Nicola Neophytou
Information Access of the Oppressed: A Problem-Posing Framework for Envisioning Emancipatory Information Access Platforms
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Online information access (IA) platforms are targets of authoritarian capture. These concerns are particularly serious and urgent today in light of the rising levels of democratic erosion worldwide, the emerging capabilities of generative AI technologies such as AI persuasion, and the increasing concentration of economic and political power in the hands of Big Tech. This raises the question of what alternative IA infrastructure we must reimagine and build to mitigate the risks of authoritarian capture of our information ecosystems. We explore this question through the lens of Paulo Freire's theories of emancipatory pedagogy. Freire's theories provide a radically different lens for exploring IA's sociotechnical concerns relative to the current dominating frames of fairness, accountability, confidentiality, transparency, and safety. We make explicit, with the intention to challenge, the dichotomy of how we relate to technology as either technologists (who envision and build technology) and its users. We posit that this mirrors the teacher-student relationship in Freire's analysis. By extending Freire's analysis to IA, we challenge the notion that it is the burden of the (altruistic) technologists to come up with interventions to mitigate the risks that emerging technologies pose to marginalized communities. Instead, we advocate that the first task for the technologists is to pose these as problems to the marginalized communities, to encourage them to make and unmake the technology as part of their material struggle against oppression. Their second task is to redesign our online technology stacks to structurally expose spaces for community members to co-opt and co-construct the technology in aid of their emancipatory struggles. We operationalize Freire's theories to develop a problem-posing framework for envisioning emancipatory IA platforms of the future.
Embedding Cultural Diversity in Prototype-based Recommender Systems
Dec 18, 2024

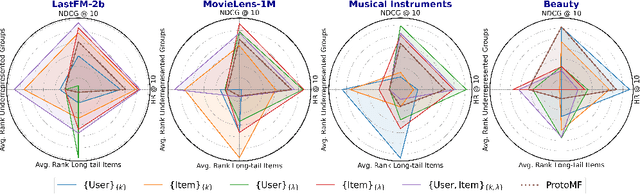

Abstract:Popularity bias in recommender systems can increase cultural overrepresentation by favoring norms from dominant cultures and marginalizing underrepresented groups. This issue is critical for platforms offering cultural products, as they influence consumption patterns and human perceptions. In this work, we address popularity bias by identifying demographic biases within prototype-based matrix factorization methods. Using the country of origin as a proxy for cultural identity, we link this demographic attribute to popularity bias by refining the embedding space learning process. First, we propose filtering out irrelevant prototypes to improve representativity. Second, we introduce a regularization technique to enforce a uniform distribution of prototypes within the embedding space. Across four datasets, our results demonstrate a 27\% reduction in the average rank of long-tail items and a 2\% reduction in the average rank of items from underrepresented countries. Additionally, our model achieves a 2\% improvement in HitRatio@10 compared to the state-of-the-art, highlighting that fairness is enhanced without compromising recommendation quality. Moreover, the distribution of prototypes leads to more inclusive explanations by better aligning items with diverse prototypes.
Advancing Cultural Inclusivity: Optimizing Embedding Spaces for Balanced Music Recommendations
May 27, 2024Abstract:Popularity bias in music recommendation systems -- where artists and tracks with the highest listen counts are recommended more often -- can also propagate biases along demographic and cultural axes. In this work, we identify these biases in recommendations for artists from underrepresented cultural groups in prototype-based matrix factorization methods. Unlike traditional matrix factorization methods, prototype-based approaches are interpretable. This allows us to directly link the observed bias in recommendations for minority artists (the effect) to specific properties of the embedding space (the cause). We mitigate popularity bias in music recommendation through capturing both users' and songs' cultural nuances in the embedding space. To address these challenges while maintaining recommendation quality, we propose two novel enhancements to the embedding space: i) we propose an approach to filter-out the irrelevant prototypes used to represent each user and item to improve generalizability, and ii) we introduce regularization techniques to reinforce a more uniform distribution of prototypes within the embedding space. Our results demonstrate significant improvements in reducing popularity bias and enhancing demographic and cultural fairness in music recommendations while achieving competitive -- if not better -- overall performance.
PrivFairFL: Privacy-Preserving Group Fairness in Federated Learning
May 23, 2022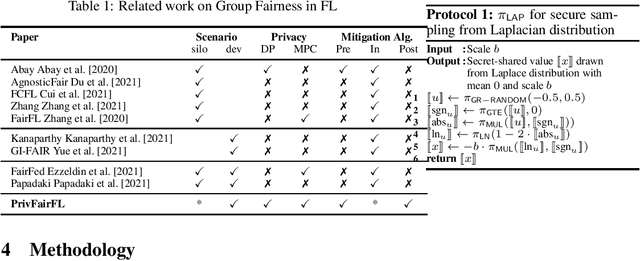
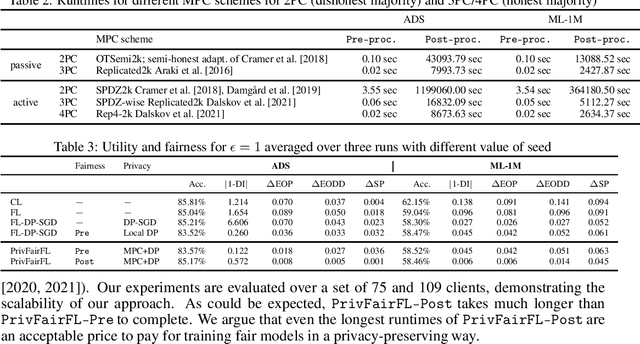
Abstract:Group fairness ensures that the outcome of machine learning (ML) based decision making systems are not biased towards a certain group of people defined by a sensitive attribute such as gender or ethnicity. Achieving group fairness in Federated Learning (FL) is challenging because mitigating bias inherently requires using the sensitive attribute values of all clients, while FL is aimed precisely at protecting privacy by not giving access to the clients' data. As we show in this paper, this conflict between fairness and privacy in FL can be resolved by combining FL with Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC) and Differential Privacy (DP). In doing so, we propose a method for training group-fair ML models in cross-device FL under complete and formal privacy guarantees, without requiring the clients to disclose their sensitive attribute values.
Revisiting Popularity and Demographic Biases in Recommender Evaluation and Effectiveness
Oct 15, 2021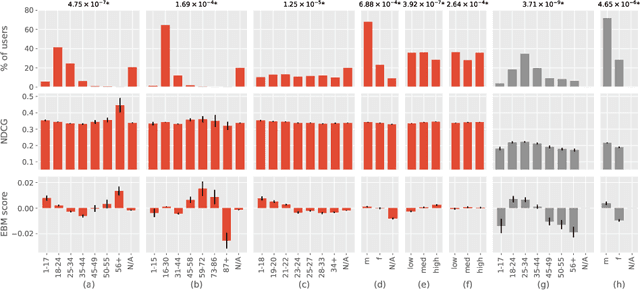
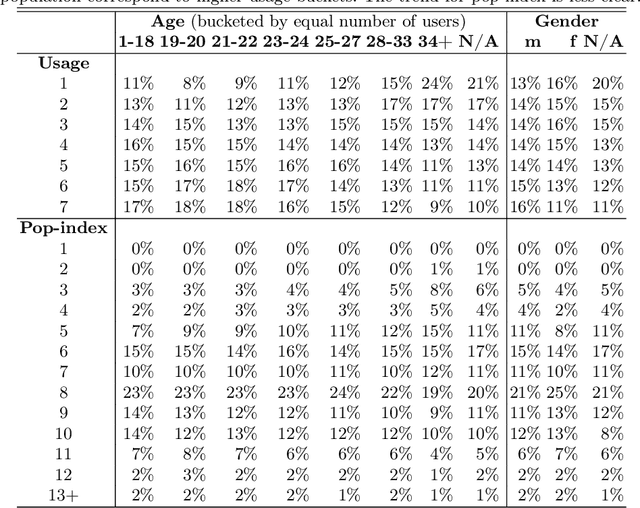
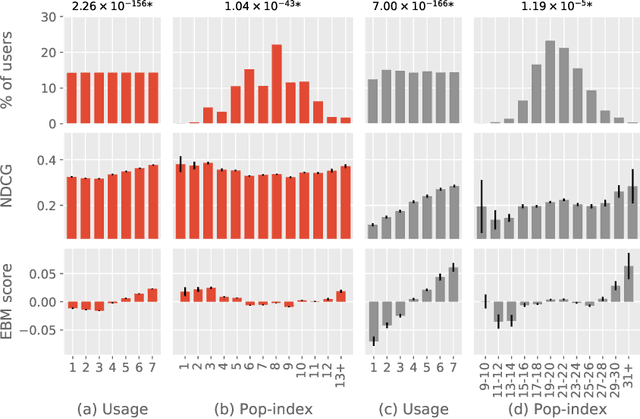
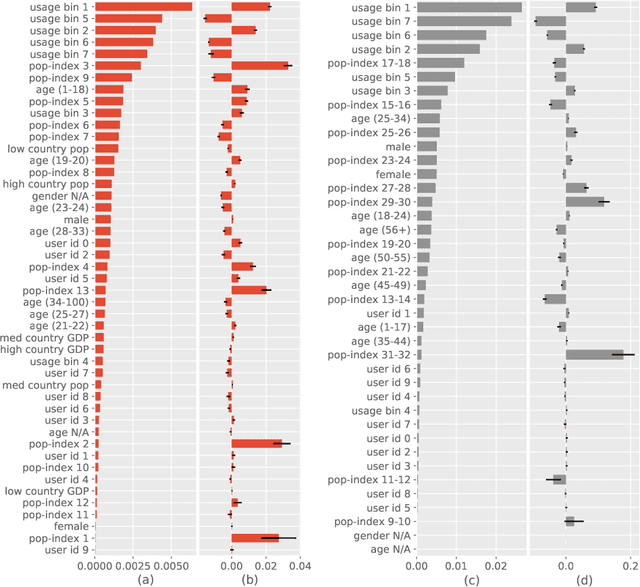
Abstract:Recommendation algorithms are susceptible to popularity bias: a tendency to recommend popular items even when they fail to meet user needs. A related issue is that the recommendation quality can vary by demographic groups. Marginalized groups or groups that are under-represented in the training data may receive less relevant recommendations from these algorithms compared to others. In a recent study, Ekstrand et al. investigate how recommender performance varies according to popularity and demographics, and find statistically significant differences in recommendation utility between binary genders on two datasets, and significant effects based on age on one dataset. Here we reproduce those results and extend them with additional analyses. We find statistically significant differences in recommender performance by both age and gender. We observe that recommendation utility steadily degrades for older users, and is lower for women than men. We also find that the utility is higher for users from countries with more representation in the dataset. In addition, we find that total usage and the popularity of consumed content are strong predictors of recommender performance and also vary significantly across demographic groups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge