Proprioceptive Sonomyographic Control: A novel method of intuitive proportional control of multiple degrees of freedom for upper-extremity amputees
Paper and Code
Aug 20, 2018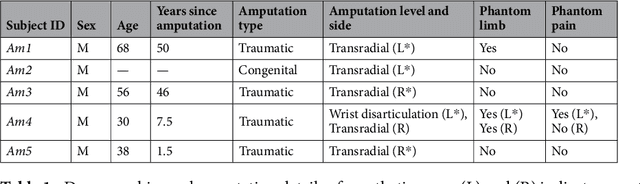
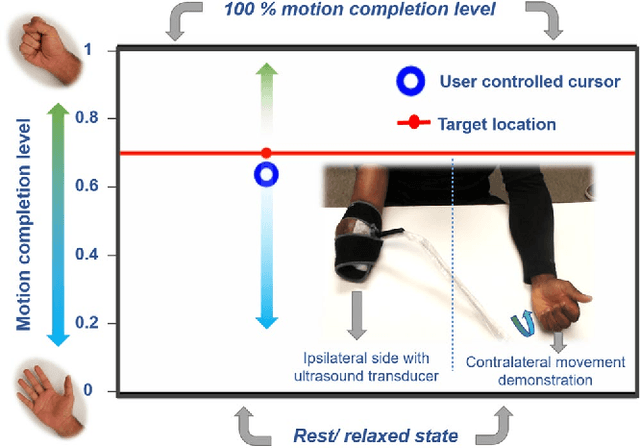
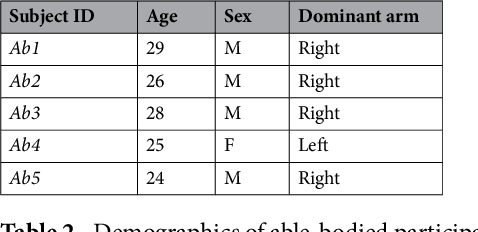
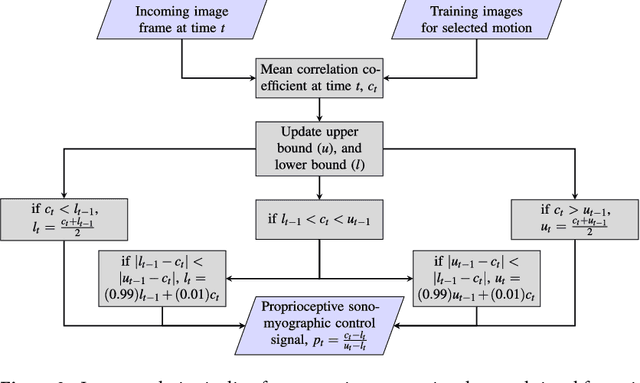
Technological advances in multi-articulated prosthetic hands have outpaced the methods available to amputees to intuitively control these devices. Amputees often cite difficulty of use as a key contributing factor for abandoning their prosthesis, creating a pressing need for improved control technology. A major challenge of traditional myoelectric control strategies using surface electromyography electrodes has been the difficulty in achieving intuitive and robust proportional control of multiple degrees of freedom. In this paper, we describe a new control method, proprioceptive sonomyographic control that overcomes several limitations of myoelectric control. In sonomyography, muscle mechanical deformation is sensed using ultrasound, as compared to electrical activation, and therefore the resulting control signals can directly control the position of the end effector. Compared to myoelectric control which controls the velocity of the end-effector device, sonomyographic control is more congruent with residual proprioception in the residual limb. We tested our approach with 5 upper-extremity amputees and able-bodied subjects using a virtual target achievement and holding task. Amputees and able-bodied participants demonstrated the ability to achieve positional control for 5 degrees of freedom with an hour of training. Our results demonstrate the potential of proprioceptive sonomyographic control for intuitive dexterous control of multiarticulated prostheses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge