Vincent Sandin
RoboCup Rescue 2025 Team Description Paper UruBots
Apr 14, 2025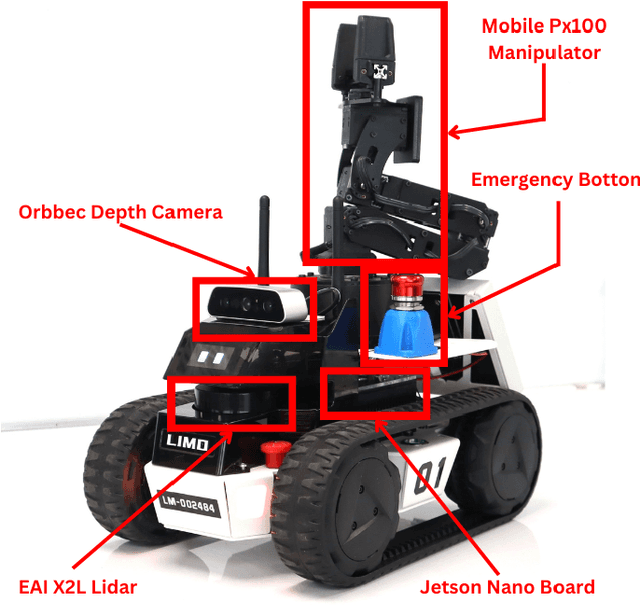
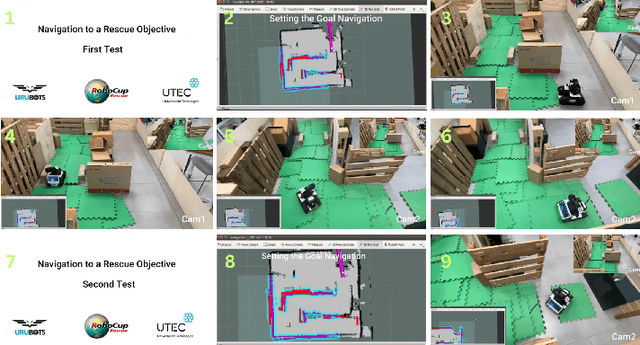
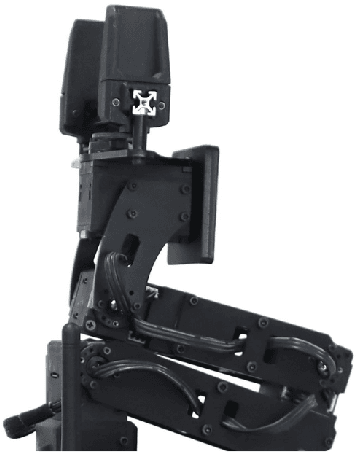
Abstract:This paper describes the approach used by Team UruBots for participation in the 2025 RoboCup Rescue Robot League competition. Our team aims to participate for the first time in this competition at RoboCup, using experience learned from previous competitions and research. We present our vehicle and our approach to tackle the task of detecting and finding victims in search and rescue environments. Our approach contains known topics in robotics, such as ROS, SLAM, Human Robot Interaction and segmentation and perception. Our proposed approach is open source, available to the RoboCup Rescue community, where we aim to learn and contribute to the league.
UruBots RoboCup Work Team Description Paper
Apr 13, 2025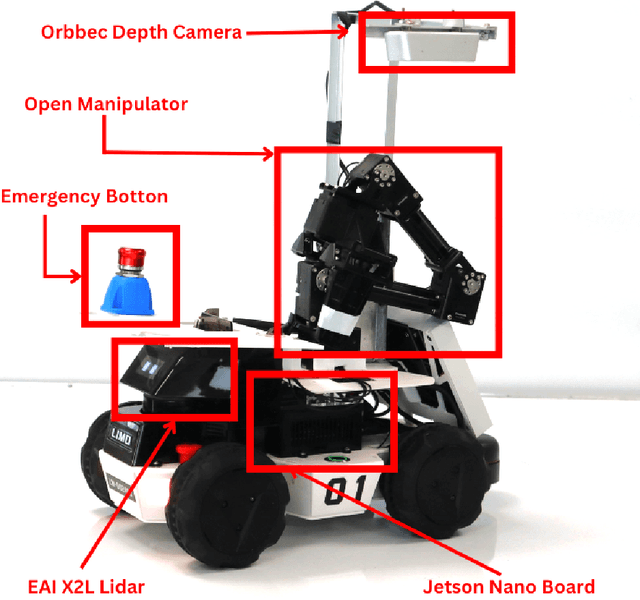
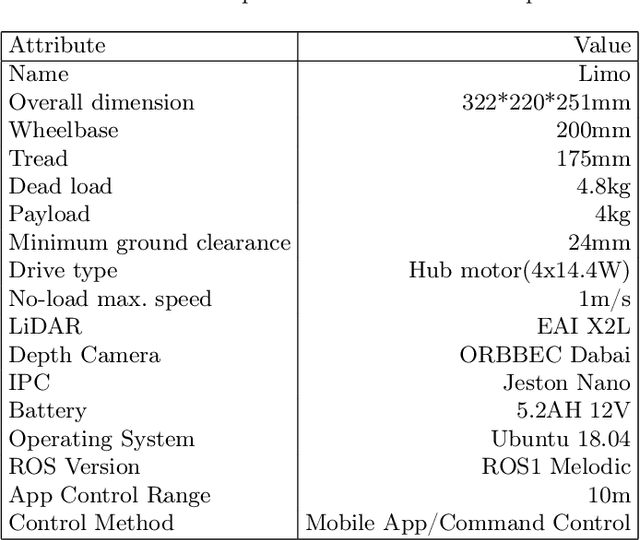
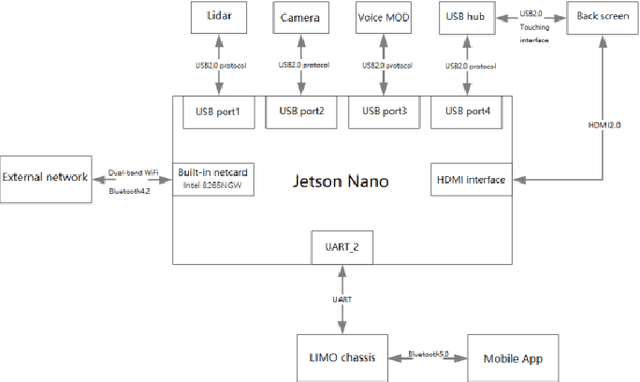
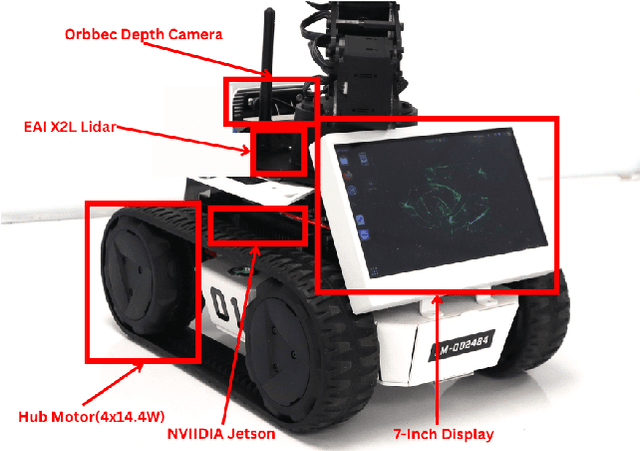
Abstract:This work presents a team description paper for the RoboCup Work League. Our team, UruBots, has been developing robots and projects for research and competitions in the last three years, attending robotics competitions in Uruguay and around the world. In this instance, we aim to participate and contribute to the RoboCup Work category, hopefully making our debut in this prestigious competition. For that, we present an approach based on the Limo robot, whose main characteristic is its hybrid locomotion system with wheels and tracks, with some extras added by the team to complement the robot's functionalities. Overall, our approach allows the robot to efficiently and autonomously navigate a Work scenario, with the ability to manipulate objects, perform autonomous navigation, and engage in a simulated industrial environment.
Implementación de Navegación en Plataforma Robótica Móvil Basada en ROS y Gazebo
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:This research focused on utilizing ROS2 and Gazebo for simulating the TurtleBot3 robot, with the aim of exploring autonomous navigation capabilities. While the study did not achieve full autonomous navigation, it successfully established the connection between ROS2 and Gazebo and enabled manual simulation of the robot's movements. The primary objective was to understand how these tools can be integrated to support autonomous functions, providing valuable insights into the development process. The results of this work lay the groundwork for future research into autonomous robotics. The topic is particularly engaging for both teenagers and adults interested in discovering how robots function independently and the underlying technology involved. This research highlights the potential for further advancements in autonomous systems and serves as a stepping stone for more in-depth studies in the field.
Configuração e operação da plataforma Clearpath Husky A200 e Manipulador Cobot UR5 2-Finger Gripper
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:This article presents initial configuration work and use of the robotic platform and manipulator in question. The development of the ideal configuration for using this robot serves as a guide for new users and also validates its functionality for use in projects. Husky is a large payload capacity and power systems robotics development platform that accommodates a wide variety of payloads, customized to meet research needs. Together with the Cobot UR5 Manipulator attached to its base, it expands the application area of its capacity in projects. Advances in robots and mobile manipulators have revolutionized industries by automating tasks that previously required human intervention. These innovations alone increase productivity but also reduce operating costs, which makes the company more competitive in an evolving global market. Therefore, this article investigates the functionalities of this robot to validate its execution in robotics projects.
UruBots Autonomous Car Team Two: Team Description Paper for FIRA 2024
Jun 13, 2024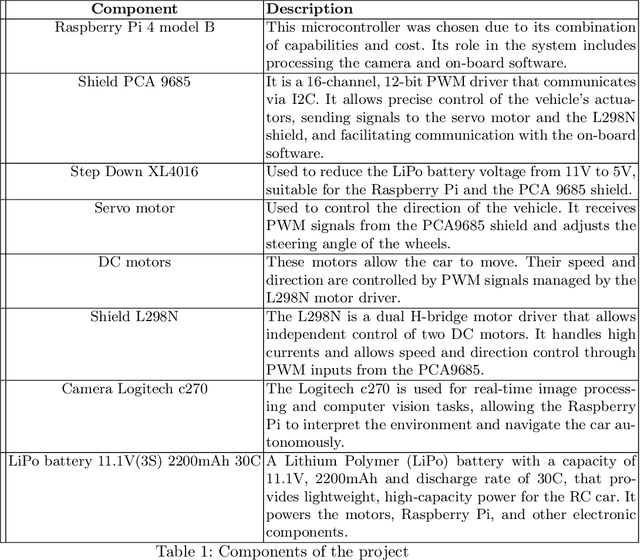
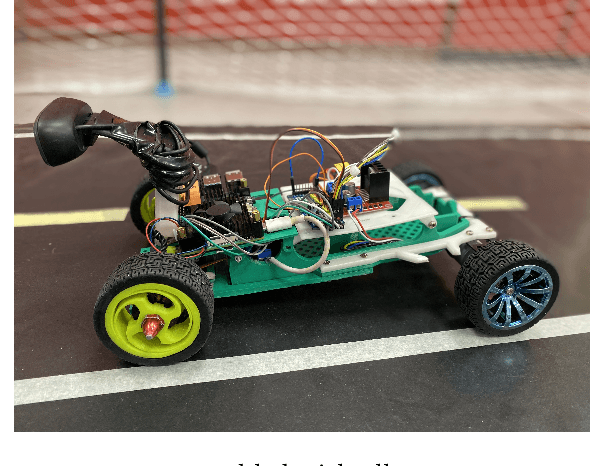
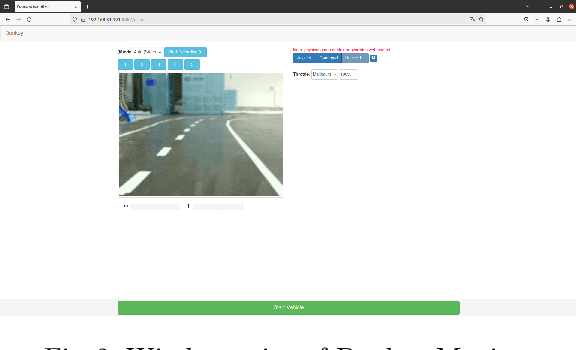

Abstract:This paper proposes a mini autonomous car to be used by the team UruBots for the 2024 FIRA Autonomous Cars Race Challenge. The vehicle is proposed focusing on a low cost and light weight setup. Powered by a Raspberry PI4 and with a total weight of 1.15 Kilograms, we show that our vehicle manages to race a track of approximately 13 meters in 11 seconds at the best evaluation that was carried out, with an average speed of 1.2m/s in average. That performance was achieved after training a convolutional neural network with 1500 samples for a total amount of 60 epochs. Overall, we believe that our vehicle are suited to perform at the FIRA Autonomous Cars Race Challenge 2024, helping the development of the field of study and the category in the competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge