Monica Rodriguez
RoboCup Rescue 2025 Team Description Paper UruBots
Apr 14, 2025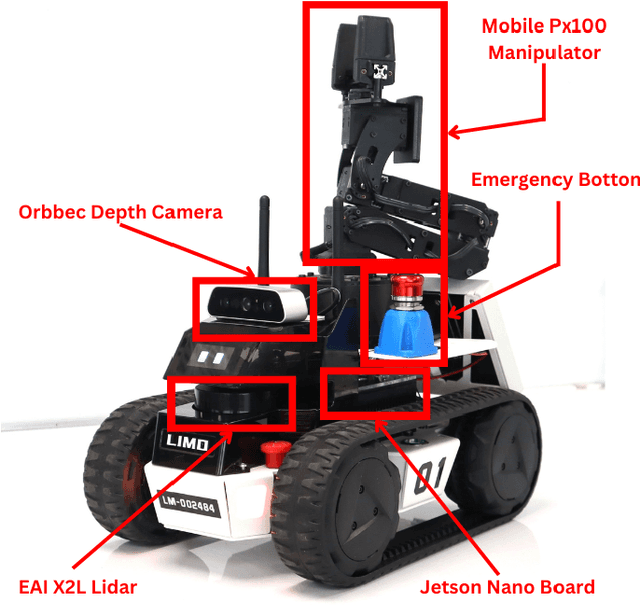
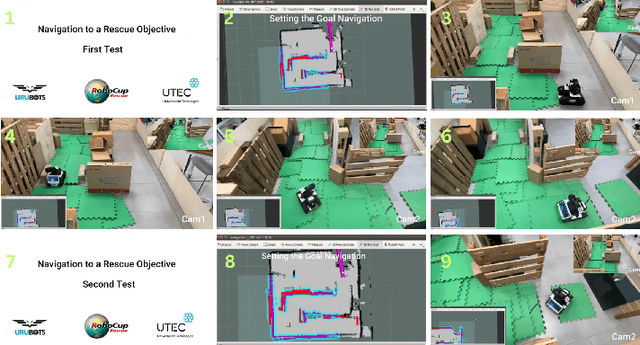
Abstract:This paper describes the approach used by Team UruBots for participation in the 2025 RoboCup Rescue Robot League competition. Our team aims to participate for the first time in this competition at RoboCup, using experience learned from previous competitions and research. We present our vehicle and our approach to tackle the task of detecting and finding victims in search and rescue environments. Our approach contains known topics in robotics, such as ROS, SLAM, Human Robot Interaction and segmentation and perception. Our proposed approach is open source, available to the RoboCup Rescue community, where we aim to learn and contribute to the league.
UruBots RoboCup Work Team Description Paper
Apr 13, 2025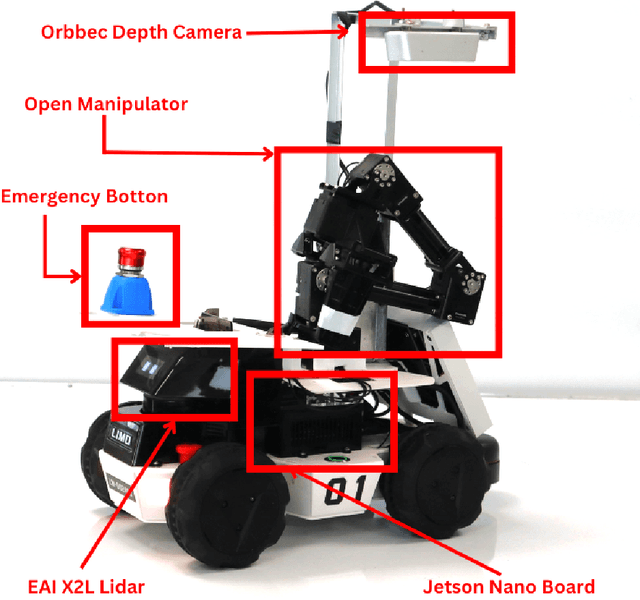
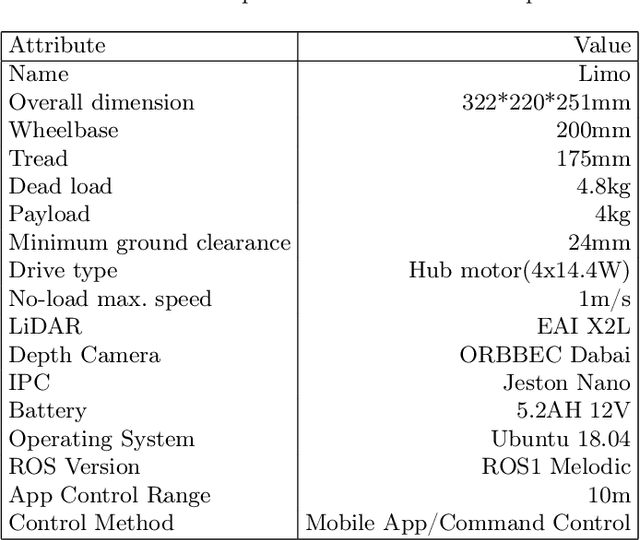
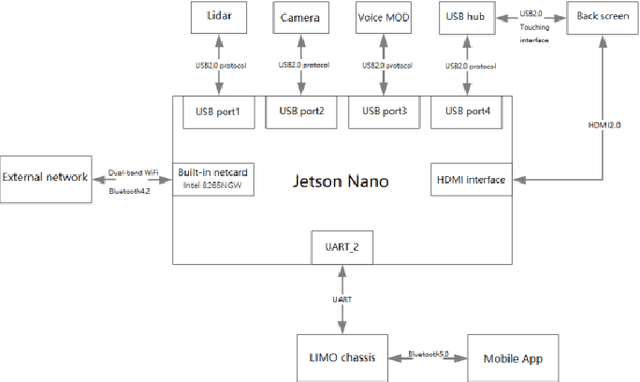
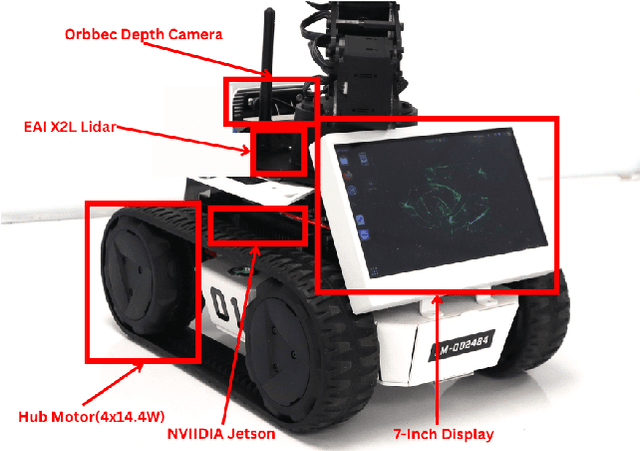
Abstract:This work presents a team description paper for the RoboCup Work League. Our team, UruBots, has been developing robots and projects for research and competitions in the last three years, attending robotics competitions in Uruguay and around the world. In this instance, we aim to participate and contribute to the RoboCup Work category, hopefully making our debut in this prestigious competition. For that, we present an approach based on the Limo robot, whose main characteristic is its hybrid locomotion system with wheels and tracks, with some extras added by the team to complement the robot's functionalities. Overall, our approach allows the robot to efficiently and autonomously navigate a Work scenario, with the ability to manipulate objects, perform autonomous navigation, and engage in a simulated industrial environment.
Aplicacion de Robots Humanoides como Guias Interactivos en Museos: Una Simulacion con el Robot NAO
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:This article presents an application that evaluates the feasibility of humanoid robots as interactive guides in art museums. The application entailes programming a NAO robot and a chatbot to provide information about art pieces in a simulated museum environment. In this controlled scenario, the learning employees interact with the robot and the chatbot. The result is a skilled participation in the interactions, along with the effectiveness of the robot and chatbot that communicates the basic details of the art objects. You see natural and fluid interactions between the students and the robot. This suggests that the addition of humanoid robots to museums may provide a better experience for visitors, but also the need to continue to do more to optimize the quality of interaction. This study contributes to understanding the possibilities and requirements of applying humanoid technologies in a cultural context.
Diseno y Desarrollo de Prototipos Roboticos para Competencias de Futbol utilizando Motores Dynamixel
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:This article describes the design and development of robotic prototypes for robotic soccer competitions using Dynamixel motors. Although the prototypes are not aimed at world-class competitions, they represent a significant step in the development of sports robots. Model XL430-W250 Dynamixel motors were chosen and electronic circuits were implemented using control boards such as OpenCR and Raspberry Pi 3. A crucial component was introduced: a step-up board that charges a capacitor to create a powerful kick to the ball via anelectromagnet controlled by Arduino Nano. The programming and coordination of the prototypes was carried out using the ROS environment (Robot Operating System), which allows effective integration of movements and communication. Although the prototypes were not optimized for global competition, they underwent extensive testing, evaluating their speed and maneuverability, as well as soccer tactics in the GRSim simulator. These prototypes contribute to the further development of sports robotics and illustrate the research potential in this exciting area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge