Nan Yu
HiEAG: Evidence-Augmented Generation for Out-of-Context Misinformation Detection
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal out-of-context (OOC) misinformation detection have made remarkable progress in checking the consistencies between different modalities for supporting or refuting image-text pairs. However, existing OOC misinformation detection methods tend to emphasize the role of internal consistency, ignoring the significant of external consistency between image-text pairs and external evidence. In this paper, we propose HiEAG, a novel Hierarchical Evidence-Augmented Generation framework to refine external consistency checking through leveraging the extensive knowledge of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Our approach decomposes external consistency checking into a comprehensive engine pipeline, which integrates reranking and rewriting, apart from retrieval. Evidence reranking module utilizes Automatic Evidence Selection Prompting (AESP) that acquires the relevant evidence item from the products of evidence retrieval. Subsequently, evidence rewriting module leverages Automatic Evidence Generation Prompting (AEGP) to improve task adaptation on MLLM-based OOC misinformation detectors. Furthermore, our approach enables explanation for judgment, and achieves impressive performance with instruction tuning. Experimental results on different benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed HiEAG surpasses previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in the accuracy over all samples.
ChatMol: A Versatile Molecule Designer Based on the Numerically Enhanced Large Language Model
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Goal-oriented de novo molecule design, namely generating molecules with specific property or substructure constraints, is a crucial yet challenging task in drug discovery. Existing methods, such as Bayesian optimization and reinforcement learning, often require training multiple property predictors and struggle to incorporate substructure constraints. Inspired by the success of Large Language Models (LLMs) in text generation, we propose ChatMol, a novel approach that leverages LLMs for molecule design across diverse constraint settings. Initially, we crafted a molecule representation compatible with LLMs and validated its efficacy across multiple online LLMs. Afterwards, we developed specific prompts geared towards diverse constrained molecule generation tasks to further fine-tune current LLMs while integrating feedback learning derived from property prediction. Finally, to address the limitations of LLMs in numerical recognition, we referred to the position encoding method and incorporated additional encoding for numerical values within the prompt. Experimental results across single-property, substructure-property, and multi-property constrained tasks demonstrate that ChatMol consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, including VAE and RL-based methods. Notably, in multi-objective binding affinity maximization task, ChatMol achieves a significantly lower KD value of 0.25 for the protein target ESR1, while maintaining the highest overall performance, surpassing previous methods by 4.76%. Meanwhile, with numerical enhancement, the Pearson correlation coefficient between the instructed property values and those of the generated molecules increased by up to 0.49. These findings highlight the potential of LLMs as a versatile framework for molecule generation, offering a promising alternative to traditional latent space and RL-based approaches.
Discourse-Aware Emotion Cause Extraction in Conversations
Oct 26, 2022



Abstract:Emotion Cause Extraction in Conversations (ECEC) aims to extract the utterances which contain the emotional cause in conversations. Most prior research focuses on modelling conversational contexts with sequential encoding, ignoring the informative interactions between utterances and conversational-specific features for ECEC. In this paper, we investigate the importance of discourse structures in handling utterance interactions and conversationspecific features for ECEC. To this end, we propose a discourse-aware model (DAM) for this task. Concretely, we jointly model ECEC with discourse parsing using a multi-task learning (MTL) framework and explicitly encode discourse structures via gated graph neural network (gated GNN), integrating rich utterance interaction information to our model. In addition, we use gated GNN to further enhance our ECEC model with conversation-specific features. Results on the benchmark corpus show that DAM outperform the state-of-theart (SOTA) systems in the literature. This suggests that the discourse structure may contain a potential link between emotional utterances and their corresponding cause expressions. It also verifies the effectiveness of conversationalspecific features. The codes of this paper will be available on GitHub.
Discontinuous Named Entity Recognition as Maximal Clique Discovery
Jun 01, 2021
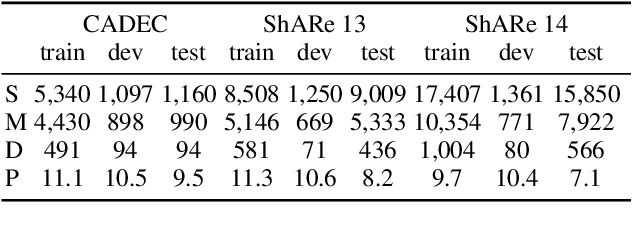
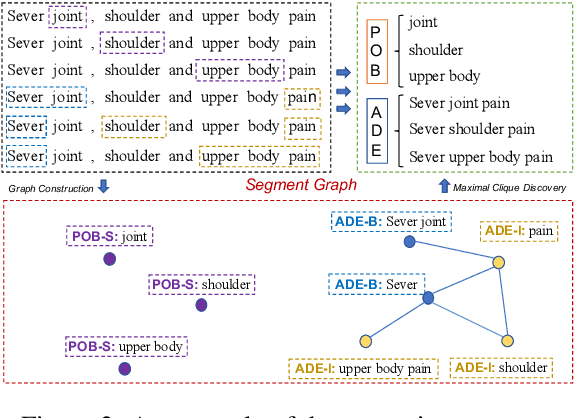
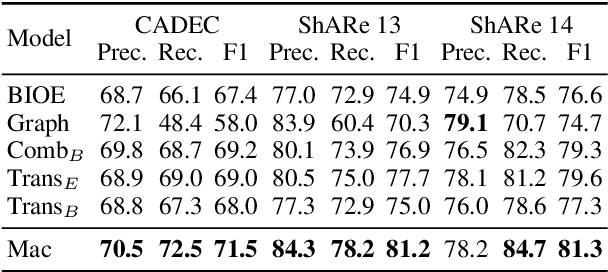
Abstract:Named entity recognition (NER) remains challenging when entity mentions can be discontinuous. Existing methods break the recognition process into several sequential steps. In training, they predict conditioned on the golden intermediate results, while at inference relying on the model output of the previous steps, which introduces exposure bias. To solve this problem, we first construct a segment graph for each sentence, in which each node denotes a segment (a continuous entity on its own, or a part of discontinuous entities), and an edge links two nodes that belong to the same entity. The nodes and edges can be generated respectively in one stage with a grid tagging scheme and learned jointly using a novel architecture named Mac. Then discontinuous NER can be reformulated as a non-parametric process of discovering maximal cliques in the graph and concatenating the spans in each clique. Experiments on three benchmarks show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) results, with up to 3.5 percentage points improvement on F1, and achieves 5x speedup over the SOTA model.
Joint POS Tagging and Dependency Parsing with Transition-based Neural Networks
Apr 25, 2017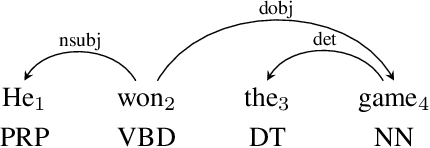


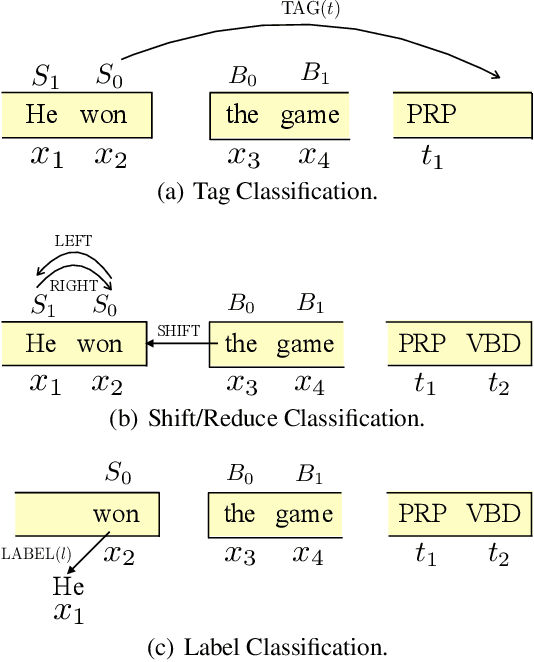
Abstract:While part-of-speech (POS) tagging and dependency parsing are observed to be closely related, existing work on joint modeling with manually crafted feature templates suffers from the feature sparsity and incompleteness problems. In this paper, we propose an approach to joint POS tagging and dependency parsing using transition-based neural networks. Three neural network based classifiers are designed to resolve shift/reduce, tagging, and labeling conflicts. Experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms previous methods for joint POS tagging and dependency parsing across a variety of natural languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge