Minjian Xin
Achieving Sample-Efficient and Online-Training-Safe Deep Reinforcement Learning with Base Controllers
Nov 24, 2020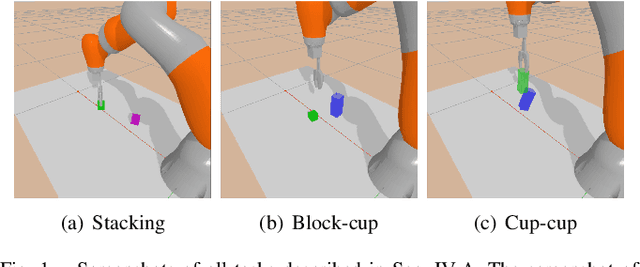
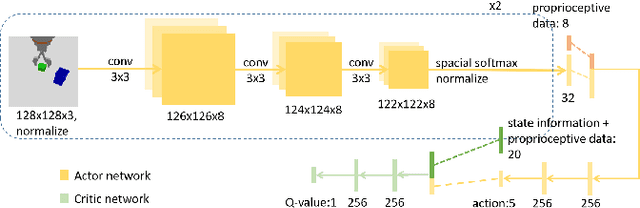
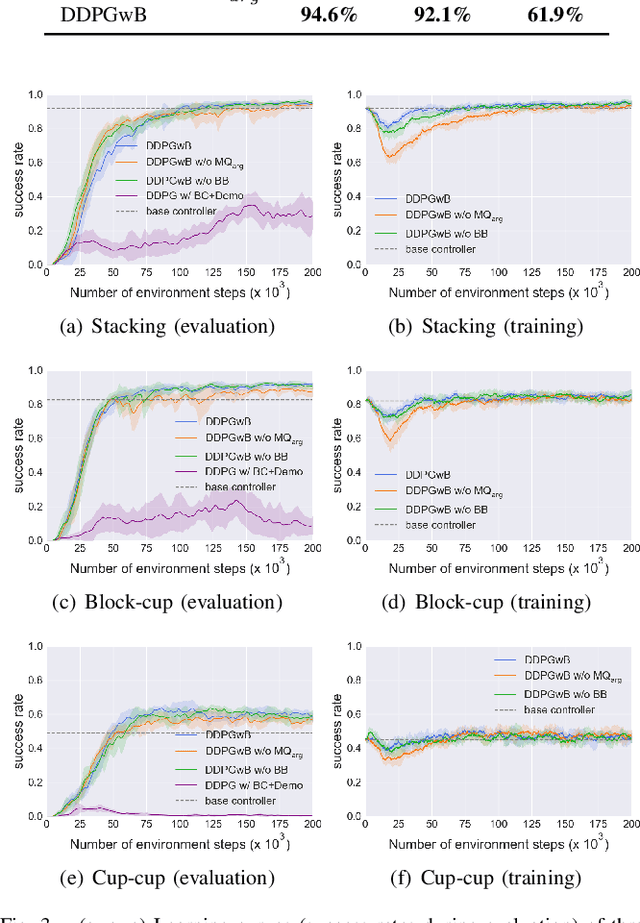
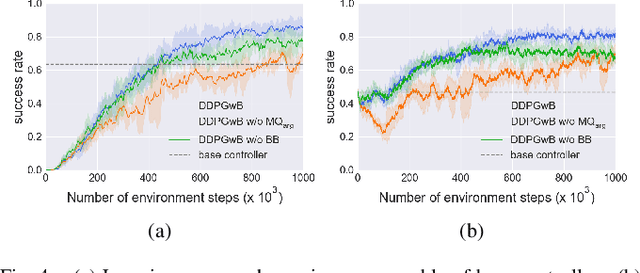
Abstract:Application of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms in real-world robotic tasks faces many challenges. On the one hand, reward-shaping for complex tasks is difficult and may result in sub-optimal performances. On the other hand, a sparse-reward setting renders exploration inefficient, and exploration using physical robots is of high-cost and unsafe. In this paper we propose a method of learning challenging sparse-reward tasks utilizing existing controllers. Built upon Deep Deterministic Policy Gradients (DDPG), our algorithm incorporates the controllers into stages of exploration, Q-value estimation as well as policy update. Through experiments ranging from stacking blocks to cups, we present a straightforward way of synthesizing these controllers, and show that the learned state-based or image-based policies steadily outperform them. Compared to previous works of learning from demonstrations, our method improves sample efficiency by orders of magnitude and can learn online in a safe manner. Overall, our method bears the potential of leveraging existing industrial robot manipulation systems to build more flexible and intelligent controllers.
Flexible and Efficient Long-Range Planning Through Curious Exploration
Apr 22, 2020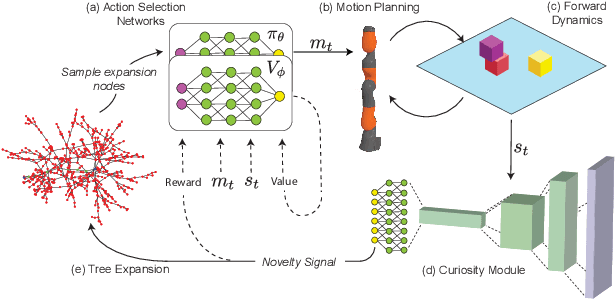
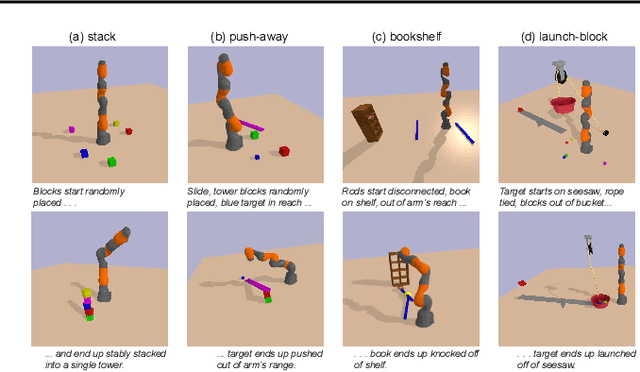
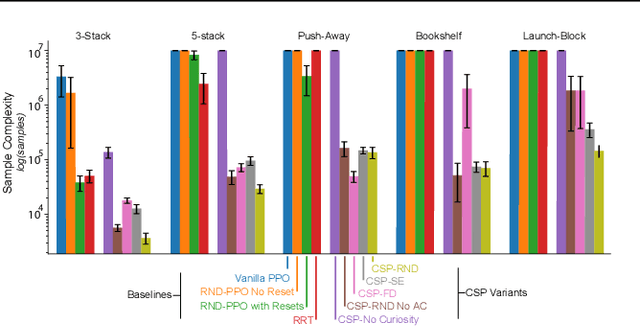
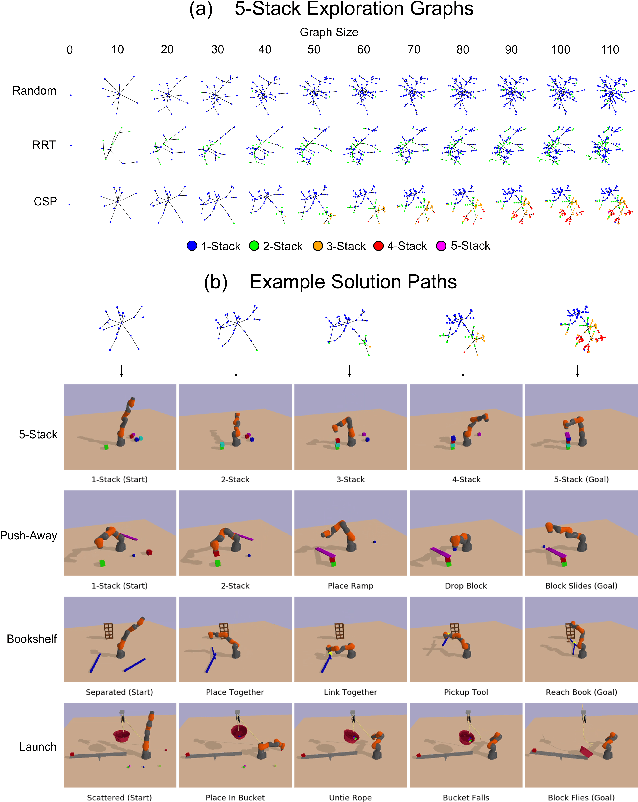
Abstract:Identifying algorithms that flexibly and efficiently discover temporally-extended multi-phase plans is an essential step for the advancement of robotics and model-based reinforcement learning. The core problem of long-range planning is finding an efficient way to search through the tree of possible action sequences. Existing non-learned planning solutions from the Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) literature rely on the existence of logical descriptions for the effects and preconditions for actions. This constraint allows TAMP methods to efficiently reduce the tree search problem but limits their ability to generalize to unseen and complex physical environments. In contrast, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methods use flexible neural-network-based function approximators to discover policies that generalize naturally to unseen circumstances. However, DRL methods struggle to handle the very sparse reward landscapes inherent to long-range multi-step planning situations. Here, we propose the Curious Sample Planner (CSP), which fuses elements of TAMP and DRL by combining a curiosity-guided sampling strategy with imitation learning to accelerate planning. We show that CSP can efficiently discover interesting and complex temporally-extended plans for solving a wide range of physically realistic 3D tasks. In contrast, standard planning and learning methods often fail to solve these tasks at all or do so only with a huge and highly variable number of training samples. We explore the use of a variety of curiosity metrics with CSP and analyze the types of solutions that CSP discovers. Finally, we show that CSP supports task transfer so that the exploration policies learned during experience with one task can help improve efficiency on related tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge