Nagender Aneja
Interpretable Question Answering with Knowledge Graphs
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a question answering system that operates exclusively on a knowledge graph retrieval without relying on retrieval augmented generation (RAG) with large language models (LLMs). Instead, a small paraphraser model is used to paraphrase the entity relationship edges retrieved from querying the knowledge graph. The proposed pipeline is divided into two main stages. The first stage involves pre-processing a document to generate sets of question-answer (QA) pairs. The second stage converts these QAs into a knowledge graph from which graph-based retrieval is performed using embeddings and fuzzy techniques. The graph is queried, re-ranked, and paraphrased to generate a final answer. This work includes an evaluation using LLM-as-a-judge on the CRAG benchmark, which resulted in accuracies of 71.9% and 54.4% using LLAMA-3.2 and GPT-3.5-Turbo, respectively.
Predictive linguistic cues for fake news: a societal artificial intelligence problem
Nov 26, 2022Abstract:Media news are making a large part of public opinion and, therefore, must not be fake. News on web sites, blogs, and social media must be analyzed before being published. In this paper, we present linguistic characteristics of media news items to differentiate between fake news and real news using machine learning algorithms. Neural fake news generation, headlines created by machines, semantic incongruities in text and image captions generated by machine are other types of fake news problems. These problems use neural networks which mainly control distributional features rather than evidence. We propose applying correlation between features set and class, and correlation among the features to compute correlation attribute evaluation metric and covariance metric to compute variance of attributes over the news items. Features unique, negative, positive, and cardinal numbers with high values on the metrics are observed to provide a high area under the curve (AUC) and F1-score.
Defense against adversarial attacks on deep convolutional neural networks through nonlocal denoising
Jun 25, 2022



Abstract:Despite substantial advances in network architecture performance, the susceptibility of adversarial attacks makes deep learning challenging to implement in safety-critical applications. This paper proposes a data-centric approach to addressing this problem. A nonlocal denoising method with different luminance values has been used to generate adversarial examples from the Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology database (MNIST) and Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR-10) data sets. Under perturbation, the method provided absolute accuracy improvements of up to 9.3% in the MNIST data set and 13% in the CIFAR-10 data set. Training using transformed images with higher luminance values increases the robustness of the classifier. We have shown that transfer learning is disadvantageous for adversarial machine learning. The results indicate that simple adversarial examples can improve resilience and make deep learning easier to apply in various applications.
Transfer learning for cancer diagnosis in histopathological images
Dec 31, 2021



Abstract:Transfer learning allows us to exploit knowledge gained from one task to assist in solving another but relevant task. In modern computer vision research, the question is which architecture performs better for a given dataset. In this paper, we compare the performance of 14 pre-trained ImageNet models on the histopathologic cancer detection dataset, where each model has been configured as a naive model, feature extractor model, or fine-tuned model. Densenet161 has been shown to have high precision whilst Resnet101 has a high recall. A high precision model is suitable to be used when follow-up examination cost is high, whilst low precision but a high recall/sensitivity model can be used when the cost of follow-up examination is low. Results also show that transfer learning helps to converge a model faster.
Collaborative adversary nodes learning on the logs of IoT devices in an IoT network
Dec 22, 2021



Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) development has encouraged many new research areas, including AI-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) network. AI analytics and intelligent paradigms greatly improve learning efficiency and accuracy. Applying these learning paradigms to network scenarios provide technical advantages of new networking solutions. In this paper, we propose an improved approach for IoT security from data perspective. The network traffic of IoT devices can be analyzed using AI techniques. The Adversary Learning (AdLIoTLog) model is proposed using Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) with attention mechanism on sequences of network events in the network traffic. We define network events as a sequence of the time series packets of protocols captured in the log. We have considered different packets TCP packets, UDP packets, and HTTP packets in the network log to make the algorithm robust. The distributed IoT devices can collaborate to cripple our world which is extending to Internet of Intelligence. The time series packets are converted into structured data by removing noise and adding timestamps. The resulting data set is trained by RNN and can detect the node pairs collaborating with each other. We used the BLEU score to evaluate the model performance. Our results show that the predicting performance of the AdLIoTLog model trained by our method degrades by 3-4% in the presence of attack in comparison to the scenario when the network is not under attack. AdLIoTLog can detect adversaries because when adversaries are present the model gets duped by the collaborative events and therefore predicts the next event with a biased event rather than a benign event. We conclude that AI can provision ubiquitous learning for the new generation of Internet of Things.
NL-Augmenter: A Framework for Task-Sensitive Natural Language Augmentation
Dec 06, 2021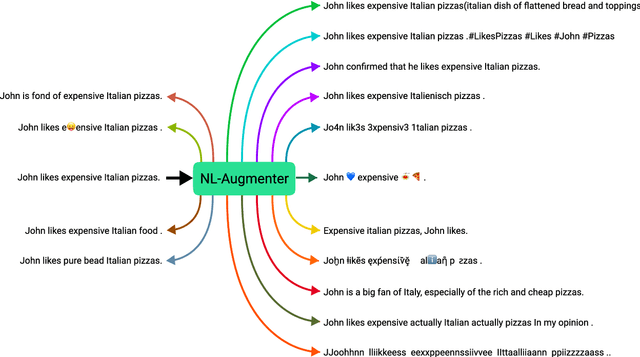
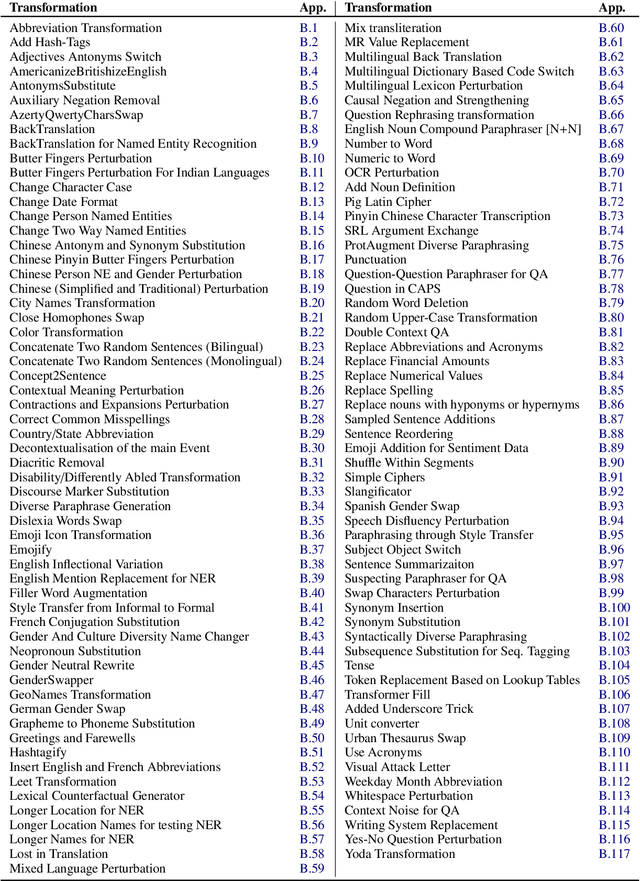
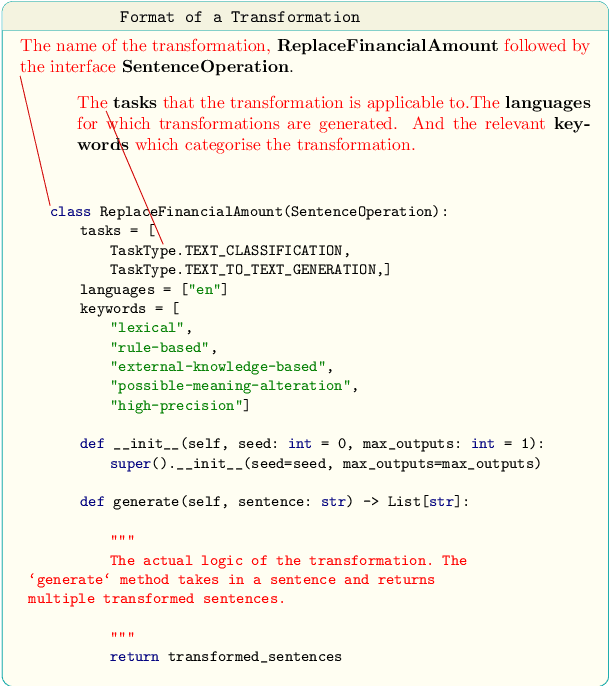
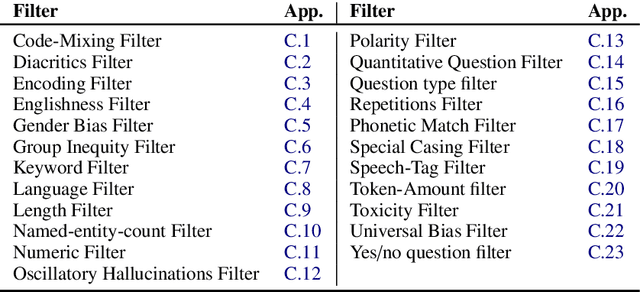
Abstract:Data augmentation is an important component in the robustness evaluation of models in natural language processing (NLP) and in enhancing the diversity of the data they are trained on. In this paper, we present NL-Augmenter, a new participatory Python-based natural language augmentation framework which supports the creation of both transformations (modifications to the data) and filters (data splits according to specific features). We describe the framework and an initial set of 117 transformations and 23 filters for a variety of natural language tasks. We demonstrate the efficacy of NL-Augmenter by using several of its transformations to analyze the robustness of popular natural language models. The infrastructure, datacards and robustness analysis results are available publicly on the NL-Augmenter repository (\url{https://github.com/GEM-benchmark/NL-Augmenter}).
Network Traffic Analysis based IoT Device Identification
Sep 10, 2020



Abstract:Device identification is the process of identifying a device on Internet without using its assigned network or other credentials. The sharp rise of usage in Internet of Things (IoT) devices has imposed new challenges in device identification due to a wide variety of devices, protocols and control interfaces. In a network, conventional IoT devices identify each other by utilizing IP or MAC addresses, which are prone to spoofing. Moreover, IoT devices are low power devices with minimal embedded security solution. To mitigate the issue in IoT devices, fingerprint (DFP) for device identification can be used. DFP identifies a device by using implicit identifiers, such as network traffic (or packets), radio signal, which a device used for its communication over the network. These identifiers are closely related to the device hardware and software features. In this paper, we exploit TCP/IP packet header features to create a device fingerprint utilizing device originated network packets. We present a set of three metrics which separate some features from a packet which contribute actively for device identification. To evaluate our approach, we used publicly accessible two datasets. We observed the accuracy of device genre classification 99.37% and 83.35% of accuracy in the identification of an individual device from IoT Sentinel dataset. However, using UNSW dataset device type identification accuracy reached up to 97.78%.
Neural Machine Translation model for University Email Application
Jul 20, 2020



Abstract:Machine translation has many applications such as news translation, email translation, official letter translation etc. Commercial translators, e.g. Google Translation lags in regional vocabulary and are unable to learn the bilingual text in the source and target languages within the input. In this paper, a regional vocabulary-based application-oriented Neural Machine Translation (NMT) model is proposed over the data set of emails used at the University for communication over a period of three years. A state-of-the-art Sequence-to-Sequence Neural Network for ML -> EN and EN -> ML translations is compared with Google Translate using Gated Recurrent Unit Recurrent Neural Network machine translation model with attention decoder. The low BLEU score of Google Translation in comparison to our model indicates that the application based regional models are better. The low BLEU score of EN -> ML of our model and Google Translation indicates that the Malay Language has complex language features corresponding to English.
* International Conference on Natural Language Processing (ICNLP 2020), July 11-13, 2020
Transfer Learning using CNN for Handwritten Devanagari Character Recognition
Sep 19, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents an analysis of pre-trained models to recognize handwritten Devanagari alphabets using transfer learning for Deep Convolution Neural Network (DCNN). This research implements AlexNet, DenseNet, Vgg, and Inception ConvNet as a fixed feature extractor. We implemented 15 epochs for each of AlexNet, DenseNet 121, DenseNet 201, Vgg 11, Vgg 16, Vgg 19, and Inception V3. Results show that Inception V3 performs better in terms of accuracy achieving 99% accuracy with average epoch time 16.3 minutes while AlexNet performs fastest with 2.2 minutes per epoch and achieving 98\% accuracy.
Semi-Supervised Learning for Cancer Detection of Lymph Node Metastases
Jun 23, 2019



Abstract:Pathologists find tedious to examine the status of the sentinel lymph node on a large number of pathological scans. The examination process of such lymph node which encompasses metastasized cancer cells is histopathologically organized. However, the task of finding metastatic tissues is gradual which is often challenging. In this work, we present our deep convolutional neural network based model validated on PatchCamelyon (PCam) benchmark dataset for fundamental machine learning research in histopathology diagnosis. We find that our proposed model trained with a semi-supervised learning approach by using pseudo labels on PCam-level significantly leads to better performances to strong CNN baseline on the AUC metric.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge