Towards Robust Spatio-Temporal Auto-Regressive Prediction: Adams-Bashforth Time Integration with Adaptive Multi-Step Rollout
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2024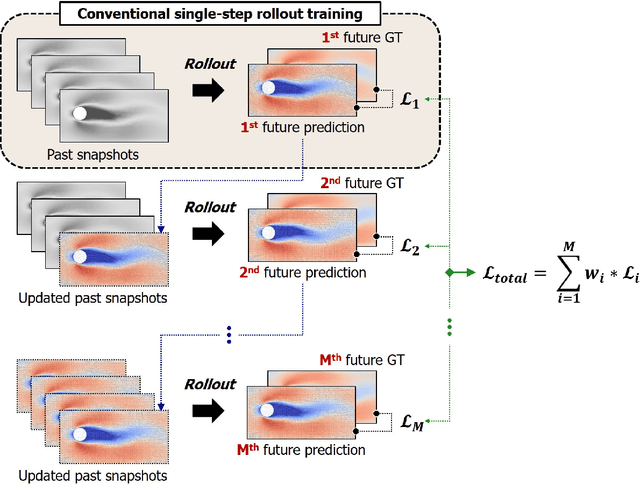
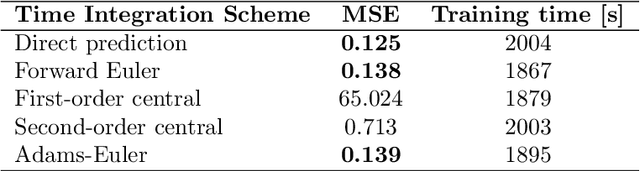
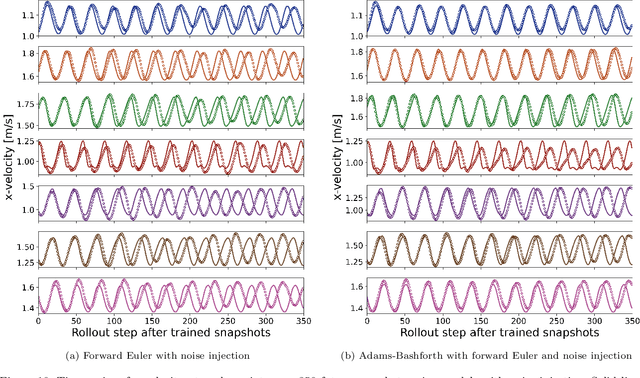
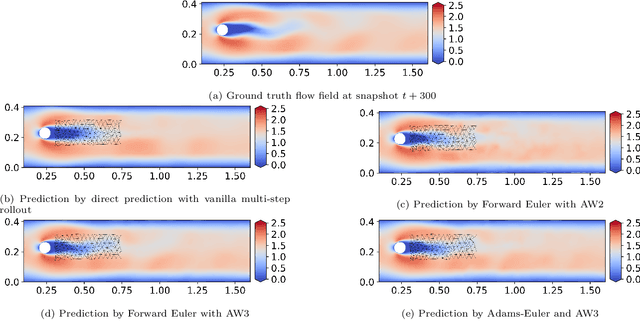
This study addresses the critical challenge of error accumulation in spatio-temporal auto-regressive predictions within scientific machine learning models by introducing innovative temporal integration schemes and adaptive multi-step rollout strategies. We present a comprehensive analysis of time integration methods, highlighting the adaptation of the two-step Adams-Bashforth scheme to enhance long-term prediction robustness in auto-regressive models. Additionally, we improve temporal prediction accuracy through a multi-step rollout strategy that incorporates multiple future time steps during training, supported by three newly proposed approaches that dynamically adjust the importance of each future step. By integrating the Adams-Bashforth scheme with adaptive multi-step strategies, our graph neural network-based auto-regressive model accurately predicts 350 future time steps, even under practical constraints such as limited training data and minimal model capacity -- achieving an error of only 1.6% compared to the vanilla auto-regressive approach. Moreover, our framework demonstrates an 83% improvement in rollout performance over the standard noise injection method, a standard technique for enhancing long-term rollout performance. Its effectiveness is further validated in more challenging scenarios with truncated meshes, showcasing its adaptability and robustness in practical applications. This work introduces a versatile framework for robust long-term spatio-temporal auto-regressive predictions, effectively mitigating error accumulation across various model types and engineering discipline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge