Eunil Park
Instance-Aware Test-Time Segmentation for Continual Domain Shifts
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Continual Test-Time Adaptation (CTTA) enables pre-trained models to adapt to continuously evolving domains. Existing methods have improved robustness but typically rely on fixed or batch-level thresholds, which cannot account for varying difficulty across classes and instances. This limitation is especially problematic in semantic segmentation, where each image requires dense, multi-class predictions. We propose an approach that adaptively adjusts pseudo labels to reflect the confidence distribution within each image and dynamically balances learning toward classes most affected by domain shifts. This fine-grained, class- and instance-aware adaptation produces more reliable supervision and mitigates error accumulation throughout continual adaptation. Extensive experiments across eight CTTA and TTA scenarios, including synthetic-to-real and long-term shifts, show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art techniques, setting a new standard for semantic segmentation under evolving conditions.
Solving Copyright Infringement on Short Video Platforms: Novel Datasets and an Audio Restoration Deep Learning Pipeline
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:Short video platforms like YouTube Shorts and TikTok face significant copyright compliance challenges, as infringers frequently embed arbitrary background music (BGM) to obscure original soundtracks (OST) and evade content originality detection. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel pipeline that integrates Music Source Separation (MSS) and cross-modal video-music retrieval (CMVMR). Our approach effectively separates arbitrary BGM from the original OST, enabling the restoration of authentic video audio tracks. To support this work, we introduce two domain-specific datasets: OASD-20K for audio separation and OSVAR-160 for pipeline evaluation. OASD-20K contains 20,000 audio clips featuring mixed BGM and OST pairs, while OSVAR160 is a unique benchmark dataset comprising 1,121 video and mixed-audio pairs, specifically designed for short video restoration tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our pipeline not only removes arbitrary BGM with high accuracy but also restores OSTs, ensuring content integrity. This approach provides an ethical and scalable solution to copyright challenges in user-generated content on short video platforms.
Preserving Old Memories in Vivid Detail: Human-Interactive Photo Restoration Framework
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Photo restoration technology enables preserving visual memories in photographs. However, physical prints are vulnerable to various forms of deterioration, ranging from physical damage to loss of image quality, etc. While restoration by human experts can improve the quality of outcomes, it often comes at a high price in terms of cost and time for restoration. In this work, we present the AI-based photo restoration framework composed of multiple stages, where each stage is tailored to enhance and restore specific types of photo damage, accelerating and automating the photo restoration process. By integrating these techniques into a unified architecture, our framework aims to offer a one-stop solution for restoring old and deteriorated photographs. Furthermore, we present a novel old photo restoration dataset because we lack a publicly available dataset for our evaluation.
MOGAM: A Multimodal Object-oriented Graph Attention Model for Depression Detection
Mar 21, 2024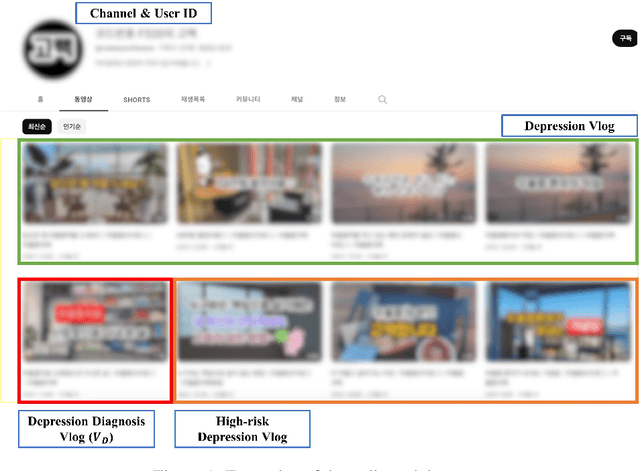
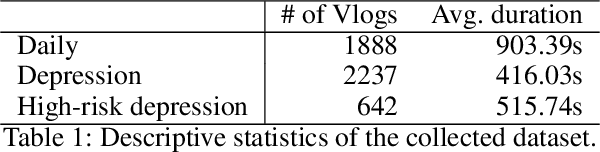
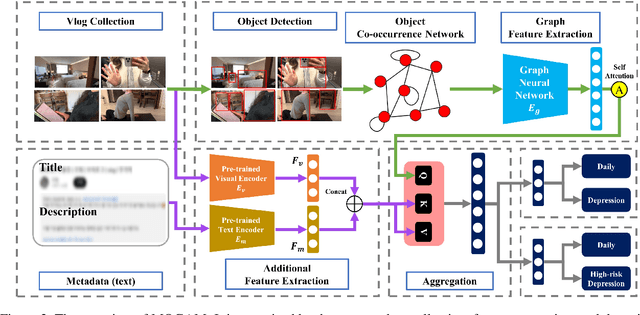
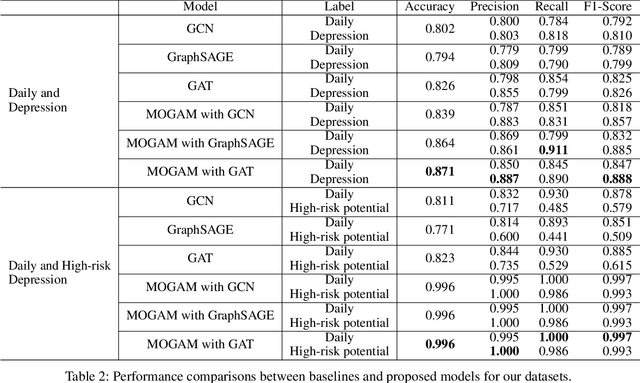
Abstract:Early detection plays a crucial role in the treatment of depression. Therefore, numerous studies have focused on social media platforms, where individuals express their emotions, aiming to achieve early detection of depression. However, the majority of existing approaches often rely on specific features, leading to limited scalability across different types of social media datasets, such as text, images, or videos. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a Multimodal Object-Oriented Graph Attention Model (MOGAM), which can be applied to diverse types of data, offering a more scalable and versatile solution. Furthermore, to ensure that our model can capture authentic symptoms of depression, we only include vlogs from users with a clinical diagnosis. To leverage the diverse features of vlogs, we adopt a multimodal approach and collect additional metadata such as the title, description, and duration of the vlogs. To effectively aggregate these multimodal features, we employed a cross-attention mechanism. MOGAM achieved an accuracy of 0.871 and an F1-score of 0.888. Moreover, to validate the scalability of MOGAM, we evaluated its performance with a benchmark dataset and achieved comparable results with prior studies (0.61 F1-score). In conclusion, we believe that the proposed model, MOGAM, is an effective solution for detecting depression in social media, offering potential benefits in the early detection and treatment of this mental health condition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge