Nick Watters
Multi-Object Representation Learning with Iterative Variational Inference
Mar 01, 2019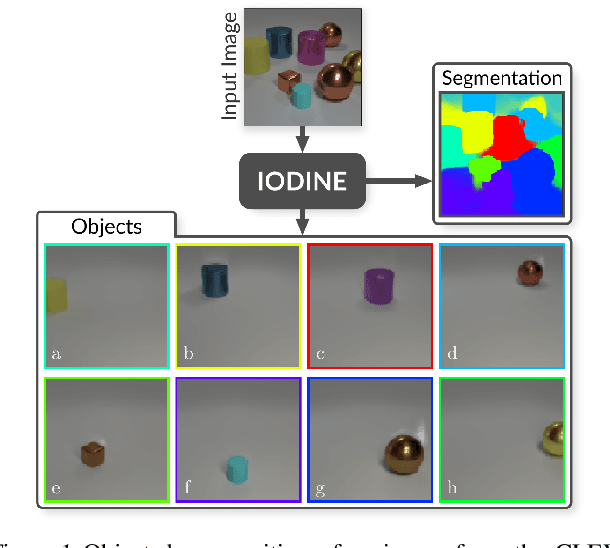
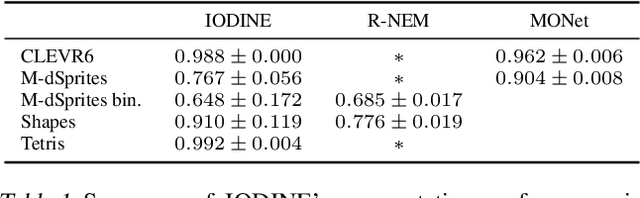
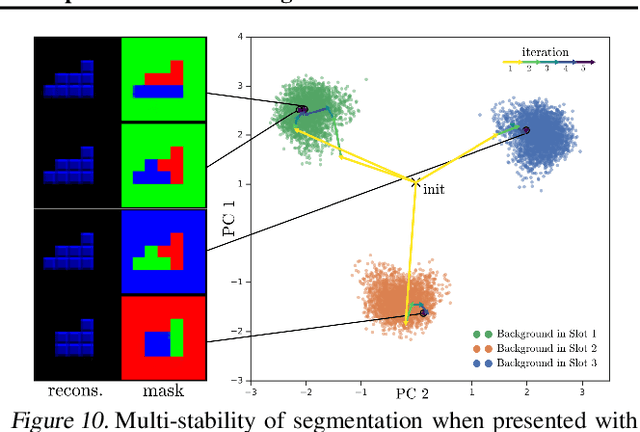
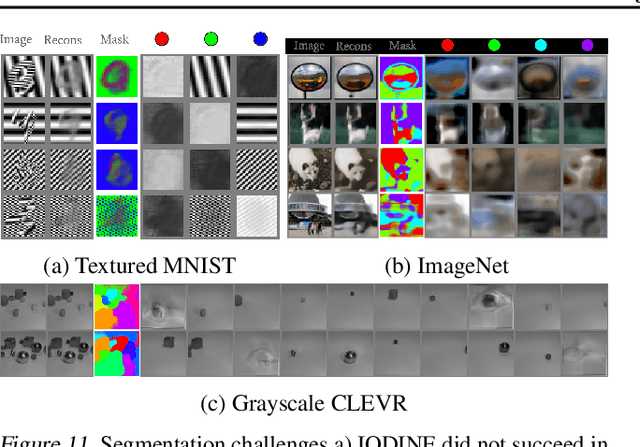
Abstract:Human perception is structured around objects which form the basis for our higher-level cognition and impressive systematic generalization abilities. Yet most work on representation learning focuses on feature learning without even considering multiple objects, or treats segmentation as an (often supervised) preprocessing step. Instead, we argue for the importance of learning to segment and represent objects jointly. We demonstrate that, starting from the simple assumption that a scene is composed of multiple entities, it is possible to learn to segment images into interpretable objects with disentangled representations. Our method learns -- without supervision -- to inpaint occluded parts, and extrapolates to scenes with more objects and to unseen objects with novel feature combinations. We also show that, due to the use of iterative variational inference, our system is able to learn multi-modal posteriors for ambiguous inputs and extends naturally to sequences.
Life-Long Disentangled Representation Learning with Cross-Domain Latent Homologies
Aug 20, 2018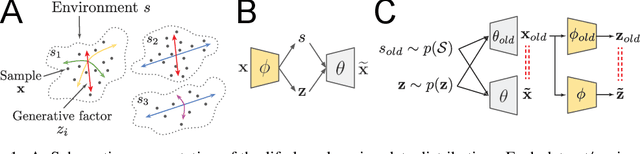
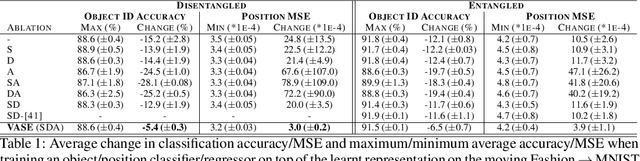
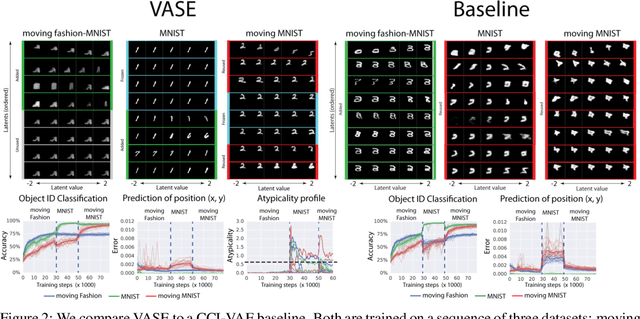
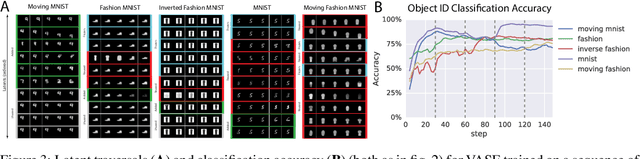
Abstract:Intelligent behaviour in the real-world requires the ability to acquire new knowledge from an ongoing sequence of experiences while preserving and reusing past knowledge. We propose a novel algorithm for unsupervised representation learning from piece-wise stationary visual data: Variational Autoencoder with Shared Embeddings (VASE). Based on the Minimum Description Length principle, VASE automatically detects shifts in the data distribution and allocates spare representational capacity to new knowledge, while simultaneously protecting previously learnt representations from catastrophic forgetting. Our approach encourages the learnt representations to be disentangled, which imparts a number of desirable properties: VASE can deal sensibly with ambiguous inputs, it can enhance its own representations through imagination-based exploration, and most importantly, it exhibits semantically meaningful sharing of latents between different datasets. Compared to baselines with entangled representations, our approach is able to reason beyond surface-level statistics and perform semantically meaningful cross-domain inference.
Understanding disentangling in $β$-VAE
Apr 10, 2018
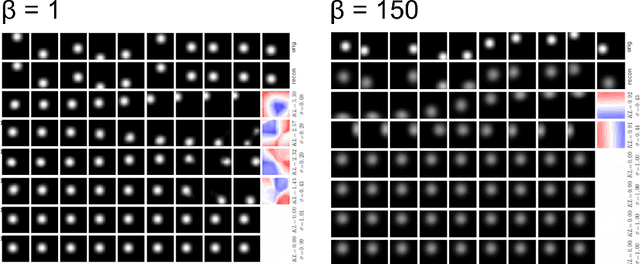
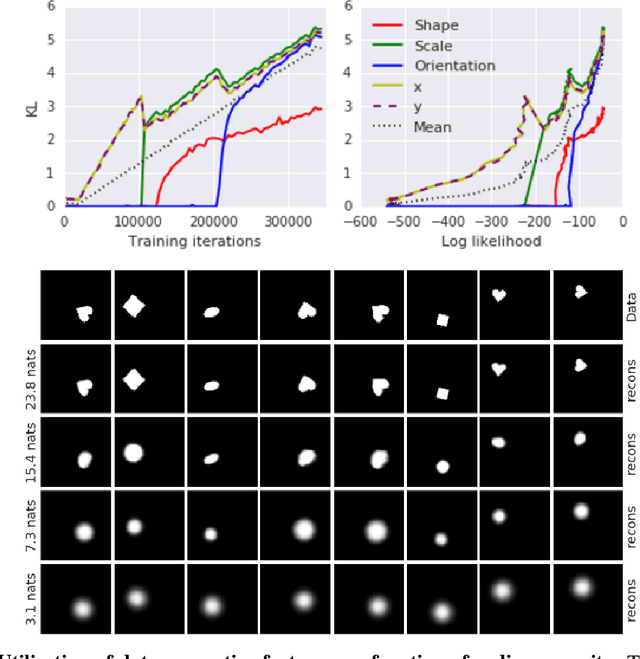

Abstract:We present new intuitions and theoretical assessments of the emergence of disentangled representation in variational autoencoders. Taking a rate-distortion theory perspective, we show the circumstances under which representations aligned with the underlying generative factors of variation of data emerge when optimising the modified ELBO bound in $\beta$-VAE, as training progresses. From these insights, we propose a modification to the training regime of $\beta$-VAE, that progressively increases the information capacity of the latent code during training. This modification facilitates the robust learning of disentangled representations in $\beta$-VAE, without the previous trade-off in reconstruction accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge