Mohammad Rami Koujan
Head2HeadFS: Video-based Head Reenactment with Few-shot Learning
Mar 30, 2021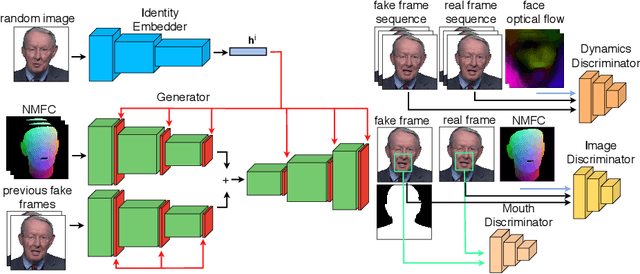
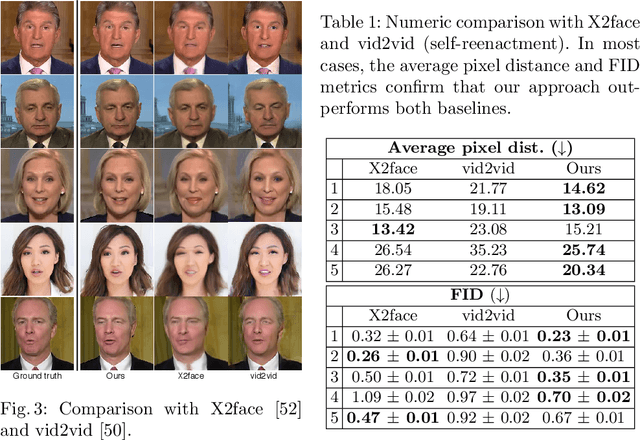

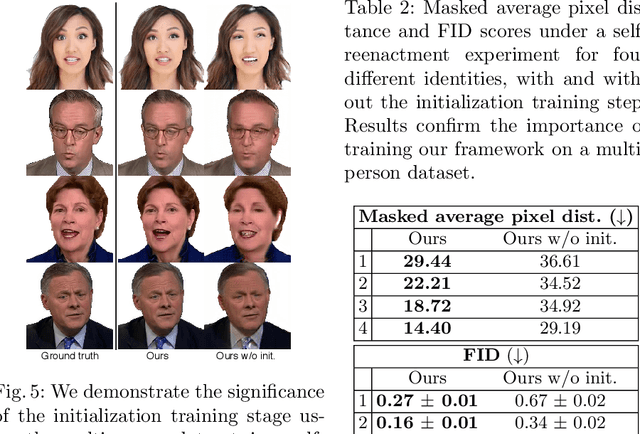
Abstract:Over the past years, a substantial amount of work has been done on the problem of facial reenactment, with the solutions coming mainly from the graphics community. Head reenactment is an even more challenging task, which aims at transferring not only the facial expression, but also the entire head pose from a source person to a target. Current approaches either train person-specific systems, or use facial landmarks to model human heads, a representation that might transfer unwanted identity attributes from the source to the target. We propose head2headFS, a novel easily adaptable pipeline for head reenactment. We condition synthesis of the target person on dense 3D face shape information from the source, which enables high quality expression and pose transfer. Our video-based rendering network is fine-tuned under a few-shot learning strategy, using only a few samples. This allows for fast adaptation of a generic generator trained on a multiple-person dataset, into a person-specific one.
Head2Head++: Deep Facial Attributes Re-Targeting
Jun 17, 2020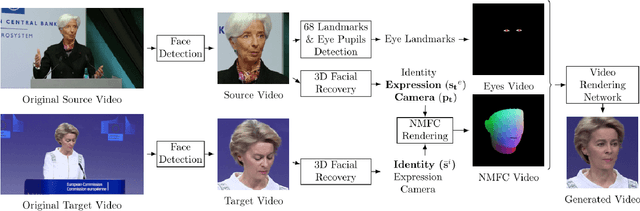
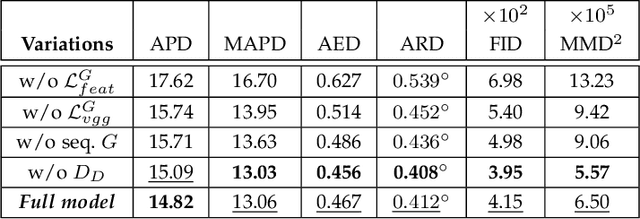

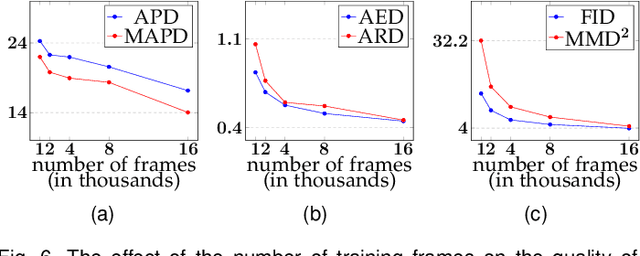
Abstract:Facial video re-targeting is a challenging problem aiming to modify the facial attributes of a target subject in a seamless manner by a driving monocular sequence. We leverage the 3D geometry of faces and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to design a novel deep learning architecture for the task of facial and head reenactment. Our method is different to purely 3D model-based approaches, or recent image-based methods that use Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) to generate individual frames. We manage to capture the complex non-rigid facial motion from the driving monocular performances and synthesise temporally consistent videos, with the aid of a sequential Generator and an ad-hoc Dynamics Discriminator network. We conduct a comprehensive set of quantitative and qualitative tests and demonstrate experimentally that our proposed method can successfully transfer facial expressions, head pose and eye gaze from a source video to a target subject, in a photo-realistic and faithful fashion, better than other state-of-the-art methods. Most importantly, our system performs end-to-end reenactment in nearly real-time speed (18 fps).
Real-Time Monocular 4D Face Reconstruction using the LSFM models
May 22, 2020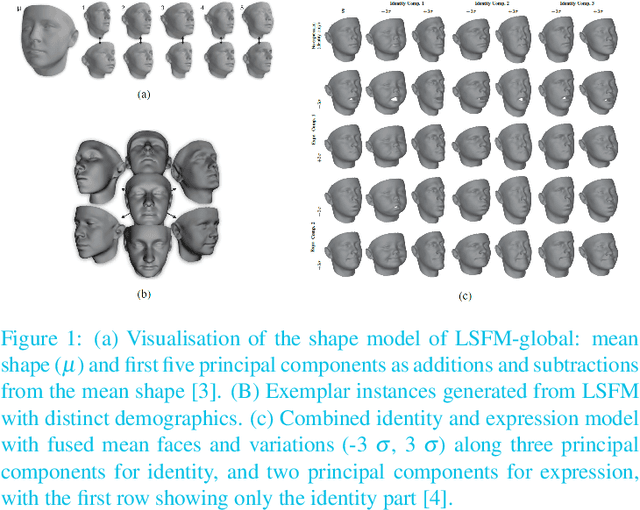
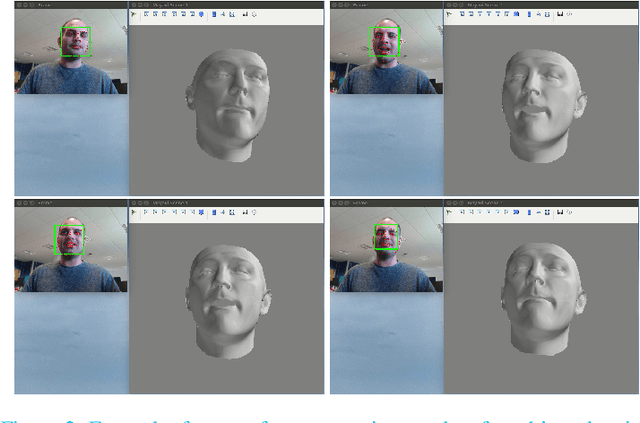
Abstract:4D face reconstruction from a single camera is a challenging task, especially when it is required to be performed in real time. We demonstrate a system of our own implementation that solves this task accurately and runs in real time on a commodity laptop, using a webcam as the only input. Our system is interactive, allowing the user to freely move their head and show various expressions while standing in front of the camera. As a result, the put forward system both reconstructs and visualises the identity of the subject in the correct pose along with the acted facial expressions in real-time. The 4D reconstruction in our framework is based on the recently-released Large-Scale Facial Models (LSFM) \cite{LSFM1, LSFM2}, which are the largest-scale 3D Morphable Models of facial shapes ever constructed, based on a dataset of more than 10,000 facial identities from a wide range of gender, age and ethnicity combinations. This is the first real-time demo that gives users the opportunity to test in practice the capabilities of the recently-released Large-Scale Facial Models (LSFM)
ReenactNet: Real-time Full Head Reenactment
May 22, 2020Abstract:Video-to-video synthesis is a challenging problem aiming at learning a translation function between a sequence of semantic maps and a photo-realistic video depicting the characteristics of a driving video. We propose a head-to-head system of our own implementation capable of fully transferring the human head 3D pose, facial expressions and eye gaze from a source to a target actor, while preserving the identity of the target actor. Our system produces high-fidelity, temporally-smooth and photo-realistic synthetic videos faithfully transferring the human time-varying head attributes from the source to the target actor. Our proposed implementation: 1) works in real time ($\sim 20$ fps), 2) runs on a commodity laptop with a webcam as the only input, 3) is interactive, allowing the participant to drive a target person, e.g. a celebrity, politician, etc, instantly by varying their expressions, head pose, and eye gaze, and visualising the synthesised video concurrently.
Head2Head: Video-based Neural Head Synthesis
May 22, 2020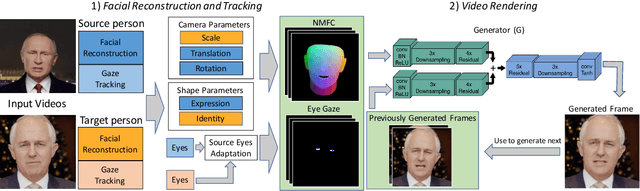
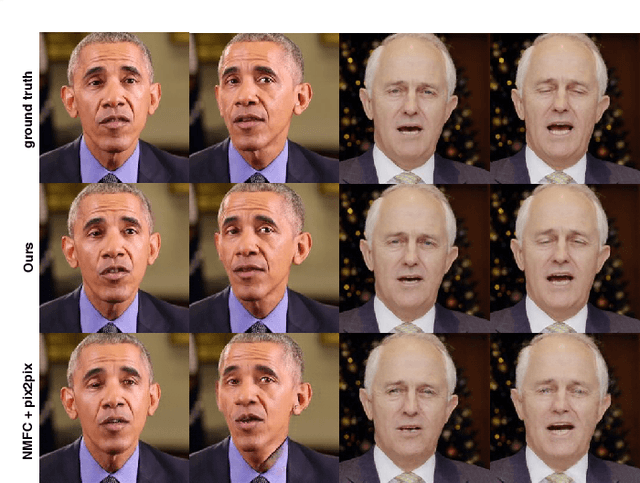

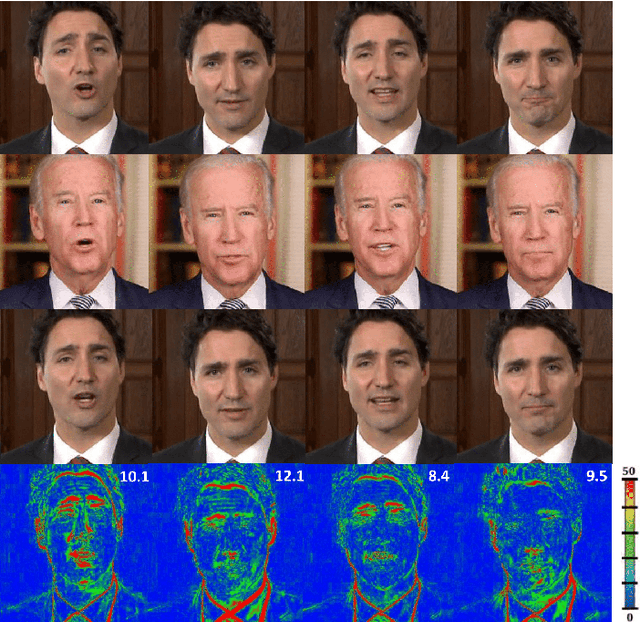

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel machine learning architecture for facial reenactment. In particular, contrary to the model-based approaches or recent frame-based methods that use Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) to generate individual frames, we propose a novel method that (a) exploits the special structure of facial motion (paying particular attention to mouth motion) and (b) enforces temporal consistency. We demonstrate that the proposed method can transfer facial expressions, pose and gaze of a source actor to a target video in a photo-realistic fashion more accurately than state-of-the-art methods.
DeepFaceFlow: In-the-wild Dense 3D Facial Motion Estimation
May 14, 2020



Abstract:Dense 3D facial motion capture from only monocular in-the-wild pairs of RGB images is a highly challenging problem with numerous applications, ranging from facial expression recognition to facial reenactment. In this work, we propose DeepFaceFlow, a robust, fast, and highly-accurate framework for the dense estimation of 3D non-rigid facial flow between pairs of monocular images. Our DeepFaceFlow framework was trained and tested on two very large-scale facial video datasets, one of them of our own collection and annotation, with the aid of occlusion-aware and 3D-based loss function. We conduct comprehensive experiments probing different aspects of our approach and demonstrating its improved performance against state-of-the-art flow and 3D reconstruction methods. Furthermore, we incorporate our framework in a full-head state-of-the-art facial video synthesis method and demonstrate the ability of our method in better representing and capturing the facial dynamics, resulting in a highly-realistic facial video synthesis. Given registered pairs of images, our framework generates 3D flow maps at ~60 fps.
Real-time Facial Expression Recognition "In The Wild'' by Disentangling 3D Expression from Identity
May 12, 2020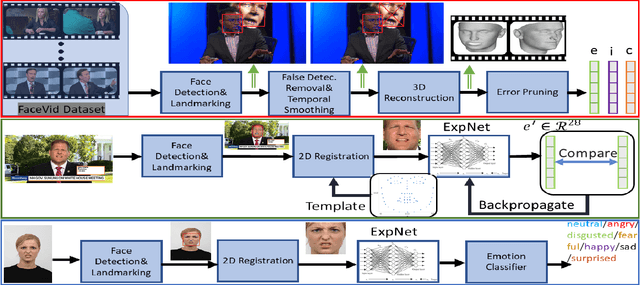

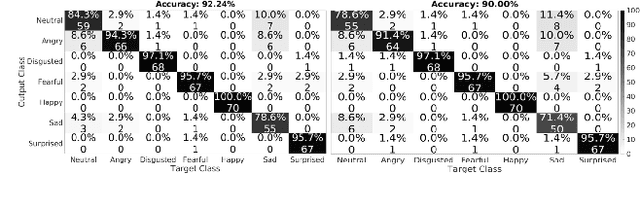
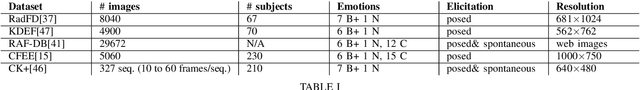
Abstract:Human emotions analysis has been the focus of many studies, especially in the field of Affective Computing, and is important for many applications, e.g. human-computer intelligent interaction, stress analysis, interactive games, animations, etc. Solutions for automatic emotion analysis have also benefited from the development of deep learning approaches and the availability of vast amount of visual facial data on the internet. This paper proposes a novel method for human emotion recognition from a single RGB image. We construct a large-scale dataset of facial videos (\textbf{FaceVid}), rich in facial dynamics, identities, expressions, appearance and 3D pose variations. We use this dataset to train a deep Convolutional Neural Network for estimating expression parameters of a 3D Morphable Model and combine it with an effective back-end emotion classifier. Our proposed framework runs at 50 frames per second and is capable of robustly estimating parameters of 3D expression variation and accurately recognizing facial expressions from in-the-wild images. We present extensive experimental evaluation that shows that the proposed method outperforms the compared techniques in estimating the 3D expression parameters and achieves state-of-the-art performance in recognising the basic emotions from facial images, as well as recognising stress from facial videos. %compared to the current state of the art in emotion recognition from facial images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge