Ndapa Nakashole
On Linearizing Structured Data in Encoder-Decoder Language Models: Insights from Text-to-SQL
Apr 03, 2024Abstract:Structured data, prevalent in tables, databases, and knowledge graphs, poses a significant challenge in its representation. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), there has been a shift towards linearization-based methods, which process structured data as sequential token streams, diverging from approaches that explicitly model structure, often as a graph. Crucially, there remains a gap in our understanding of how these linearization-based methods handle structured data, which is inherently non-linear. This work investigates the linear handling of structured data in encoder-decoder language models, specifically T5. Our findings reveal the model's ability to mimic human-designed processes such as schema linking and syntax prediction, indicating a deep, meaningful learning of structure beyond simple token sequencing. We also uncover insights into the model's internal mechanisms, including the ego-centric nature of structure node encodings and the potential for model compression due to modality fusion redundancy. Overall, this work sheds light on the inner workings of linearization-based methods and could potentially provide guidance for future research.
Zero-shot Triplet Extraction by Template Infilling
Dec 21, 2022

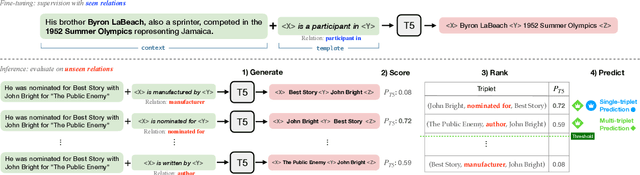
Abstract:Triplet extraction aims to extract entities and their corresponding relations in unstructured text. Most existing methods train an extraction model on high-quality training data, and hence are incapable of extracting relations that were not observed during training. Generalizing the model to unseen relations typically requires fine-tuning on synthetic training data which is often noisy and unreliable. In this paper, we argue that reducing triplet extraction to a template filling task over a pre-trained language model can equip the model with zero-shot learning capabilities and enable it to leverage the implicit knowledge in the language model. Embodying these ideas, we propose a novel framework, ZETT (ZEro-shot Triplet extraction by Template infilling), that is based on end-to-end generative transformers. Our experiments show that without any data augmentation or pipeline systems, ZETT can outperform previous state-of-the-art models with 25% less parameters. We further show that ZETT is more robust in detecting entities and can be incorporated with automatically generated templates for relations.
Medical Question Understanding and Answering with Knowledge Grounding and Semantic Self-Supervision
Sep 30, 2022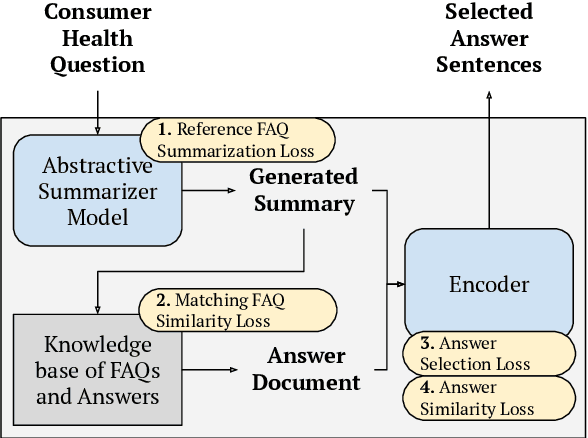
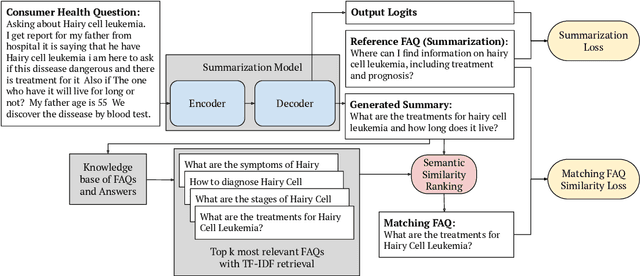
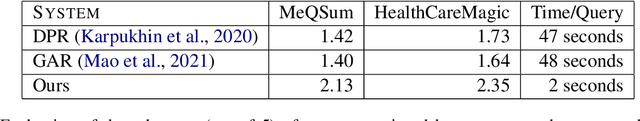
Abstract:Current medical question answering systems have difficulty processing long, detailed and informally worded questions submitted by patients, called Consumer Health Questions (CHQs). To address this issue, we introduce a medical question understanding and answering system with knowledge grounding and semantic self-supervision. Our system is a pipeline that first summarizes a long, medical, user-written question, using a supervised summarization loss. Then, our system performs a two-step retrieval to return answers. The system first matches the summarized user question with an FAQ from a trusted medical knowledge base, and then retrieves a fixed number of relevant sentences from the corresponding answer document. In the absence of labels for question matching or answer relevance, we design 3 novel, self-supervised and semantically-guided losses. We evaluate our model against two strong retrieval-based question answering baselines. Evaluators ask their own questions and rate the answers retrieved by our baselines and own system according to their relevance. They find that our system retrieves more relevant answers, while achieving speeds 20 times faster. Our self-supervised losses also help the summarizer achieve higher scores in ROUGE, as well as in human evaluation metrics. We release our code to encourage further research.
A Grounded Well-being Conversational Agent with Multiple Interaction Modes: Preliminary Results
Nov 28, 2021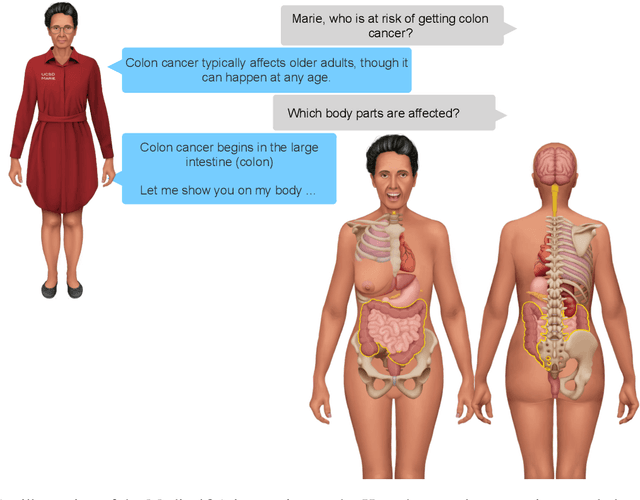


Abstract:Technologies for enhancing well-being, healthcare vigilance and monitoring are on the rise. However, despite patient interest, such technologies suffer from low adoption. One hypothesis for this limited adoption is loss of human interaction that is central to doctor-patient encounters. In this paper we seek to address this limitation via a conversational agent that adopts one aspect of in-person doctor-patient interactions: A human avatar to facilitate medical grounded question answering. This is akin to the in-person scenario where the doctor may point to the human body or the patient may point to their own body to express their conditions. Additionally, our agent has multiple interaction modes, that may give more options for the patient to use the agent, not just for medical question answering, but also to engage in conversations about general topics and current events. Both the avatar, and the multiple interaction modes could help improve adherence. We present a high level overview of the design of our agent, Marie Bot Wellbeing. We also report implementation details of our early prototype , and present preliminary results.
Extracting the Unknown from Long Math Problems
Mar 22, 2021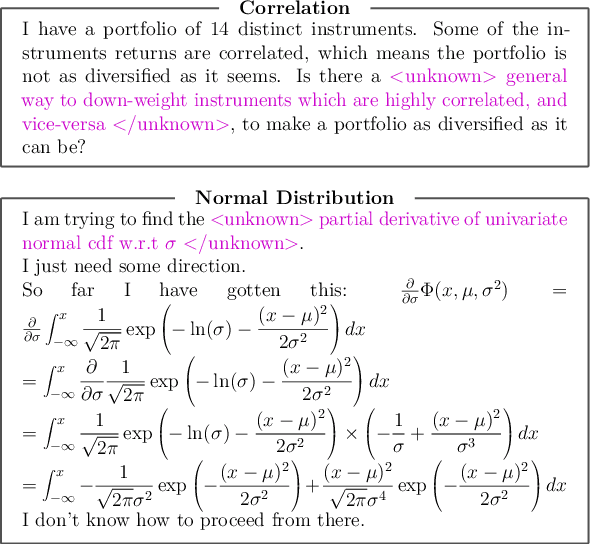
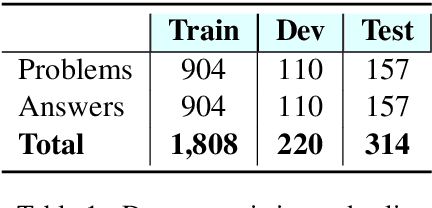
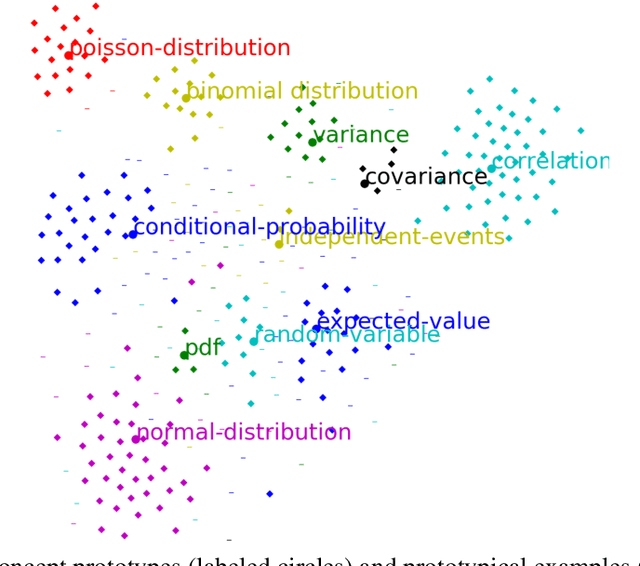
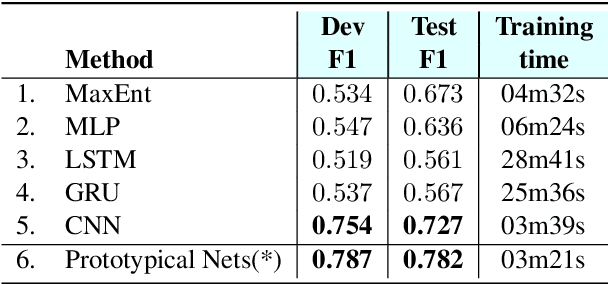
Abstract:In problem solving, understanding the problem that one seeks to solve is an essential initial step. In this paper, we propose computational methods for facilitating problem understanding through the task of recognizing the unknown in specifications of long Math problems. We focus on the topic of Probability. Our experimental results show that learning models yield strong results on the task, a promising first step towards human interpretable, modular approaches to understanding long Math problems.
Rethinking Self-Attention: An Interpretable Self-Attentive Encoder-Decoder Parser
Nov 10, 2019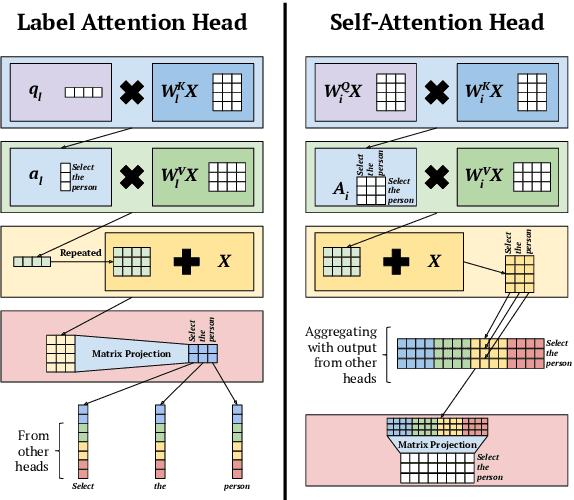
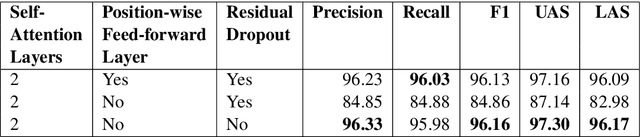
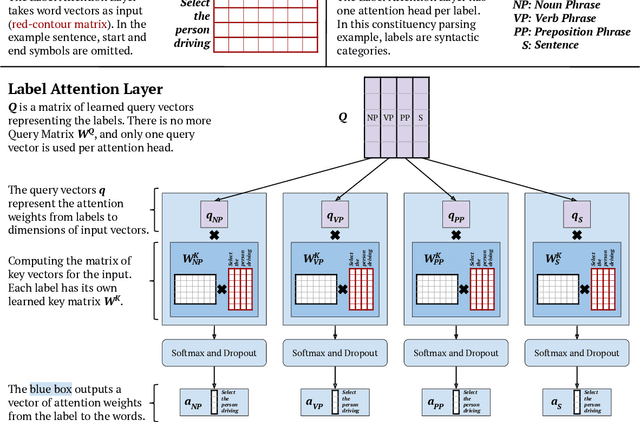
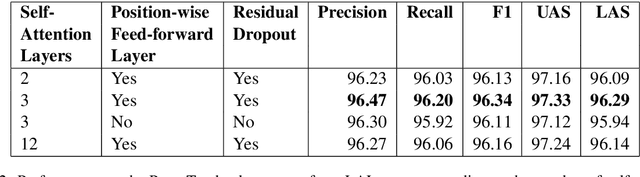
Abstract:Attention mechanisms have improved the performance of NLP tasks while providing for appearance of model interpretability. Self-attention is currently widely used in NLP models, however it is difficult to interpret due to the numerous attention distributions. We hypothesize that model representations can benefit from label-specific information, while facilitating interpretation of predictions. We introduce the Label Attention Layer: a new form of self-attention where attention heads represent labels. We validate our hypothesis by running experiments in constituency and dependency parsing and show our new model obtains new state-of-the-art results for both tasks on the English Penn Treebank. Our neural parser obtains 96.34 F1 score for constituency parsing, and 97.33 UAS and 96.29 LAS for dependency parsing. Additionally, our model requires fewer layers, therefore, fewer parameters compared to existing work.
Fine-Grained Spoiler Detection from Large-Scale Review Corpora
May 31, 2019
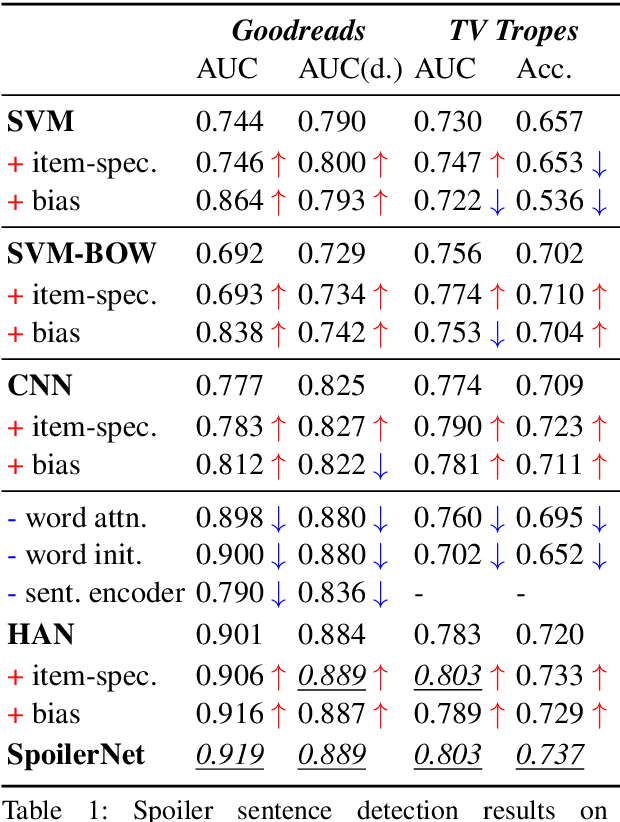
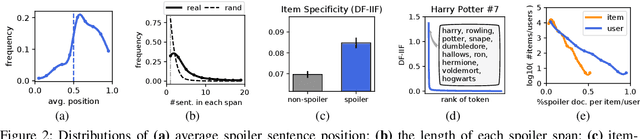

Abstract:This paper presents computational approaches for automatically detecting critical plot twists in reviews of media products. First, we created a large-scale book review dataset that includes fine-grained spoiler annotations at the sentence-level, as well as book and (anonymized) user information. Second, we carefully analyzed this dataset, and found that: spoiler language tends to be book-specific; spoiler distributions vary greatly across books and review authors; and spoiler sentences tend to jointly appear in the latter part of reviews. Third, inspired by these findings, we developed an end-to-end neural network architecture to detect spoiler sentences in review corpora. Quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate that the proposed method substantially outperforms existing baselines.
Sense Perception Common Sense Relationships
Nov 17, 2018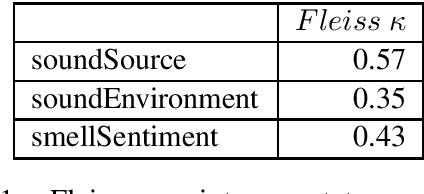

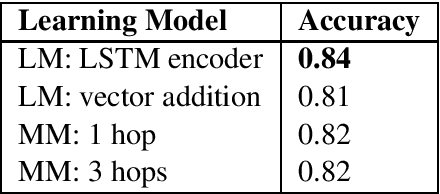
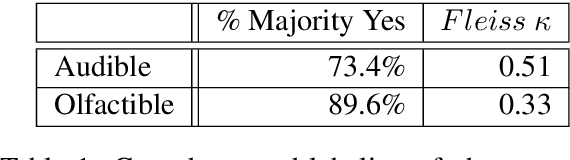
Abstract:Often missing in existing knowledge bases of facts, are relationships that encode common sense knowledge about unnamed entities. In this paper, we propose to extract novel, common sense relationships pertaining to sense perception concepts such as sound and smell.
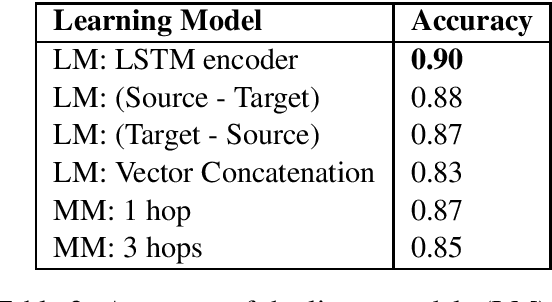
Unnamed Entity Recognition of Sense Mentions
Nov 17, 2018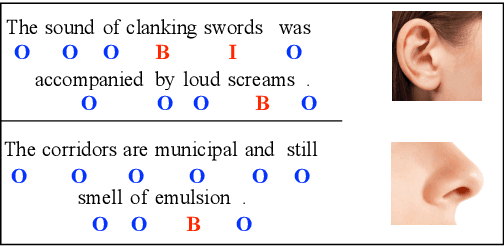


Abstract:We consider the problem of recognizing mentions of human senses in text. Our contribution is a method for acquiring labeled data, and a learning method that is trained on this data. Experiments show the effectiveness of our proposed data labeling approach and our learning model on the task of sense recognition in text.
Bilingual Dictionary Induction for Bantu Languages
Nov 17, 2018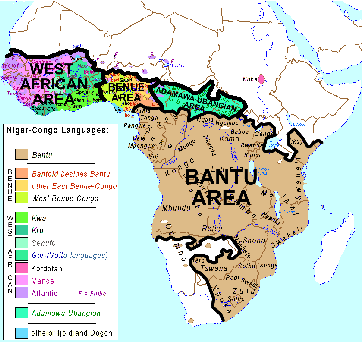
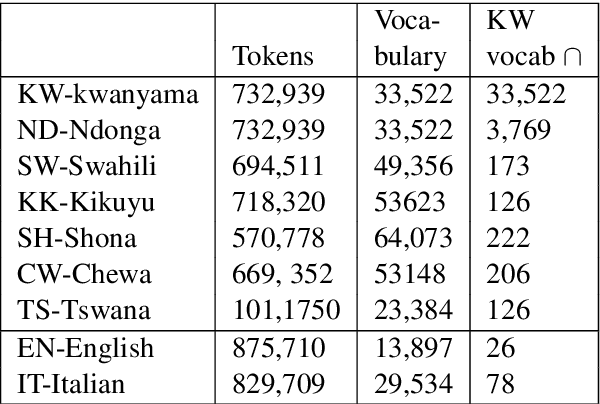
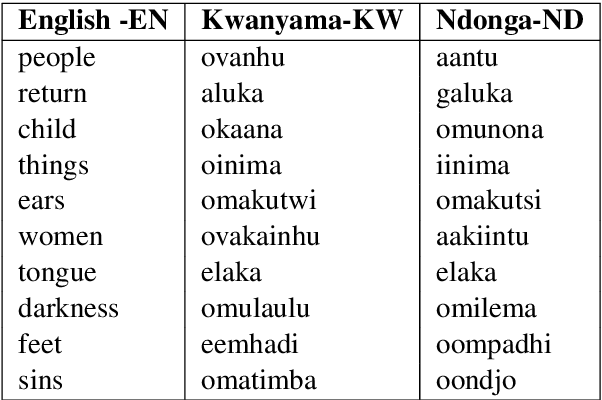
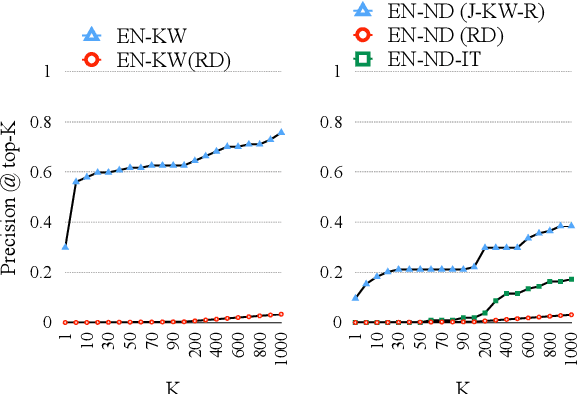
Abstract:We present a method for learning bilingual translation dictionaries between English and Bantu languages. We show that exploiting the grammatical structure common to Bantu languages enables bilingual dictionary induction for languages where training data is unavailable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge