Young-Koo Lee
MQ-GNN: A Multi-Queue Pipelined Architecture for Scalable and Efficient GNN Training
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are powerful tools for learning graph-structured data, but their scalability is hindered by inefficient mini-batch generation, data transfer bottlenecks, and costly inter-GPU synchronization. Existing training frameworks fail to overlap these stages, leading to suboptimal resource utilization. This paper proposes MQ-GNN, a multi-queue pipelined framework that maximizes training efficiency by interleaving GNN training stages and optimizing resource utilization. MQ-GNN introduces Ready-to-Update Asynchronous Consistent Model (RaCoM), which enables asynchronous gradient sharing and model updates while ensuring global consistency through adaptive periodic synchronization. Additionally, it employs global neighbor sampling with caching to reduce data transfer overhead and an adaptive queue-sizing strategy to balance computation and memory efficiency. Experiments on four large-scale datasets and ten baseline models demonstrate that MQ-GNN achieves up to \boldmath $\bm{4.6\,\times}$ faster training time and 30% improved GPU utilization while maintaining competitive accuracy. These results establish MQ-GNN as a scalable and efficient solution for multi-GPU GNN training.
Optimizing Keyphrase Ranking for Relevance and Diversity Using Submodular Function Optimization (SFO)
Oct 26, 2024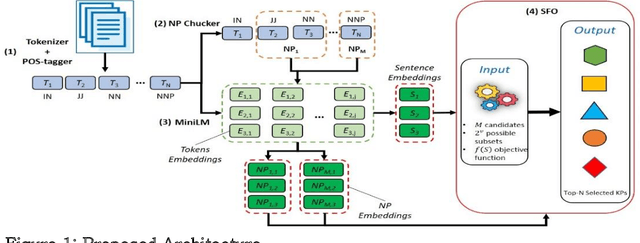
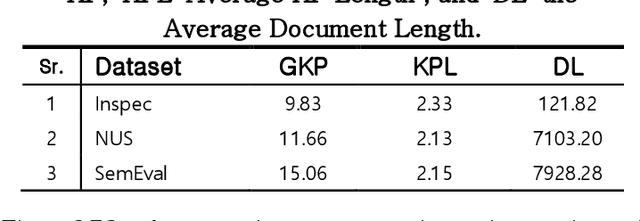
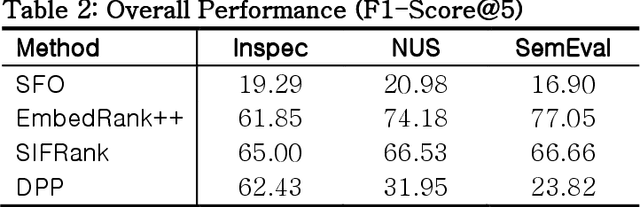

Abstract:Keyphrase ranking plays a crucial role in information retrieval and summarization by indexing and retrieving relevant information efficiently. Advances in natural language processing, especially large language models (LLMs), have improved keyphrase extraction and ranking. However, traditional methods often overlook diversity, resulting in redundant keyphrases. We propose a novel approach using Submodular Function Optimization (SFO) to balance relevance and diversity in keyphrase ranking. By framing the task as submodular maximization, our method selects diverse and representative keyphrases. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our approach outperforms existing methods in both relevance and diversity metrics, achieving SOTA performance in execution time. Our code is available online.
RweetMiner: Automatic identification and categorization of help requests on twitter during disasters
Mar 04, 2023



Abstract:Catastrophic events create uncertain situations for humanitarian organizations locating and providing aid to affected people. Many people turn to social media during disasters for requesting help and/or providing relief to others. However, the majority of social media posts seeking help could not properly be detected and remained concealed because often they are noisy and ill-formed. Existing systems lack in planning an effective strategy for tweet preprocessing and grasping the contexts of tweets. This research, first of all, formally defines request tweets in the context of social networking sites, hereafter rweets, along with their different primary types and sub-types. Our main contributions are the identification and categorization of rweets. For rweet identification, we employ two approaches, namely a rule-based and logistic regression, and show their high precision and F1 scores. The rweets classification into sub-types such as medical, food, and shelter, using logistic regression shows promising results and outperforms existing works. Finally, we introduce an architecture to store intermediate data to accelerate the development process of the machine learning classifiers.
A Multimodal Memes Classification: A Survey and Open Research Issues
Sep 17, 2020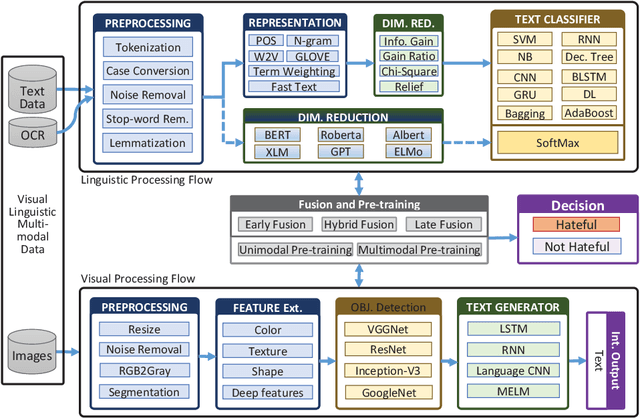
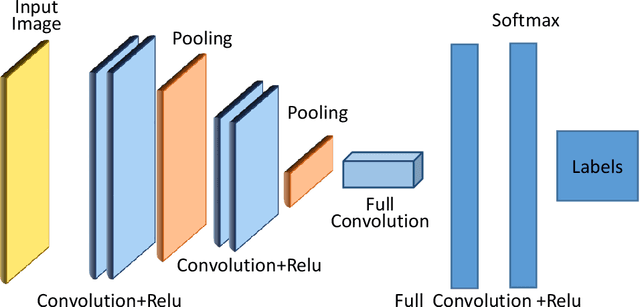
Abstract:Memes are graphics and text overlapped so that together they present concepts that become dubious if one of them is absent. It is spread mostly on social media platforms, in the form of jokes, sarcasm, motivating, etc. After the success of BERT in Natural Language Processing (NLP), researchers inclined to Visual-Linguistic (VL) multimodal problems like memes classification, image captioning, Visual Question Answering (VQA), and many more. Unfortunately, many memes get uploaded each day on social media platforms that need automatic censoring to curb misinformation and hate. Recently, this issue has attracted the attention of researchers and practitioners. State-of-the-art methods that performed significantly on other VL dataset, tends to fail on memes classification. In this context, this work aims to conduct a comprehensive study on memes classification, generally on the VL multimodal problems and cutting edge solutions. We propose a generalized framework for VL problems. We cover the early and next-generation works on VL problems. Finally, we identify and articulate several open research issues and challenges. This is the first study that presents the generalized view of the advanced classification techniques concerning memes classification to the best of our knowledge. We believe this study presents a clear road-map for the Machine Learning (ML) research community to implement and enhance memes classification techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge