Mireille Fares
META4: Semantically-Aligned Generation of Metaphoric Gestures Using Self-Supervised Text and Speech Representation
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Image Schemas are repetitive cognitive patterns that influence the way we conceptualize and reason about various concepts present in speech. These patterns are deeply embedded within our cognitive processes and are reflected in our bodily expressions including gestures. Particularly, metaphoric gestures possess essential characteristics and semantic meanings that align with Image Schemas, to visually represent abstract concepts. The shape and form of gestures can convey abstract concepts, such as extending the forearm and hand or tracing a line with hand movements to visually represent the image schema of PATH. Previous behavior generation models have primarily focused on utilizing speech (acoustic features and text) to drive the generation model of virtual agents. They have not considered key semantic information as those carried by Image Schemas to effectively generate metaphoric gestures. To address this limitation, we introduce META4, a deep learning approach that generates metaphoric gestures from both speech and Image Schemas. Our approach has two primary goals: computing Image Schemas from input text to capture the underlying semantic and metaphorical meaning, and generating metaphoric gestures driven by speech and the computed image schemas. Our approach is the first method for generating speech driven metaphoric gestures while leveraging the potential of Image Schemas. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach and highlight the importance of both speech and image schemas in modeling metaphoric gestures.
TranSTYLer: Multimodal Behavioral Style Transfer for Facial and Body Gestures Generation
Aug 08, 2023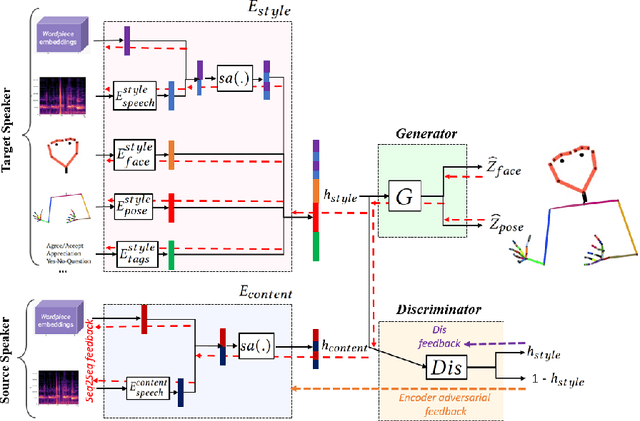
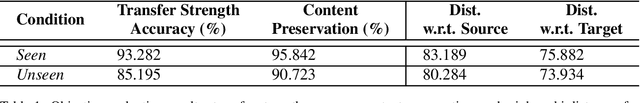
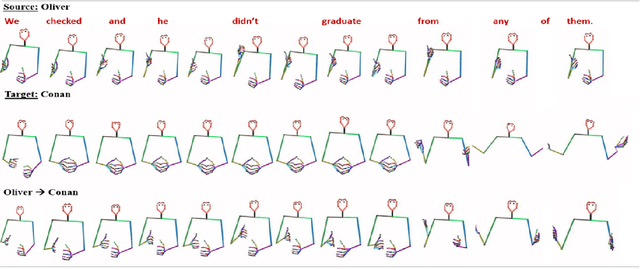
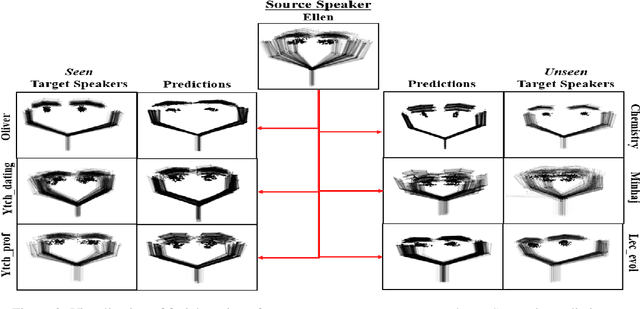
Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of transferring the behavior expressivity style of a virtual agent to another one while preserving behaviors shape as they carry communicative meaning. Behavior expressivity style is viewed here as the qualitative properties of behaviors. We propose TranSTYLer, a multimodal transformer based model that synthesizes the multimodal behaviors of a source speaker with the style of a target speaker. We assume that behavior expressivity style is encoded across various modalities of communication, including text, speech, body gestures, and facial expressions. The model employs a style and content disentanglement schema to ensure that the transferred style does not interfere with the meaning conveyed by the source behaviors. Our approach eliminates the need for style labels and allows the generalization to styles that have not been seen during the training phase. We train our model on the PATS corpus, which we extended to include dialog acts and 2D facial landmarks. Objective and subjective evaluations show that our model outperforms state of the art models in style transfer for both seen and unseen styles during training. To tackle the issues of style and content leakage that may arise, we propose a methodology to assess the degree to which behavior and gestures associated with the target style are successfully transferred, while ensuring the preservation of the ones related to the source content.
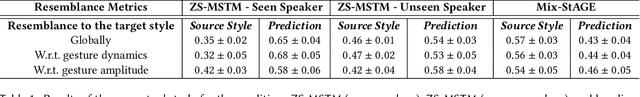
ZS-MSTM: Zero-Shot Style Transfer for Gesture Animation driven by Text and Speech using Adversarial Disentanglement of Multimodal Style Encoding
May 22, 2023Abstract:In this study, we address the importance of modeling behavior style in virtual agents for personalized human-agent interaction. We propose a machine learning approach to synthesize gestures, driven by prosodic features and text, in the style of different speakers, even those unseen during training. Our model incorporates zero-shot multimodal style transfer using multimodal data from the PATS database, which contains videos of diverse speakers. We recognize style as a pervasive element during speech, influencing the expressivity of communicative behaviors, while content is conveyed through multimodal signals and text. By disentangling content and style, we directly infer the style embedding, even for speakers not included in the training phase, without the need for additional training or fine-tuning. Objective and subjective evaluations are conducted to validate our approach and compare it against two baseline methods.
AMII: Adaptive Multimodal Inter-personal and Intra-personal Model for Adapted Behavior Synthesis
May 18, 2023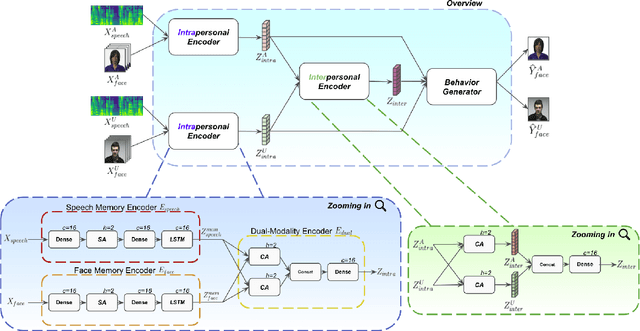
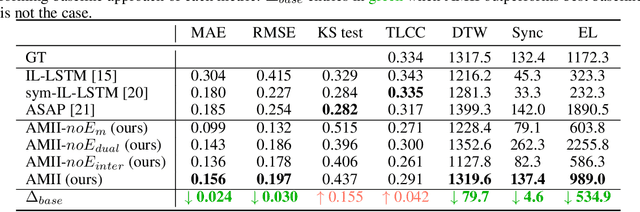
Abstract:Socially Interactive Agents (SIAs) are physical or virtual embodied agents that display similar behavior as human multimodal behavior. Modeling SIAs' non-verbal behavior, such as speech and facial gestures, has always been a challenging task, given that a SIA can take the role of a speaker or a listener. A SIA must emit appropriate behavior adapted to its own speech, its previous behaviors (intra-personal), and the User's behaviors (inter-personal) for both roles. We propose AMII, a novel approach to synthesize adaptive facial gestures for SIAs while interacting with Users and acting interchangeably as a speaker or as a listener. AMII is characterized by modality memory encoding schema - where modality corresponds to either speech or facial gestures - and makes use of attention mechanisms to capture the intra-personal and inter-personal relationships. We validate our approach by conducting objective evaluations and comparing it with the state-of-the-art approaches.
Zero-Shot Style Transfer for Gesture Animation driven by Text and Speech using Adversarial Disentanglement of Multimodal Style Encoding
Aug 03, 2022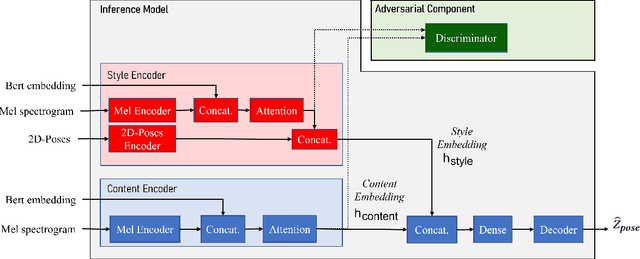
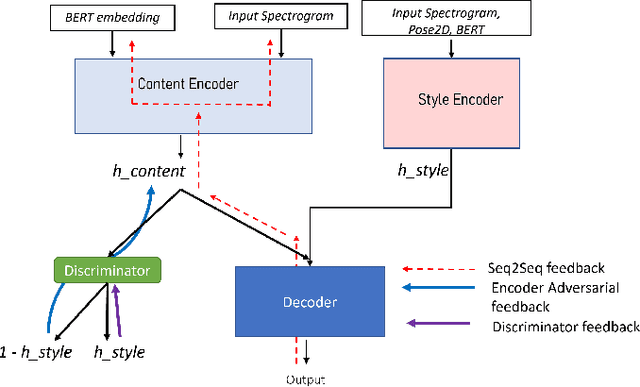
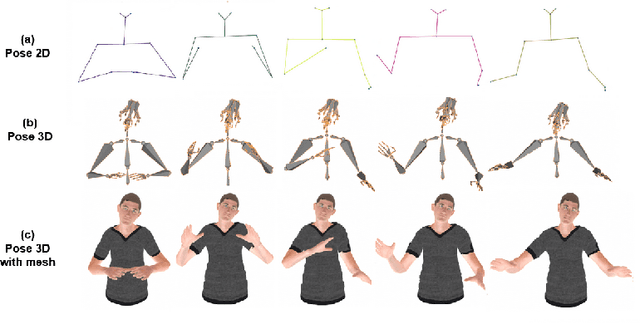
Abstract:Modeling virtual agents with behavior style is one factor for personalizing human agent interaction. We propose an efficient yet effective machine learning approach to synthesize gestures driven by prosodic features and text in the style of different speakers including those unseen during training. Our model performs zero shot multimodal style transfer driven by multimodal data from the PATS database containing videos of various speakers. We view style as being pervasive while speaking, it colors the communicative behaviors expressivity while speech content is carried by multimodal signals and text. This disentanglement scheme of content and style allows us to directly infer the style embedding even of speaker whose data are not part of the training phase, without requiring any further training or fine tuning. The first goal of our model is to generate the gestures of a source speaker based on the content of two audio and text modalities. The second goal is to condition the source speaker predicted gestures on the multimodal behavior style embedding of a target speaker. The third goal is to allow zero shot style transfer of speakers unseen during training without retraining the model. Our system consists of: (1) a speaker style encoder network that learns to generate a fixed dimensional speaker embedding style from a target speaker multimodal data and (2) a sequence to sequence synthesis network that synthesizes gestures based on the content of the input modalities of a source speaker and conditioned on the speaker style embedding. We evaluate that our model can synthesize gestures of a source speaker and transfer the knowledge of target speaker style variability to the gesture generation task in a zero shot setup. We convert the 2D gestures to 3D poses and produce 3D animations. We conduct objective and subjective evaluations to validate our approach and compare it with a baseline.
Multimodal generation of upper-facial and head gestures with a Transformer Network using speech and text
Oct 09, 2021



Abstract:We propose a semantically-aware speech driven method to generate expressive and natural upper-facial and head motion for Embodied Conversational Agents (ECA). In this work, we tackle two key challenges: produce natural and continuous head motion and upper-facial gestures. We propose a model that generates gestures based on multimodal input features: the first modality is text, and the second one is speech prosody. Our model makes use of Transformers and Convolutions to map the multimodal features that correspond to an utterance to continuous eyebrows and head gestures. We conduct subjective and objective evaluations to validate our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge