subjects using a virtual target achievement and holding task. Amputees and able-bodied participants demonstrated the ability to achieve positional control for 5 degrees of freedom with an hour of training. Our results demonstrate the potential of proprioceptive sonomyographic control for intuitive dexterous control of multiarticulated prostheses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge