Namwoo Kang
Three-dimensional Deep Shape Optimization with a Limited Dataset
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Generative models have attracted considerable attention for their ability to produce novel shapes. However, their application in mechanical design remains constrained due to the limited size and variability of available datasets. This study proposes a deep learning-based optimization framework specifically tailored for shape optimization with limited datasets, leveraging positional encoding and a Lipschitz regularization term to robustly learn geometric characteristics and maintain a meaningful latent space. Through extensive experiments, the proposed approach demonstrates robustness, generalizability and effectiveness in addressing typical limitations of conventional optimization frameworks. The validity of the methodology is confirmed through multi-objective shape optimization experiments conducted on diverse three-dimensional datasets, including wheels and cars, highlighting the model's versatility in producing practical and high-quality design outcomes even under data-constrained conditions.
DeepWheel: Generating a 3D Synthetic Wheel Dataset for Design and Performance Evaluation
Apr 16, 2025



Abstract:Data-driven design is emerging as a powerful strategy to accelerate engineering innovation. However, its application to vehicle wheel design remains limited due to the lack of large-scale, high-quality datasets that include 3D geometry and physical performance metrics. To address this gap, this study proposes a synthetic design-performance dataset generation framework using generative AI. The proposed framework first generates 2D rendered images using Stable Diffusion, and then reconstructs the 3D geometry through 2.5D depth estimation. Structural simulations are subsequently performed to extract engineering performance data. To further expand the design and performance space, topology optimization is applied, enabling the generation of a more diverse set of wheel designs. The final dataset, named DeepWheel, consists of over 6,000 photo-realistic images and 900 structurally analyzed 3D models. This multi-modal dataset serves as a valuable resource for surrogate model training, data-driven inverse design, and design space exploration. The proposed methodology is also applicable to other complex design domains. The dataset is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International(CC BY-NC 4.0) and is available on the https://www.smartdesignlab.org/datasets
PyTopo3D: A Python Framework for 3D SIMP-based Topology Optimization
Apr 08, 2025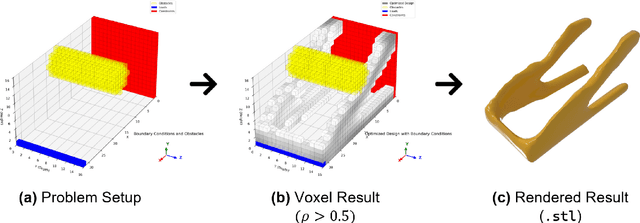
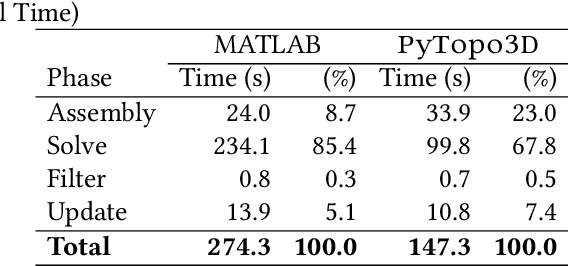
Abstract:Three-dimensional topology optimization (TO) is a powerful technique in engineering design, but readily usable, open-source implementations remain limited within the popular Python scientific environment. This paper introduces PyTopo3D, a software framework developed to address this gap. PyTopo3D provides a feature-rich tool for 3D TO by implementing the well-established Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization (SIMP) method and an Optimality Criteria (OC) update scheme, adapted and significantly enhanced from the efficient MATLAB code by Liu and Tovar (2014). While building on proven methodology, PyTopo3D's primary contribution is its integration and extension within Python, leveraging sparse matrix operations, optional parallel solvers, and accelerated KD-Tree sensitivity filtering for performance. Crucially, it incorporates functionalities vital for practical engineering workflows, including the direct import of complex design domains and non-design obstacles via STL files, integrated 3D visualization of the optimization process, and direct STL export of optimized geometries for manufacturing or further analysis. PyTopo3D is presented as an accessible, performance-aware tool and citable reference designed to empower engineers, students, and researchers to more easily utilize 3D TO within their existing Python-based workflows.
Decoupled Dynamics Framework with Neural Fields for 3D Spatio-temporal Prediction of Vehicle Collisions
Mar 25, 2025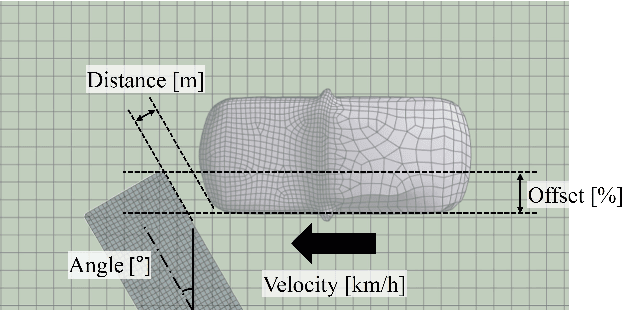
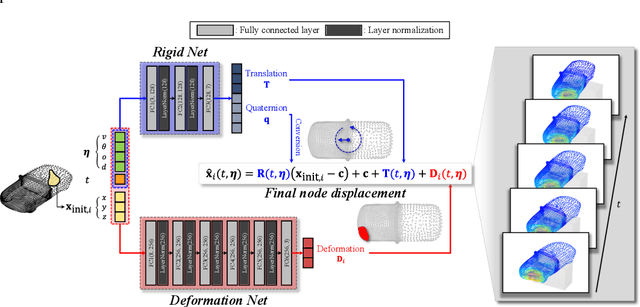
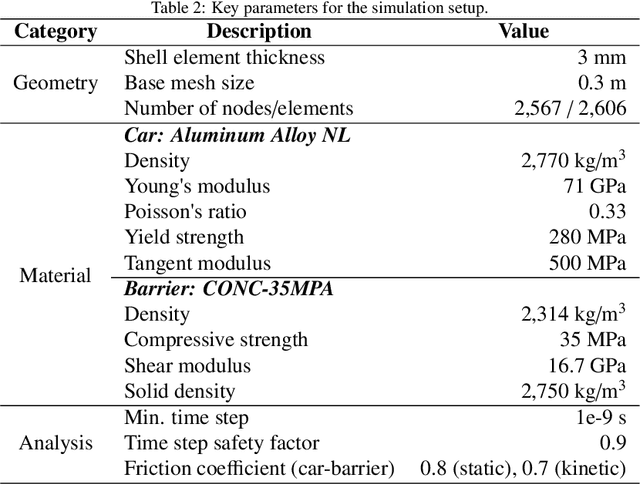
Abstract:This study proposes a neural framework that predicts 3D vehicle collision dynamics by independently modeling global rigid-body motion and local structural deformation. Unlike approaches directly predicting absolute displacement, this method explicitly separates the vehicle's overall translation and rotation from its structural deformation. Two specialized networks form the core of the framework: a quaternion-based Rigid Net for rigid motion and a coordinate-based Deformation Net for local deformation. By independently handling fundamentally distinct physical phenomena, the proposed architecture achieves accurate predictions without requiring separate supervision for each component. The model, trained on only 10% of available simulation data, significantly outperforms baseline models, including single multi-layer perceptron (MLP) and deep operator networks (DeepONet), with prediction errors reduced by up to 83%. Extensive validation demonstrates strong generalization to collision conditions outside the training range, accurately predicting responses even under severe impacts involving extreme velocities and large impact angles. Furthermore, the framework successfully reconstructs high-resolution deformation details from low-resolution inputs without increased computational effort. Consequently, the proposed approach provides an effective, computationally efficient method for rapid and reliable assessment of vehicle safety across complex collision scenarios, substantially reducing the required simulation data and time while preserving prediction fidelity.
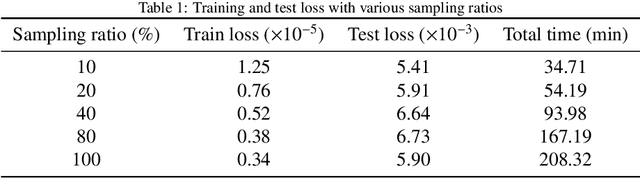
Point-DeepONet: A Deep Operator Network Integrating PointNet for Nonlinear Analysis of Non-Parametric 3D Geometries and Load Conditions
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Nonlinear structural analyses in engineering often require extensive finite element simulations, limiting their applicability in design optimization, uncertainty quantification, and real-time control. Conventional deep learning surrogates, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), physics-informed neural networks (PINNs), and fourier neural operators (FNOs), face challenges with complex non-parametric three-dimensional (3D) geometries, directionally varying loads, and high-fidelity predictions on unstructured meshes. This work presents Point-DeepONet, an operator-learning-based surrogate that integrates PointNet into the DeepONet framework. By directly processing non-parametric point clouds and incorporating signed distance functions (SDF) for geometric context, Point-DeepONet accurately predicts three-dimensional displacement and von Mises stress fields without mesh parameterization or retraining. Trained using only about 5,000 nodes (2.5% of the original 200,000-node mesh), Point-DeepONet can still predict the entire mesh at high fidelity, achieving a coefficient of determination reaching 0.987 for displacement and 0.923 for von Mises stress under a horizontal load case. Compared to nonlinear finite element analyses that require about 19.32 minutes per case, Point-DeepONet provides predictions in mere seconds-approximately 400 times faster-while maintaining excellent scalability and accuracy with increasing dataset sizes. These findings highlight the potential of Point-DeepONet to enable rapid, high-fidelity structural analyses, ultimately supporting more effective design exploration and informed decision-making in complex engineering workflows.
Towards Robust Spatio-Temporal Auto-Regressive Prediction: Adams-Bashforth Time Integration with Adaptive Multi-Step Rollout
Dec 07, 2024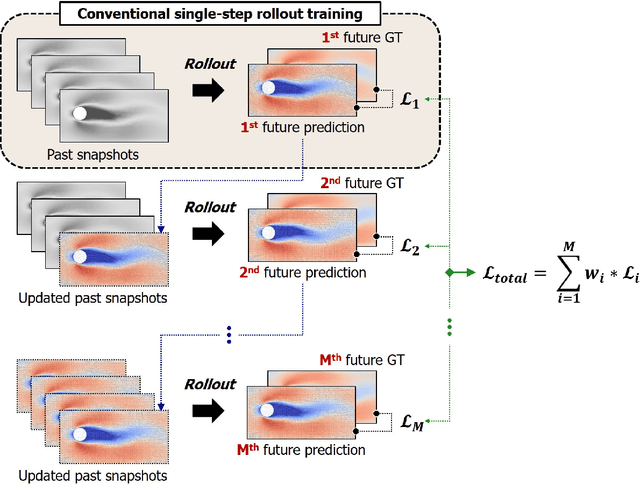
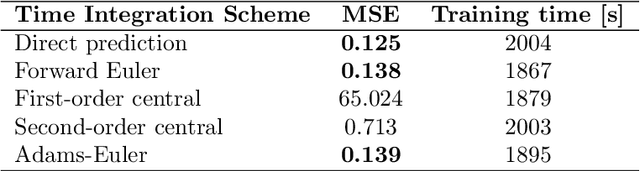
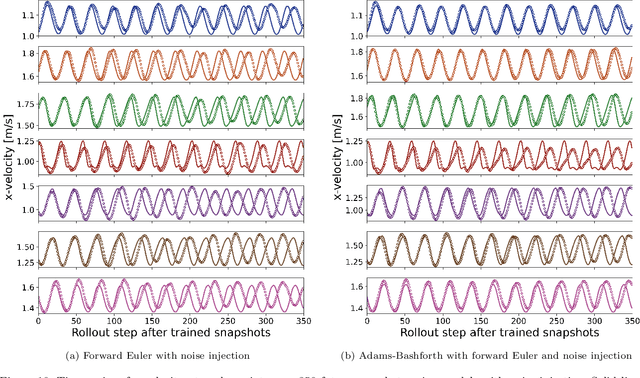
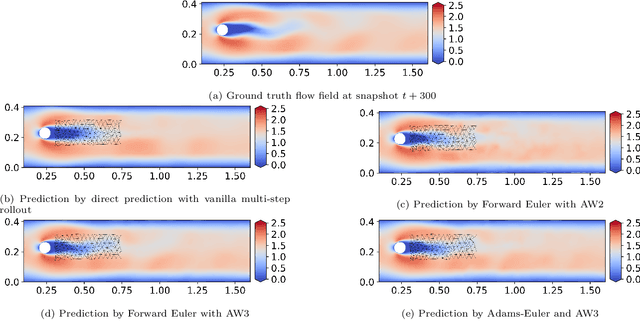
Abstract:This study addresses the critical challenge of error accumulation in spatio-temporal auto-regressive predictions within scientific machine learning models by introducing innovative temporal integration schemes and adaptive multi-step rollout strategies. We present a comprehensive analysis of time integration methods, highlighting the adaptation of the two-step Adams-Bashforth scheme to enhance long-term prediction robustness in auto-regressive models. Additionally, we improve temporal prediction accuracy through a multi-step rollout strategy that incorporates multiple future time steps during training, supported by three newly proposed approaches that dynamically adjust the importance of each future step. By integrating the Adams-Bashforth scheme with adaptive multi-step strategies, our graph neural network-based auto-regressive model accurately predicts 350 future time steps, even under practical constraints such as limited training data and minimal model capacity -- achieving an error of only 1.6% compared to the vanilla auto-regressive approach. Moreover, our framework demonstrates an 83% improvement in rollout performance over the standard noise injection method, a standard technique for enhancing long-term rollout performance. Its effectiveness is further validated in more challenging scenarios with truncated meshes, showcasing its adaptability and robustness in practical applications. This work introduces a versatile framework for robust long-term spatio-temporal auto-regressive predictions, effectively mitigating error accumulation across various model types and engineering discipline.
AI-powered Digital Twin of the Ocean: Reliable Uncertainty Quantification for Real-time Wave Height Prediction with Deep Ensemble
Dec 07, 2024

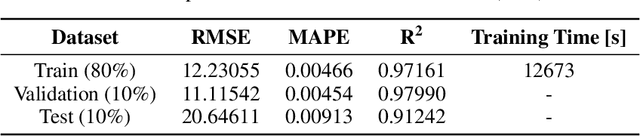
Abstract:Environmental pollution and the depletion of fossil fuels have prompted the need for eco-friendly power generation methods based on renewable energy. However, renewable energy sources often face challenges in providing stable power due to low energy density and non-stationary. Wave energy converters (WECs), in particular, need reliable real-time wave height prediction to address these issues caused by irregular wave patterns, which can lead to the inefficient and unstable operation of WECs. In this study, we propose an AI-powered reliable real-time wave height prediction model, aiming both high predictive accuracy and reliable uncertainty quantification (UQ). The proposed architecture LSTM-DE, integrates long short-term memory (LSTM) networks for temporal prediction with deep ensemble (DE) for robust UQ, achieving accuracy and reliability in wave height prediction. To further enhance the reliability of the predictive models, uncertainty calibration is applied, which has proven to significantly improve the quality of the quantified uncertainty. Based on the real operational data obtained from an oscillating water column-wave energy converter (OWC-WEC) system in Jeju, South Korea, we demonstrate that the proposed LSTM-DE model architecture achieves notable predictive accuracy (R2 > 0.9) while increasing the uncertainty quality by over 50% through simple calibration technique. Furthermore, a comprehensive parametric study is conducted to explore the effects of key model hyperparameters, offering valuable guidelines for diverse operational scenarios, characterized by differences in wavelength, amplitude, and period. The findings show that the proposed method provides robust and reliable real-time wave height predictions, facilitating digital twin of the ocean.
Vehicle Suspension Recommendation System: Multi-Fidelity Neural Network-based Mechanism Design Optimization
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Mechanisms are designed to perform functions in various fields. Often, there is no unique mechanism that performs a well-defined function. For example, vehicle suspensions are designed to improve driving performance and ride comfort, but different types are available depending on the environment. This variability in design makes performance comparison difficult. Additionally, the traditional design process is multi-step, gradually reducing the number of design candidates while performing costly analyses to meet target performance. Recently, AI models have been used to reduce the computational cost of FEA. However, there are limitations in data availability and different analysis environments, especially when transitioning from low-fidelity to high-fidelity analysis. In this paper, we propose a multi-fidelity design framework aimed at recommending optimal types and designs of mechanical mechanisms. As an application, vehicle suspension systems were selected, and several types were defined. For each type, mechanism parameters were generated and converted into 3D CAD models, followed by low-fidelity rigid body dynamic analysis under driving conditions. To effectively build a deep learning-based multi-fidelity surrogate model, the results of the low-fidelity analysis were analyzed using DBSCAN and sampled at 5% for high-cost flexible body dynamic analysis. After training the multi-fidelity model, a multi-objective optimization problem was formulated for the performance metrics of each suspension type. Finally, we recommend the optimal type and design based on the input to optimize ride comfort-related performance metrics. To validate the proposed methodology, we extracted basic design rules of Pareto solutions using data mining techniques. We also verified the effectiveness and applicability by comparing the results with those obtained from a conventional deep learning-based design process.
Enhancing Graph U-Nets for Mesh-Agnostic Spatio-Temporal Flow Prediction
Jun 06, 2024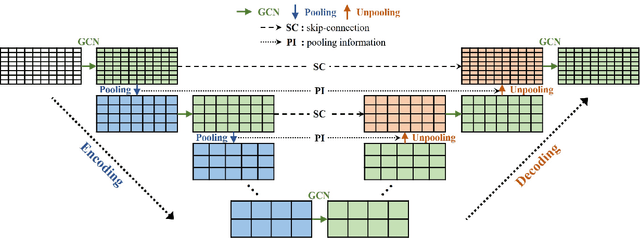
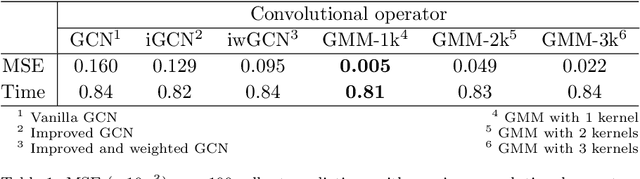
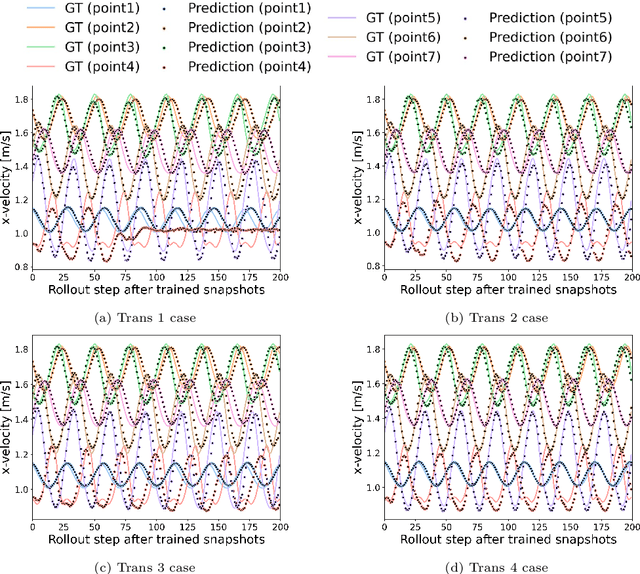
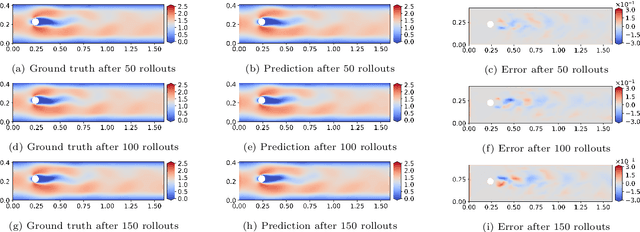
Abstract:This study aims to overcome the conventional deep-learning approaches based on convolutional neural networks, whose applicability to complex geometries and unstructured meshes is limited due to their inherent mesh dependency. We propose novel approaches to improve mesh-agnostic spatio-temporal prediction of transient flow fields using graph U-Nets, enabling accurate prediction on diverse mesh configurations. Key enhancements to the graph U-Net architecture, including the Gaussian mixture model convolutional operator and noise injection approaches, provide increased flexibility in modeling node dynamics: the former reduces prediction error by 95\% compared to conventional convolutional operators, while the latter improves long-term prediction robustness, resulting in an error reduction of 86\%. We also investigate transductive and inductive-learning perspectives of graph U-Nets with proposed improvements. In the transductive setting, they effectively predict quantities for unseen nodes within the trained graph. In the inductive setting, they successfully perform in mesh scenarios with different vortex-shedding periods, showing 98\% improvement in predicting the future flow fields compared to a model trained without the inductive settings. It is found that graph U-Nets without pooling operations, i.e. without reducing and restoring the node dimensionality of the graph data, perform better in inductive settings due to their ability to learn from the detailed structure of each graph. Meanwhile, we also discover that the choice of normalization technique significantly impacts graph U-Net performance.
Bayesian Mesh Optimization for Graph Neural Networks to Enhance Engineering Performance Prediction
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:In engineering design, surrogate models are widely employed to replace computationally expensive simulations by leveraging design variables and geometric parameters from computer-aided design (CAD) models. However, these models often lose critical information when simplified to lower dimensions and face challenges in parameter definition, especially with the complex 3D shapes commonly found in industrial datasets. To address these limitations, we propose a Bayesian graph neural network (GNN) framework for a 3D deep-learning-based surrogate model that predicts engineering performance by directly learning geometric features from CAD using mesh representation. Our framework determines the optimal size of mesh elements through Bayesian optimization, resulting in a high-accuracy surrogate model. Additionally, it effectively handles the irregular and complex structures of 3D CADs, which differ significantly from the regular and uniform pixel structures of 2D images typically used in deep learning. Experimental results demonstrate that the quality of the mesh significantly impacts the prediction accuracy of the surrogate model, with an optimally sized mesh achieving superior performance. We compare the performance of models based on various 3D representations such as voxel, point cloud, and graph, and evaluate the computational costs of Monte Carlo simulation and Bayesian optimization methods to find the optimal mesh size. We anticipate that our proposed framework has the potential to be applied to mesh-based simulations across various engineering fields, leveraging physics-based information commonly used in computer-aided engineering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge