Neelesh Kumar
Automated Measurement of Eczema Severity with Self-Supervised Learning
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Automated diagnosis of eczema using images acquired from digital camera can enable individuals to self-monitor their recovery. The process entails first segmenting out the eczema region from the image and then measuring the severity of eczema in the segmented region. The state-of-the-art methods for automated eczema diagnosis rely on deep neural networks such as convolutional neural network (CNN) and have shown impressive performance in accurately measuring the severity of eczema. However, these methods require massive volume of annotated data to train which can be hard to obtain. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised learning framework for automated eczema diagnosis under limited training data regime. Our framework consists of two stages: i) Segmentation, where we use an in-context learning based algorithm called SegGPT for few-shot segmentation of eczema region from the image; ii) Feature extraction and classification, where we extract DINO features from the segmented regions and feed it to a multi-layered perceptron (MLP) for 4-class classification of eczema severity. When evaluated on a dataset of annotated "in-the-wild" eczema images, we show that our method outperforms (Weighted F1: 0.67 $\pm$ 0.01) the state-of-the-art deep learning methods such as finetuned Resnet-18 (Weighted F1: 0.44 $\pm$ 0.16) and Vision Transformer (Weighted F1: 0.40 $\pm$ 0.22). Our results show that self-supervised learning can be a viable solution for automated skin diagnosis where labeled data is scarce.
Ubiquitous Robot Control Through Multimodal Motion Capture Using Smartwatch and Smartphone Data
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:We present an open-source library for seamless robot control through motion capture using smartphones and smartwatches. Our library features three modes: Watch Only Mode, enabling control with a single smartwatch; Upper Arm Mode, offering heightened accuracy by incorporating the smartphone attached to the upper arm; and Pocket Mode, determining body orientation via the smartphone placed in any pocket. These modes are applied in two real-robot tasks, showcasing placement accuracy within 2 cm compared to a gold-standard motion capture system. WearMoCap stands as a suitable alternative to conventional motion capture systems, particularly in environments where ubiquity is essential. The library is available at: www.github.com/wearable-motion-capture.
iRoCo: Intuitive Robot Control From Anywhere Using a Smartwatch
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces iRoCo (intuitive Robot Control) - a framework for ubiquitous human-robot collaboration using a single smartwatch and smartphone. By integrating probabilistic differentiable filters, iRoCo optimizes a combination of precise robot control and unrestricted user movement from ubiquitous devices. We demonstrate and evaluate the effectiveness of iRoCo in practical teleoperation and drone piloting applications. Comparative analysis shows no significant difference between task performance with iRoCo and gold-standard control systems in teleoperation tasks. Additionally, iRoCo users complete drone piloting tasks 32\% faster than with a traditional remote control and report less frustration in a subjective load index questionnaire. Our findings strongly suggest that iRoCo is a promising new approach for intuitive robot control through smartwatches and smartphones from anywhere, at any time. The code is available at www.github.com/wearable-motion-capture
Visual In-Context Learning for Few-Shot Eczema Segmentation
Sep 28, 2023



Abstract:Automated diagnosis of eczema from digital camera images is crucial for developing applications that allow patients to self-monitor their recovery. An important component of this is the segmentation of eczema region from such images. Current methods for eczema segmentation rely on deep neural networks such as convolutional (CNN)-based U-Net or transformer-based Swin U-Net. While effective, these methods require high volume of annotated data, which can be difficult to obtain. Here, we investigate the capabilities of visual in-context learning that can perform few-shot eczema segmentation with just a handful of examples and without any need for retraining models. Specifically, we propose a strategy for applying in-context learning for eczema segmentation with a generalist vision model called SegGPT. When benchmarked on a dataset of annotated eczema images, we show that SegGPT with just 2 representative example images from the training dataset performs better (mIoU: 36.69) than a CNN U-Net trained on 428 images (mIoU: 32.60). We also discover that using more number of examples for SegGPT may in fact be harmful to its performance. Our result highlights the importance of visual in-context learning in developing faster and better solutions to skin imaging tasks. Our result also paves the way for developing inclusive solutions that can cater to minorities in the demographics who are typically heavily under-represented in the training data.
BioGrad: Biologically Plausible Gradient-Based Learning for Spiking Neural Networks
Oct 27, 2021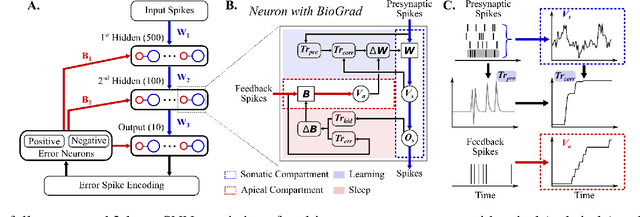
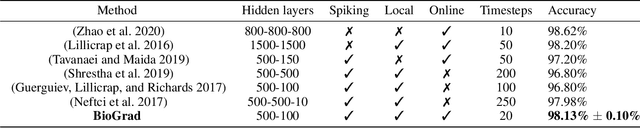
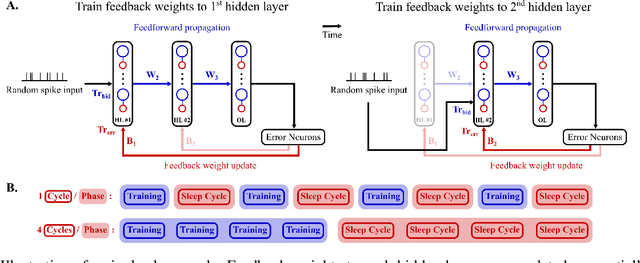

Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNN) are delivering energy-efficient, massively parallel, and low-latency solutions to AI problems, facilitated by the emerging neuromorphic chips. To harness these computational benefits, SNN need to be trained by learning algorithms that adhere to brain-inspired neuromorphic principles, namely event-based, local, and online computations. Yet, the state-of-the-art SNN training algorithms are based on backprop that does not follow the above principles. Due to its limited biological plausibility, the application of backprop to SNN requires non-local feedback pathways for transmitting continuous-valued errors, and relies on gradients from future timesteps. The introduction of biologically plausible modifications to backprop has helped overcome several of its limitations, but limits the degree to which backprop is approximated, which hinders its performance. We propose a biologically plausible gradient-based learning algorithm for SNN that is functionally equivalent to backprop, while adhering to all three neuromorphic principles. We introduced multi-compartment spiking neurons with local eligibility traces to compute the gradients required for learning, and a periodic "sleep" phase to further improve the approximation to backprop during which a local Hebbian rule aligns the feedback and feedforward weights. Our method achieved the same level of performance as backprop with multi-layer fully connected SNN on MNIST (98.13%) and the event-based N-MNIST (97.59%) datasets. We deployed our learning algorithm on Intel's Loihi to train a 1-hidden-layer network for MNIST, and obtained 93.32% test accuracy while consuming 400 times less energy per training sample than BioGrad on GPU. Our work shows that optimal learning is feasible in neuromorphic computing, and further pursuing its biological plausibility can better capture the benefits of this emerging computing paradigm.
Deep Reinforcement Learning with Population-Coded Spiking Neural Network for Continuous Control
Oct 19, 2020



Abstract:The energy-efficient control of mobile robots is crucial as the complexity of their real-world applications increasingly involves high-dimensional observation and action spaces, which cannot be offset by limited on-board resources. An emerging non-Von Neumann model of intelligence, where spiking neural networks (SNNs) are run on neuromorphic processors, is regarded as an energy-efficient and robust alternative to the state-of-the-art real-time robotic controllers for low dimensional control tasks. The challenge now for this new computing paradigm is to scale so that it can keep up with real-world tasks. To do so, SNNs need to overcome the inherent limitations of their training, namely the limited ability of their spiking neurons to represent information and the lack of effective learning algorithms. Here, we propose a population-coded spiking actor network (PopSAN) trained in conjunction with a deep critic network using deep reinforcement learning (DRL). The population coding scheme dramatically increased the representation capacity of the network and the hybrid learning combined the training advantages of deep networks with the energy-efficient inference of spiking networks. To show the general applicability of our approach, we integrated it with a spectrum of both on-policy and off-policy DRL algorithms. We deployed the trained PopSAN on Intel's Loihi neuromorphic chip and benchmarked our method against the mainstream DRL algorithms for continuous control. To allow for a fair comparison among all methods, we validated them on OpenAI gym tasks. Our Loihi-run PopSAN consumed 140 times less energy per inference when compared against the deep actor network on Jetson TX2, and had the same level of performance. Our results support the efficiency of neuromorphic controllers and suggest our hybrid RL as an alternative to deep learning, when both energy-efficiency and robustness are important.
Reinforcement co-Learning of Deep and Spiking Neural Networks for Energy-Efficient Mapless Navigation with Neuromorphic Hardware
Mar 02, 2020



Abstract:Energy-efficient mapless navigation is crucial for mobile robots as they explore unknown environments with limited on-board resources. Although the recent deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approaches have been successfully applied to navigation, their high energy consumption limits their use in many robotic applications. Here, we propose a neuromorphic approach that combines the energy-efficiency of spiking neural networks with the optimality of DRL to learn control policies for mapless navigation. Our hybrid framework, Spiking deep deterministic policy gradient (SDDPG), consists of a spiking actor network (SAN) and a deep critic network, where the two networks were trained jointly using gradient descent. The trained SAN was deployed on Intel's Loihi neuromorphic processor. The co-learning enabled synergistic information exchange between the two networks, allowing them to overcome each other's limitations through a shared representation learning. When validated on both simulated and real-world complex environments, our method on Loihi not only consumed 75 times less energy per inference as compared to DDPG on Jetson TX2, but also had a higher rate of successfully navigating to the goal which ranged by 1\% to 4.2\%, depending on the forward-propagation timestep size. These results reinforce our ongoing effort to design brain-inspired algorithms for controlling autonomous robots with neuromorphic hardware.
Machine Learning for Motor Learning: EEG-based Continuous Assessment of Cognitive Engagement for Adaptive Rehabilitation Robots
Feb 19, 2020



Abstract:Although cognitive engagement (CE) is crucial for motor learning, it remains underutilized in rehabilitation robots, partly because its assessment currently relies on subjective and gross measurements taken intermittently. Here, we propose an end-to-end computational framework that assesses CE in real-time, using electroencephalography (EEG) signals as objective measurements. The framework consists of i) a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) that extracts task-discriminative spatiotemporal EEG to predict the level of CE for two classes -- cognitively engaged vs. disengaged; and ii) a novel sliding window method that predicts continuous levels of CE in real-time. We evaluated our framework on 8 subjects using an in-house Go/No-Go experiment that adapted its gameplay parameters to induce cognitive fatigue. The proposed CNN had an average leave-one-out accuracy of 88.13\%. The CE prediction correlated well with a commonly used behavioral metric based on self-reports taken every 5 minutes ($\rho$=0.93). Our results objectify CE in real-time and pave the way for using CE as a rehabilitation parameter for tailoring robotic therapy to each patient's needs and skills.
Deep Learning of Movement Intent and Reaction Time for EEG-informed Adaptation of Rehabilitation Robots
Feb 18, 2020



Abstract:Mounting evidence suggests that adaptation is a crucial mechanism for rehabilitation robots in promoting motor learning. Yet, it is commonly based on robot-derived movement kinematics, which is a rather subjective measurement of performance, especially in the presence of a sensorimotor impairment. Here, we propose a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) that uses electroencephalography (EEG) as an objective measurement of two kinematics components that are typically used to assess motor learning and thereby adaptation: i) the intent to initiate a goal-directed movement, and ii) the reaction time (RT) of that movement. We evaluated our CNN on data acquired from an in-house experiment where 13 subjects moved a rehabilitation robotic arm in four directions on a plane, in response to visual stimuli. Our CNN achieved average test accuracies of 80.08% and 79.82% in a binary classification of the intent (intent vs. no intent) and RT (slow vs. fast), respectively. Our results demonstrate how individual movement components implicated in distinct types of motor learning can be predicted from synchronized EEG data acquired before the start of the movement. Our approach can, therefore, inform robotic adaptation in real-time and has the potential to further improve one's ability to perform the rehabilitation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge