Minsu Park
MAVIS: A Benchmark for Multimodal Source Attribution in Long-form Visual Question Answering
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Source attribution aims to enhance the reliability of AI-generated answers by including references for each statement, helping users validate the provided answers. However, existing work has primarily focused on text-only scenario and largely overlooked the role of multimodality. We introduce MAVIS, the first benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal source attribution systems that understand user intent behind visual questions, retrieve multimodal evidence, and generate long-form answers with citations. Our dataset comprises 157K visual QA instances, where each answer is annotated with fact-level citations referring to multimodal documents. We develop fine-grained automatic metrics along three dimensions of informativeness, groundedness, and fluency, and demonstrate their strong correlation with human judgments. Our key findings are threefold: (1) LVLMs with multimodal RAG generate more informative and fluent answers than unimodal RAG, but they exhibit weaker groundedness for image documents than for text documents, a gap amplified in multimodal settings. (2) Given the same multimodal documents, there is a trade-off between informativeness and groundedness across different prompting methods. (3) Our proposed method highlights mitigating contextual bias in interpreting image documents as a crucial direction for future research. The dataset and experimental code are available at https://github.com/seokwon99/MAVIS
GlobalMood: A cross-cultural benchmark for music emotion recognition
May 14, 2025Abstract:Human annotations of mood in music are essential for music generation and recommender systems. However, existing datasets predominantly focus on Western songs with mood terms derived from English, which may limit generalizability across diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds. To address this, we introduce `GlobalMood', a novel cross-cultural benchmark dataset comprising 1,180 songs sampled from 59 countries, with large-scale annotations collected from 2,519 individuals across five culturally and linguistically distinct locations: U.S., France, Mexico, S. Korea, and Egypt. Rather than imposing predefined mood categories, we implement a bottom-up, participant-driven approach to organically elicit culturally specific music-related mood terms. We then recruit another pool of human participants to collect 988,925 ratings for these culture-specific descriptors. Our analysis confirms the presence of a valence-arousal structure shared across cultures, yet also reveals significant divergences in how certain mood terms, despite being dictionary equivalents, are perceived cross-culturally. State-of-the-art multimodal models benefit substantially from fine-tuning on our cross-culturally balanced dataset, as evidenced by improved alignment with human evaluations - particularly in non-English contexts. More broadly, our findings inform the ongoing debate on the universality versus cultural specificity of emotional descriptors, and our methodology can contribute to other multimodal and cross-lingual research.
Solving Copyright Infringement on Short Video Platforms: Novel Datasets and an Audio Restoration Deep Learning Pipeline
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:Short video platforms like YouTube Shorts and TikTok face significant copyright compliance challenges, as infringers frequently embed arbitrary background music (BGM) to obscure original soundtracks (OST) and evade content originality detection. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel pipeline that integrates Music Source Separation (MSS) and cross-modal video-music retrieval (CMVMR). Our approach effectively separates arbitrary BGM from the original OST, enabling the restoration of authentic video audio tracks. To support this work, we introduce two domain-specific datasets: OASD-20K for audio separation and OSVAR-160 for pipeline evaluation. OASD-20K contains 20,000 audio clips featuring mixed BGM and OST pairs, while OSVAR160 is a unique benchmark dataset comprising 1,121 video and mixed-audio pairs, specifically designed for short video restoration tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our pipeline not only removes arbitrary BGM with high accuracy but also restores OSTs, ensuring content integrity. This approach provides an ethical and scalable solution to copyright challenges in user-generated content on short video platforms.
Improving Multi-lingual Alignment Through Soft Contrastive Learning
May 28, 2024Abstract:Making decent multi-lingual sentence representations is critical to achieve high performances in cross-lingual downstream tasks. In this work, we propose a novel method to align multi-lingual embeddings based on the similarity of sentences measured by a pre-trained mono-lingual embedding model. Given translation sentence pairs, we train a multi-lingual model in a way that the similarity between cross-lingual embeddings follows the similarity of sentences measured at the mono-lingual teacher model. Our method can be considered as contrastive learning with soft labels defined as the similarity between sentences. Our experimental results on five languages show that our contrastive loss with soft labels far outperforms conventional contrastive loss with hard labels in various benchmarks for bitext mining tasks and STS tasks. In addition, our method outperforms existing multi-lingual embeddings including LaBSE, for Tatoeba dataset. The code is available at https://github.com/YAI12xLinq-B/IMASCL
ICLN: Input Convex Loss Network for Decision Focused Learning
Mar 04, 2024


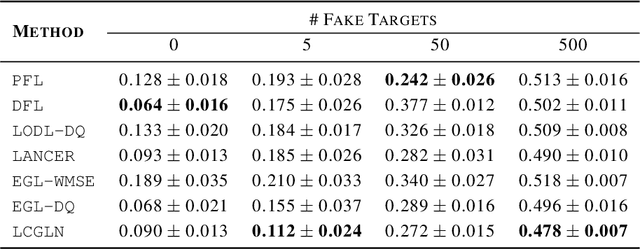
Abstract:In decision-making problem under uncertainty, predicting unknown parameters is often considered independent of the optimization part. Decision-focused Learning (DFL) is a task-oriented framework to integrate prediction and optimization by adapting predictive model to give better decision for the corresponding task. Here, an inevitable challenge arises when computing gradients of the optimal decision with respect to the parameters. Existing researches cope this issue by smoothly reforming surrogate optimization or construct surrogate loss function that mimic task loss. However, they are applied to restricted optimization domain or build functions in a local manner leading a large computational time. In this paper, we propose Input Convex Loss Network (ICLN), a novel global surrogate loss which can be implemented in a general DFL paradigm. ICLN learns task loss via Input Convex Neural Networks which is guaranteed to be convex for some inputs, while keeping the global structure for the other inputs. This enables ICLN to admit general DFL through only a single surrogate loss without any sense for choosing appropriate parametric forms. We confirm effectiveness and flexibility of ICLN by evaluating our proposed model with three stochastic decision-making problems.
Cross-cultural Mood Perception in Pop Songs and its Alignment with Mood Detection Algorithms
Aug 02, 2021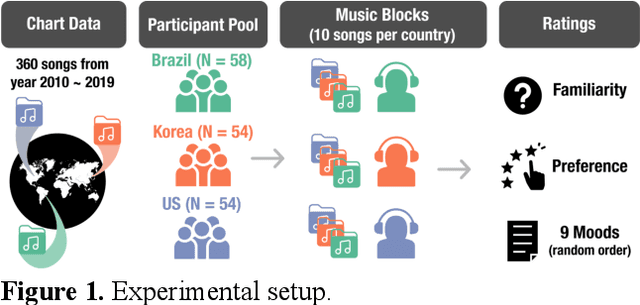
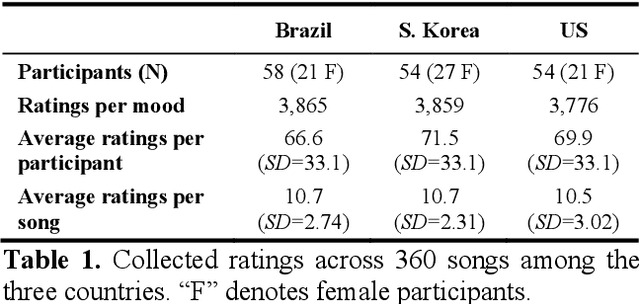
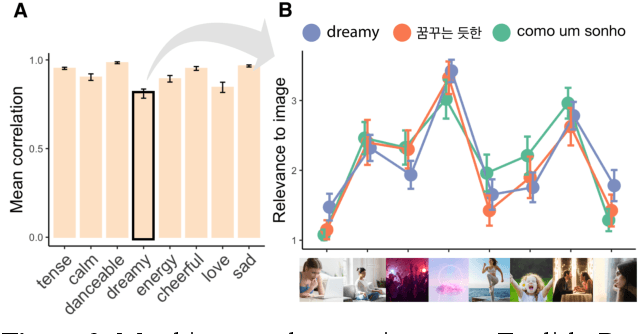
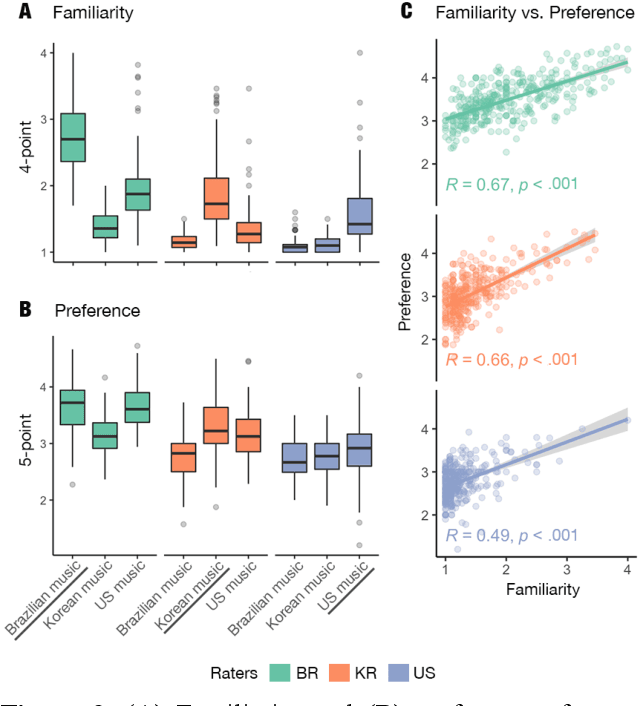
Abstract:Do people from different cultural backgrounds perceive the mood in music the same way? How closely do human ratings across different cultures approximate automatic mood detection algorithms that are often trained on corpora of predominantly Western popular music? Analyzing 166 participants responses from Brazil, South Korea, and the US, we examined the similarity between the ratings of nine categories of perceived moods in music and estimated their alignment with four popular mood detection algorithms. We created a dataset of 360 recent pop songs drawn from major music charts of the countries and constructed semantically identical mood descriptors across English, Korean, and Portuguese languages. Multiple participants from the three countries rated their familiarity, preference, and perceived moods for a given song. Ratings were highly similar within and across cultures for basic mood attributes such as sad, cheerful, and energetic. However, we found significant cross-cultural differences for more complex characteristics such as dreamy and love. To our surprise, the results of mood detection algorithms were uniformly correlated across human ratings from all three countries and did not show a detectable bias towards any particular culture. Our study thus suggests that the mood detection algorithms can be considered as an objective measure at least within the popular music context.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge