Mirela Ostrek
Stable Video Portraits
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Rapid advances in the field of generative AI and text-to-image methods in particular have transformed the way we interact with and perceive computer-generated imagery today. In parallel, much progress has been made in 3D face reconstruction, using 3D Morphable Models (3DMM). In this paper, we present SVP, a novel hybrid 2D/3D generation method that outputs photorealistic videos of talking faces leveraging a large pre-trained text-to-image prior (2D), controlled via a 3DMM (3D). Specifically, we introduce a person-specific fine-tuning of a general 2D stable diffusion model which we lift to a video model by providing temporal 3DMM sequences as conditioning and by introducing a temporal denoising procedure. As an output, this model generates temporally smooth imagery of a person with 3DMM-based controls, i.e., a person-specific avatar. The facial appearance of this person-specific avatar can be edited and morphed to text-defined celebrities, without any fine-tuning at test time. The method is analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively, and we show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art monocular head avatar methods.
Environment-Specific People
Dec 22, 2023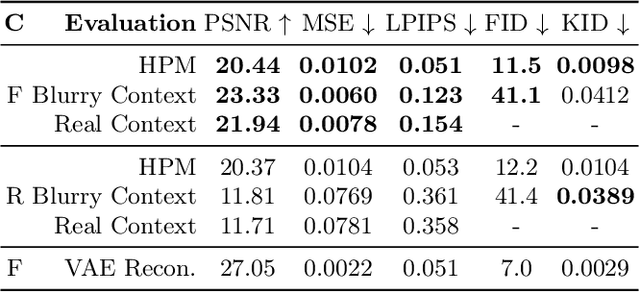
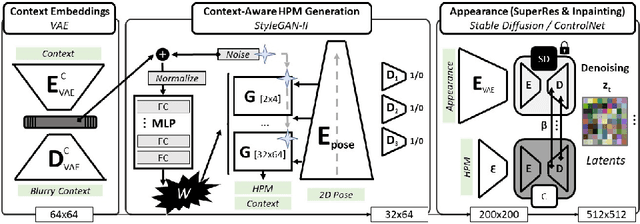
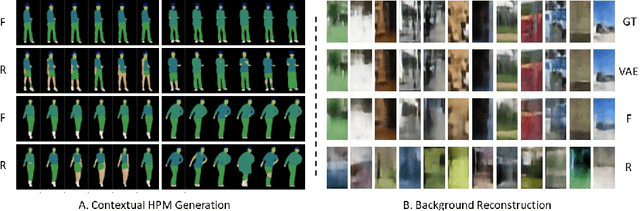
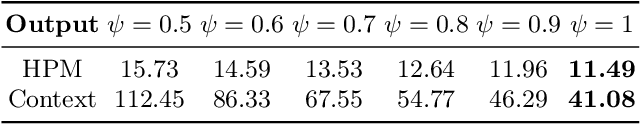
Abstract:Despite significant progress in generative image synthesis and full-body generation in particular, state-of-the-art methods are either context-independent, overly reliant to text prompts, or bound to the curated training datasets, such as fashion images with monotonous backgrounds. Here, our goal is to generate people in clothing that is semantically appropriate for a given scene. To this end, we present ESP, a novel method for context-aware full-body generation, that enables photo-realistic inpainting of people into existing "in-the-wild" photographs. ESP is conditioned on a 2D pose and contextual cues that are extracted from the environment photograph and integrated into the generation process. Our models are trained on a dataset containing a set of in-the-wild photographs of people covering a wide range of different environments. The method is analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively, and we show that ESP outperforms state-of-the-art on the task of contextual full-body generation.
Deformation-aware Unpaired Image Translation for Pose Estimation on Laboratory Animals
Jan 23, 2020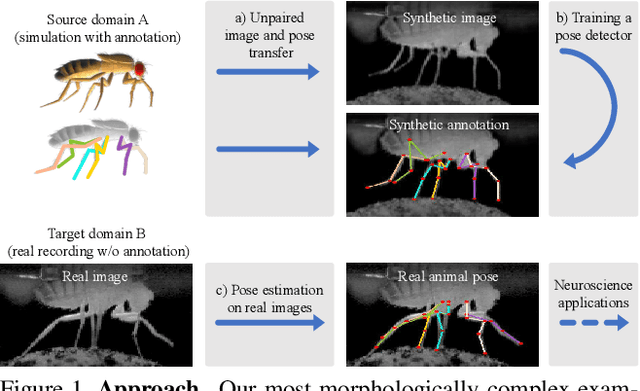
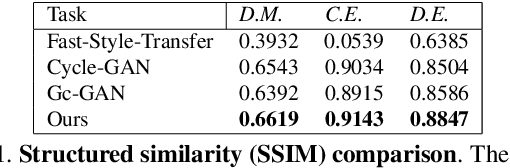
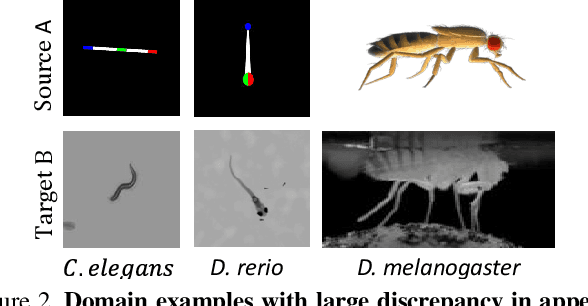
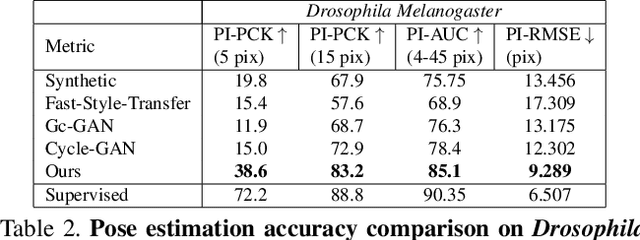
Abstract:Our goal is to capture the pose of neuroscience model organisms, without using any manual supervision, to be able to study how neural circuits orchestrate behaviour. Human pose estimation attains remarkable accuracy when trained on real or simulated datasets consisting of millions of frames. However, for many applications simulated models are unrealistic and real training datasets with comprehensive annotations do not exist. We address this problem with a new sim2real domain transfer method. Our key contribution is the explicit and independent modeling of appearance, shape and poses in an unpaired image translation framework. Our model lets us train a pose estimator on the target domain by transferring readily available body keypoint locations from the source domain to generated target images. We compare our approach with existing domain transfer methods and demonstrate improved pose estimation accuracy on Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly), Caenorhabditis elegans (worm) and Danio rerio (zebrafish), without requiring any manual annotation on the target domain and despite using simplistic off-the-shelf animal characters for simulation, or simple geometric shapes as models. Our new datasets, code, and trained models will be published to support future neuroscientific studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge