Muhammad Umair
Optimizing Keyphrase Ranking for Relevance and Diversity Using Submodular Function Optimization (SFO)
Oct 26, 2024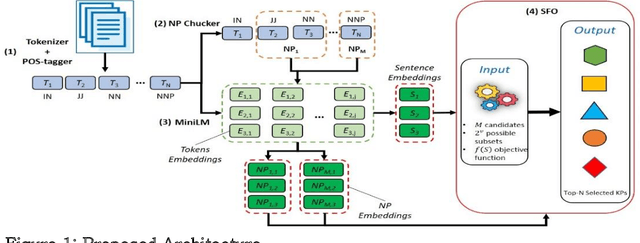
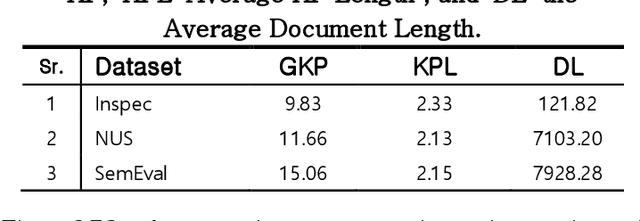
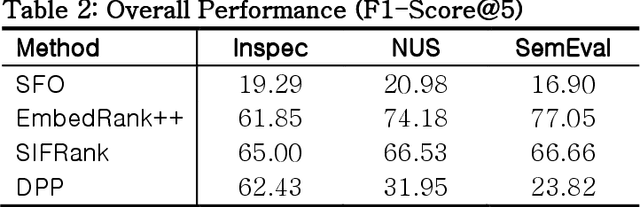

Abstract:Keyphrase ranking plays a crucial role in information retrieval and summarization by indexing and retrieving relevant information efficiently. Advances in natural language processing, especially large language models (LLMs), have improved keyphrase extraction and ranking. However, traditional methods often overlook diversity, resulting in redundant keyphrases. We propose a novel approach using Submodular Function Optimization (SFO) to balance relevance and diversity in keyphrase ranking. By framing the task as submodular maximization, our method selects diverse and representative keyphrases. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our approach outperforms existing methods in both relevance and diversity metrics, achieving SOTA performance in execution time. Our code is available online.
Large Language Models Know What To Say But Not When To Speak
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Turn-taking is a fundamental mechanism in human communication that ensures smooth and coherent verbal interactions. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have motivated their use in improving the turn-taking capabilities of Spoken Dialogue Systems (SDS), such as their ability to respond at appropriate times. However, existing models often struggle to predict opportunities for speaking -- called Transition Relevance Places (TRPs) -- in natural, unscripted conversations, focusing only on turn-final TRPs and not within-turn TRPs. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel dataset of participant-labeled within-turn TRPs and use it to evaluate the performance of state-of-the-art LLMs in predicting opportunities for speaking. Our experiments reveal the current limitations of LLMs in modeling unscripted spoken interactions, highlighting areas for improvement and paving the way for more naturalistic dialogue systems.
AI-Driven Chatbot for Intrusion Detection in Edge Networks: Enhancing Cybersecurity with Ethical User Consent
Aug 08, 2024Abstract:In today's contemporary digital landscape, chatbots have become indispensable tools across various sectors, streamlining customer service, providing personal assistance, automating routine tasks, and offering health advice. However, their potential remains underexplored in the realm of network security, particularly for intrusion detection. To bridge this gap, we propose an architecture chatbot specifically designed to enhance security within edge networks specifically for intrusion detection. Leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms, this chatbot will monitor network traffic to identify and mitigate potential intrusions. By securing the network environment using an edge network managed by a Raspberry Pi module and ensuring ethical user consent promoting transparency and trust, this innovative solution aims to safeguard sensitive data and maintain a secure workplace, thereby addressing the growing need for robust network security measures in the digital age.
Leveraging Deep Stein's Unbiased Risk Estimator for Unsupervised X-ray Denoising
Nov 29, 2018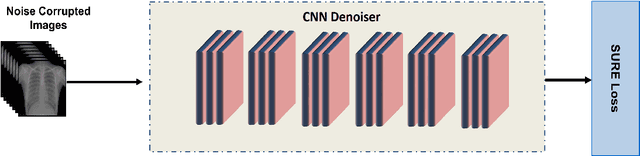
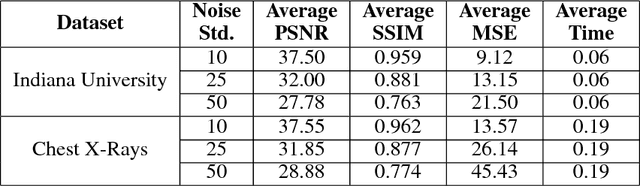
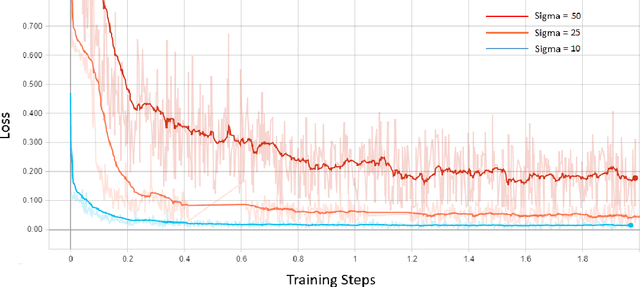
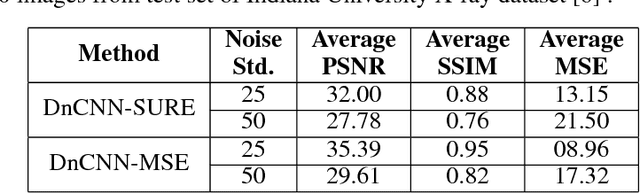
Abstract:Among the plethora of techniques devised to curb the prevalence of noise in medical images, deep learning based approaches have shown the most promise. However, one critical limitation of these deep learning based denoisers is the requirement of high-quality noiseless ground truth images that are difficult to obtain in many medical imaging applications such as X-rays. To circumvent this issue, we leverage recently proposed approach of [7] that incorporates Stein's Unbiased Risk Estimator (SURE) to train a deep convolutional neural network without requiring denoised ground truth X-ray data. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of SURE based approach for denoising X-ray images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge