Nam Huynh
A Survey On Large Language Models For Code Generation
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated their remarkable capabilities in numerous fields. This survey focuses on how LLMs empower users, regardless of their technical background, to use human languages to automatically generate executable code. We begin with understanding LLMs' limitations and challenges in automated code generation. Subsequently, we review various fine-tuning techniques designed to enhance both the performance and adaptability of LLMs in code generation tasks. We then review the existing metrics and benchmarks for evaluations to assess model performance based on fine-tuning techniques. Finally, we explore the applications of LLMs (e.g. CodeLlama, GitHub Copilot, ToolGen) in code generation tasks to illustrate their roles and functionalities. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of LLMs for code generation, helps researchers in diverse fields better understand the current state-of-the-art technologies, and offers the potential of effectively leveraging LLMs for code generation tasks.
Photoacoustic Reconstruction Using Sparsity in Curvelet Frame
Nov 26, 2020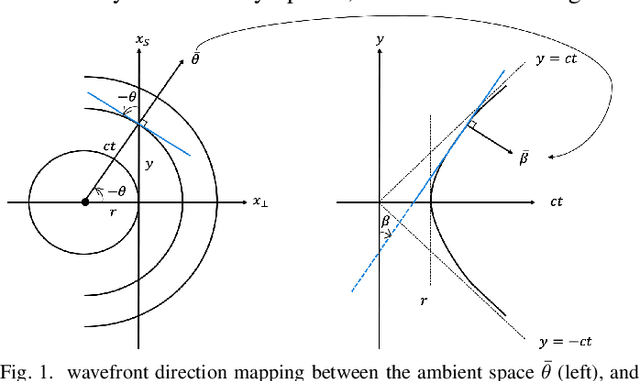
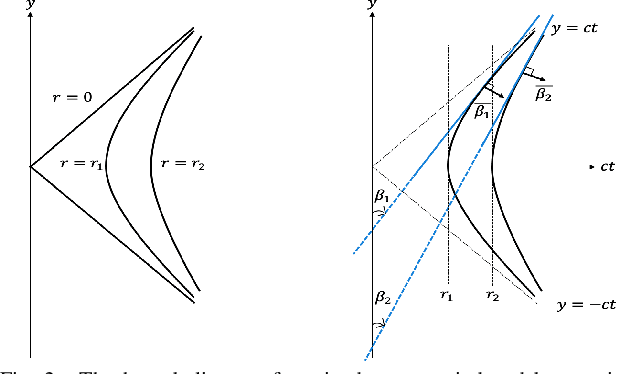
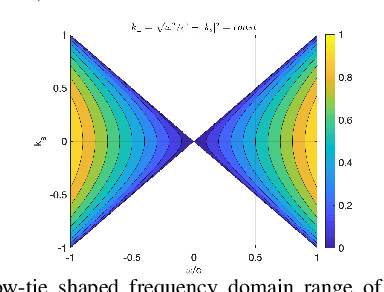
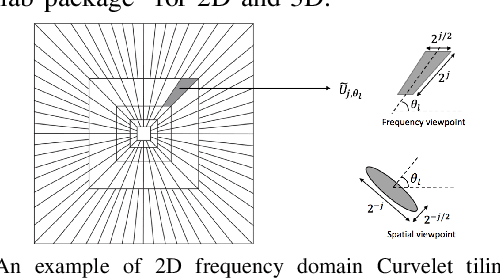
Abstract:We compare two approaches to photoacoustic image reconstruction from compressed/subsampled photoacoustic data based on assumption of sparsity in the Curvelet frame: DR, a two step approach based on the recovery of the complete volume of the photoacoustic data from the subsampled data followed by the acoustic inversion, and p0R, a one step approach where the photoacoustic image (the initial pressure, p0) is directly recovered from the subsampled data. For representation of the photoacoustic data, we propose a modification of the Curvelet transform corresponding to the restriction to the range of the photoacoustic forward operator. Both recovery problems are formulated in a variational framework. As the Curvelet frame is heavily overdetermined, we use reweighted l1 norm penalties to enhance the sparsity of the solution. The data reconstruction problem DR is a standard compressed sensing recovery problem, which we solve using an ADMM-type algorithm, SALSA. Subsequently, the initial pressure is recovered using time reversal as implemented in the k-Wave Toolbox. The p0 reconstruction problem, p0R, aims to recover the photoacoustic image directly via FISTA, or ADMM when in addition including a non-negativity constraint. We compare and discuss the relative merits of the two approaches and illustrate them on 2D simulated and 3D real data.
Approximate k-space models and Deep Learning for fast photoacoustic reconstruction
Jul 09, 2018



Abstract:We present a framework for accelerated iterative reconstructions using a fast and approximate forward model that is based on k-space methods for photoacoustic tomography. The approximate model introduces aliasing artefacts in the gradient information for the iterative reconstruction, but these artefacts are highly structured and we can train a CNN that can use the approximate information to perform an iterative reconstruction. We show feasibility of the method for human in-vivo measurements in a limited-view geometry. The proposed method is able to produce superior results to total variation reconstructions with a speed-up of 32 times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge