Nikola Cenikj
Multi-View Stenosis Classification Leveraging Transformer-Based Multiple-Instance Learning Using Real-World Clinical Data
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Coronary artery stenosis is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, diagnosed by analyzing the coronary arteries from multiple angiography views. Although numerous deep-learning models have been proposed for stenosis detection from a single angiography view, their performance heavily relies on expensive view-level annotations, which are often not readily available in hospital systems. Moreover, these models fail to capture the temporal dynamics and dependencies among multiple views, which are crucial for clinical diagnosis. To address this, we propose SegmentMIL, a transformer-based multi-view multiple-instance learning framework for patient-level stenosis classification. Trained on a real-world clinical dataset, using patient-level supervision and without any view-level annotations, SegmentMIL jointly predicts the presence of stenosis and localizes the affected anatomical region, distinguishing between the right and left coronary arteries and their respective segments. SegmentMIL obtains high performance on internal and external evaluations and outperforms both view-level models and classical MIL baselines, underscoring its potential as a clinically viable and scalable solution for coronary stenosis diagnosis. Our code is available at https://github.com/NikolaCenic/mil-stenosis.
Landscape Features in Single-Objective Continuous Optimization: Have We Hit a Wall in Algorithm Selection Generalization?
Jan 29, 2025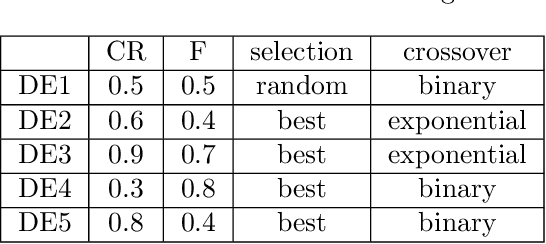
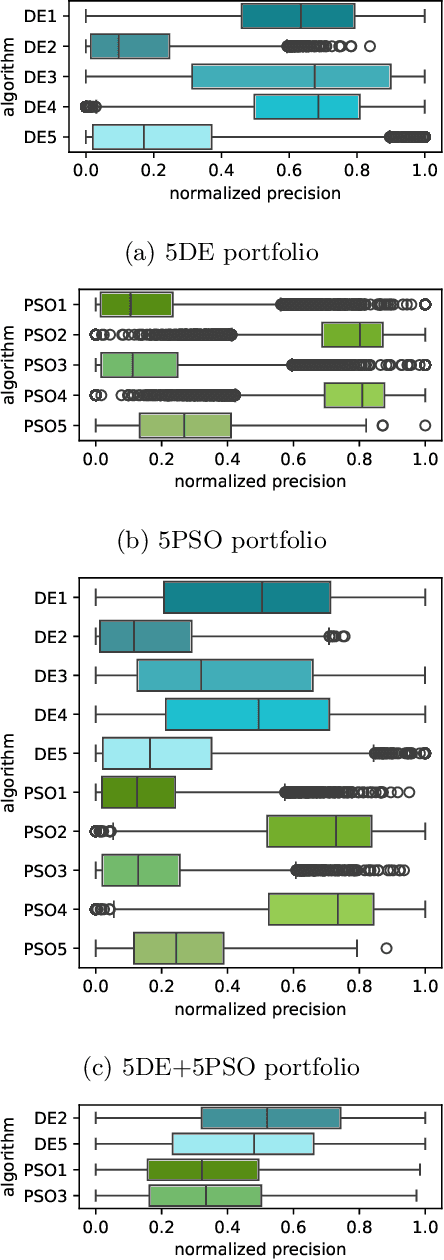
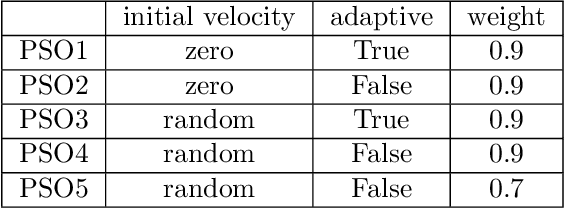
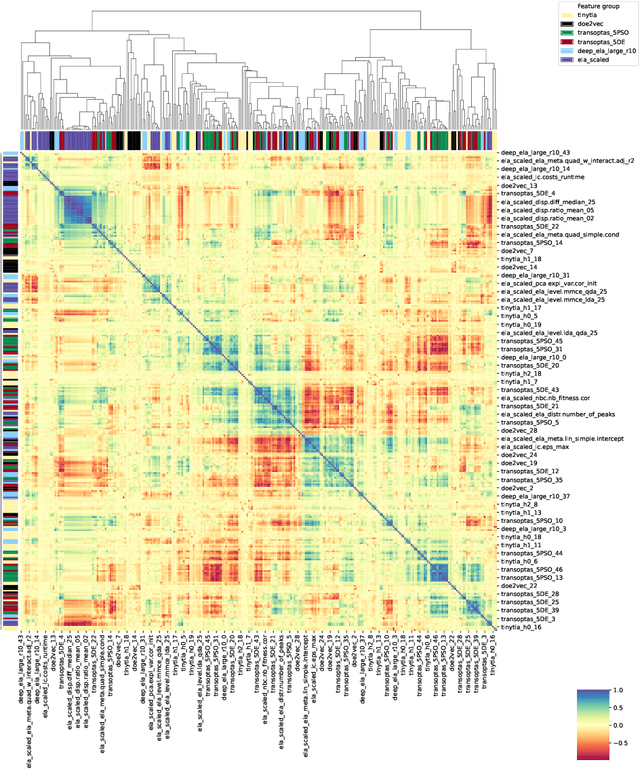
Abstract:%% Text of abstract The process of identifying the most suitable optimization algorithm for a specific problem, referred to as algorithm selection (AS), entails training models that leverage problem landscape features to forecast algorithm performance. A significant challenge in this domain is ensuring that AS models can generalize effectively to novel, unseen problems. This study evaluates the generalizability of AS models based on different problem representations in the context of single-objective continuous optimization. In particular, it considers the most widely used Exploratory Landscape Analysis features, as well as recently proposed Topological Landscape Analysis features, and features based on deep learning, such as DeepELA, TransOptAS and Doe2Vec. Our results indicate that when presented with out-of-distribution evaluation data, none of the feature-based AS models outperform a simple baseline model, i.e., a Single Best Solver.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge