Musen Wen
Semantic Ads Retrieval at Walmart eCommerce with Language Models Progressively Trained on Multiple Knowledge Domains
Feb 13, 2025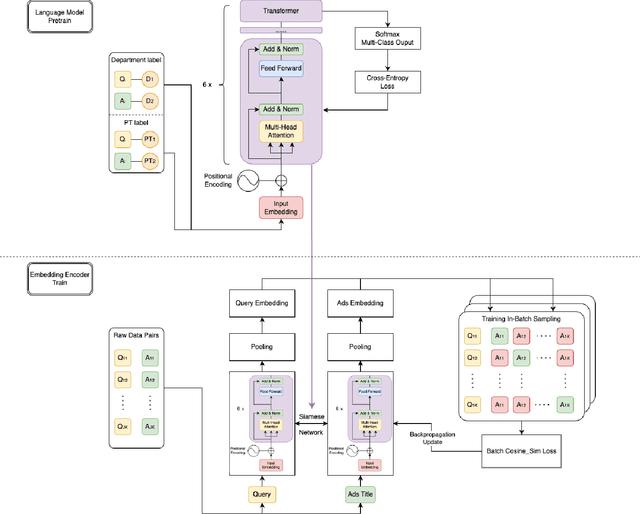
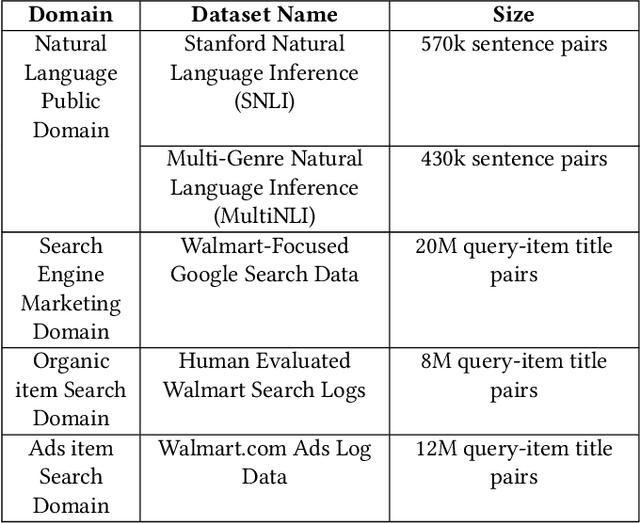
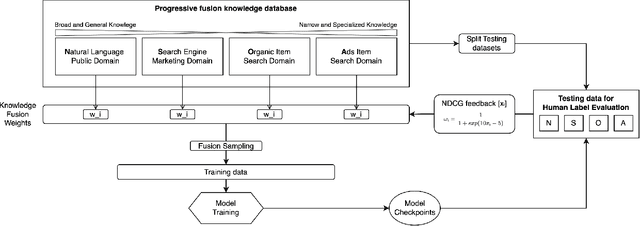
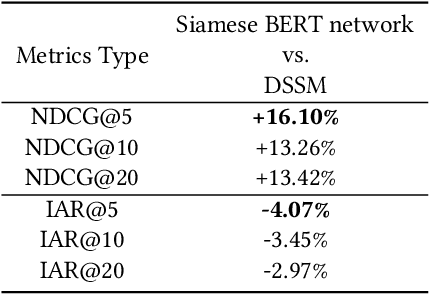
Abstract:Sponsored search in e-commerce poses several unique and complex challenges. These challenges stem from factors such as the asymmetric language structure between search queries and product names, the inherent ambiguity in user search intent, and the vast volume of sparse and imbalanced search corpus data. The role of the retrieval component within a sponsored search system is pivotal, serving as the initial step that directly affects the subsequent ranking and bidding systems. In this paper, we present an end-to-end solution tailored to optimize the ads retrieval system on Walmart.com. Our approach is to pretrain the BERT-like classification model with product category information, enhancing the model's understanding of Walmart product semantics. Second, we design a two-tower Siamese Network structure for embedding structures to augment training efficiency. Third, we introduce a Human-in-the-loop Progressive Fusion Training method to ensure robust model performance. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of this pipeline. It enhances the search relevance metric by up to 16% compared to a baseline DSSM-based model. Moreover, our large-scale online A/B testing demonstrates that our approach surpasses the ad revenue of the existing production model.
Enhanced E-Commerce Attribute Extraction: Innovating with Decorative Relation Correction and LLAMA 2.0-Based Annotation
Dec 09, 2023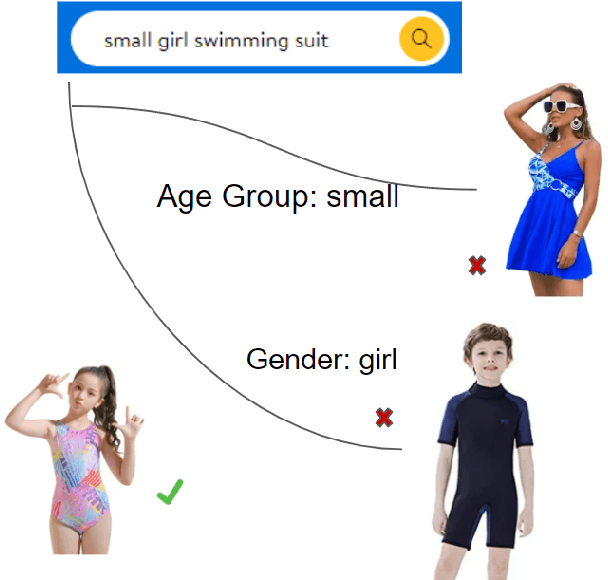
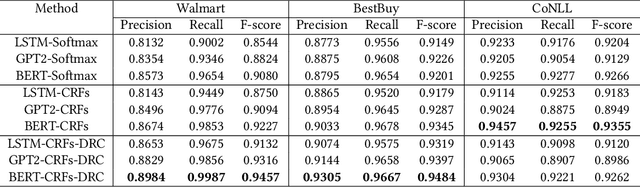
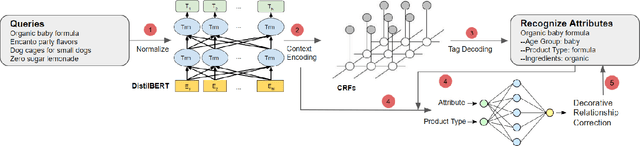
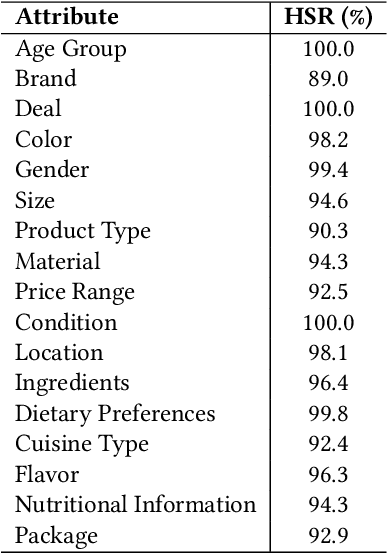
Abstract:The rapid proliferation of e-commerce platforms accentuates the need for advanced search and retrieval systems to foster a superior user experience. Central to this endeavor is the precise extraction of product attributes from customer queries, enabling refined search, comparison, and other crucial e-commerce functionalities. Unlike traditional Named Entity Recognition (NER) tasks, e-commerce queries present a unique challenge owing to the intrinsic decorative relationship between product types and attributes. In this study, we propose a pioneering framework that integrates BERT for classification, a Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) layer for attribute value extraction, and Large Language Models (LLMs) for data annotation, significantly advancing attribute recognition from customer inquiries. Our approach capitalizes on the robust representation learning of BERT, synergized with the sequence decoding prowess of CRFs, to adeptly identify and extract attribute values. We introduce a novel decorative relation correction mechanism to further refine the extraction process based on the nuanced relationships between product types and attributes inherent in e-commerce data. Employing LLMs, we annotate additional data to expand the model's grasp and coverage of diverse attributes. Our methodology is rigorously validated on various datasets, including Walmart, BestBuy's e-commerce NER dataset, and the CoNLL dataset, demonstrating substantial improvements in attribute recognition performance. Particularly, the model showcased promising results during a two-month deployment in Walmart's Sponsor Product Search, underscoring its practical utility and effectiveness.
Leveraging Large Language Models for Enhanced Product Descriptions in eCommerce
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:In the dynamic field of eCommerce, the quality and comprehensiveness of product descriptions are pivotal for enhancing search visibility and customer engagement. Effective product descriptions can address the 'cold start' problem, align with market trends, and ultimately lead to increased click-through rates. Traditional methods for crafting these descriptions often involve significant human effort and may lack both consistency and scalability. This paper introduces a novel methodology for automating product description generation using the LLAMA 2.0 7B language model. We train the model on a dataset of authentic product descriptions from Walmart, one of the largest eCommerce platforms. The model is then fine-tuned for domain-specific language features and eCommerce nuances to enhance its utility in sales and user engagement. We employ multiple evaluation metrics, including NDCG, customer click-through rates, and human assessments, to validate the effectiveness of our approach. Our findings reveal that the system is not only scalable but also significantly reduces the human workload involved in creating product descriptions. This study underscores the considerable potential of large language models like LLAMA 2.0 7B in automating and optimizing various facets of eCommerce platforms, offering significant business impact, including improved search functionality and increased sales.
Click-Conversion Multi-Task Model with Position Bias Mitigation for Sponsored Search in eCommerce
Jul 29, 2023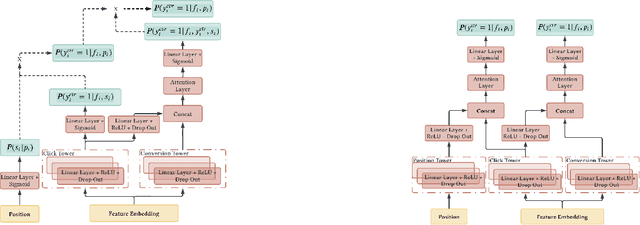
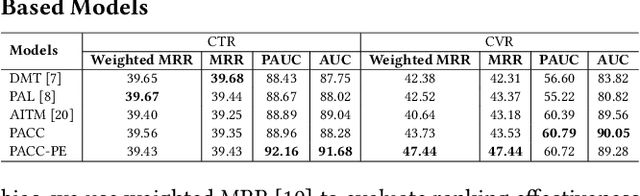
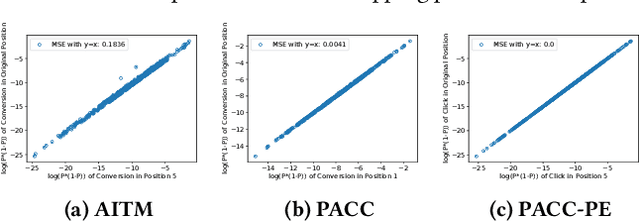
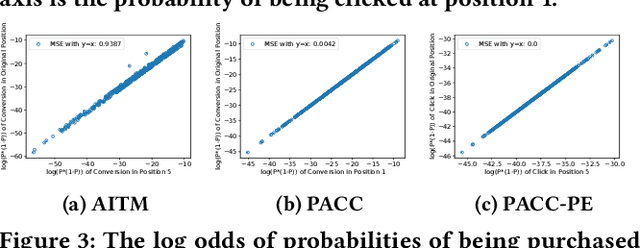
Abstract:Position bias, the phenomenon whereby users tend to focus on higher-ranked items of the search result list regardless of the actual relevance to queries, is prevailing in many ranking systems. Position bias in training data biases the ranking model, leading to increasingly unfair item rankings, click-through-rate (CTR), and conversion rate (CVR) predictions. To jointly mitigate position bias in both item CTR and CVR prediction, we propose two position-bias-free CTR and CVR prediction models: Position-Aware Click-Conversion (PACC) and PACC via Position Embedding (PACC-PE). PACC is built upon probability decomposition and models position information as a probability. PACC-PE utilizes neural networks to model product-specific position information as embedding. Experiments on the E-commerce sponsored product search dataset show that our proposed models have better ranking effectiveness and can greatly alleviate position bias in both CTR and CVR prediction.
* Modified some typos of the published SIGIR version
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge