Minijn Choi
SpaDE: Improving Sparse Representations using a Dual Document Encoder for First-stage Retrieval
Sep 13, 2022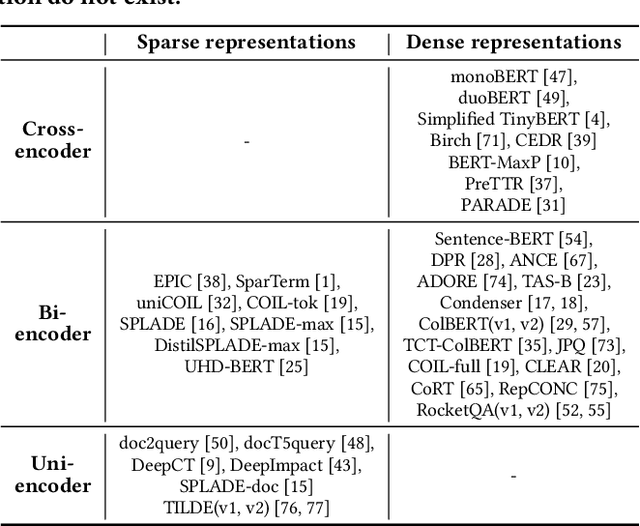
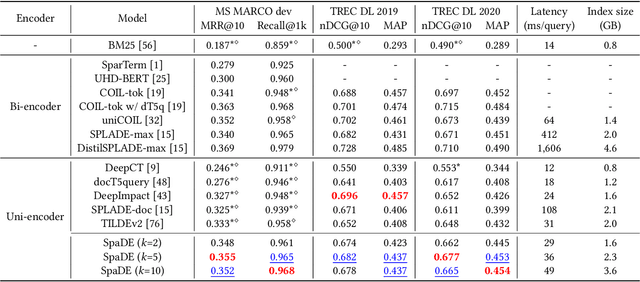
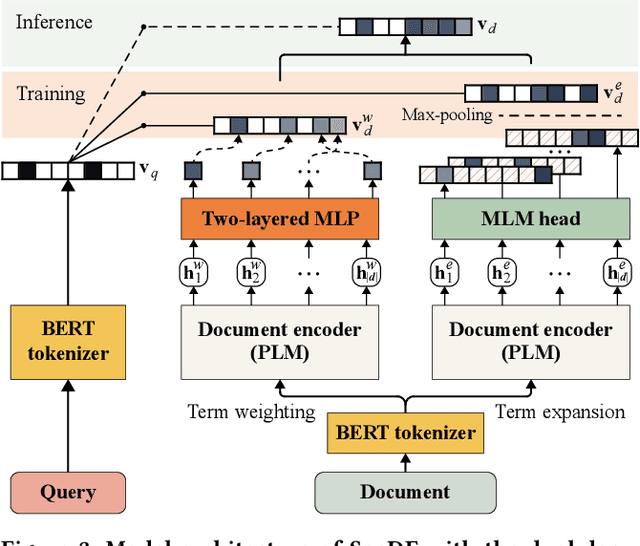
Abstract:Sparse document representations have been widely used to retrieve relevant documents via exact lexical matching. Owing to the pre-computed inverted index, it supports fast ad-hoc search but incurs the vocabulary mismatch problem. Although recent neural ranking models using pre-trained language models can address this problem, they usually require expensive query inference costs, implying the trade-off between effectiveness and efficiency. Tackling the trade-off, we propose a novel uni-encoder ranking model, Sparse retriever using a Dual document Encoder (SpaDE), learning document representation via the dual encoder. Each encoder plays a central role in (i) adjusting the importance of terms to improve lexical matching and (ii) expanding additional terms to support semantic matching. Furthermore, our co-training strategy trains the dual encoder effectively and avoids unnecessary intervention in training each other. Experimental results on several benchmarks show that SpaDE outperforms existing uni-encoder ranking models.
Session-aware Linear Item-Item Models for Session-based Recommendation
Mar 30, 2021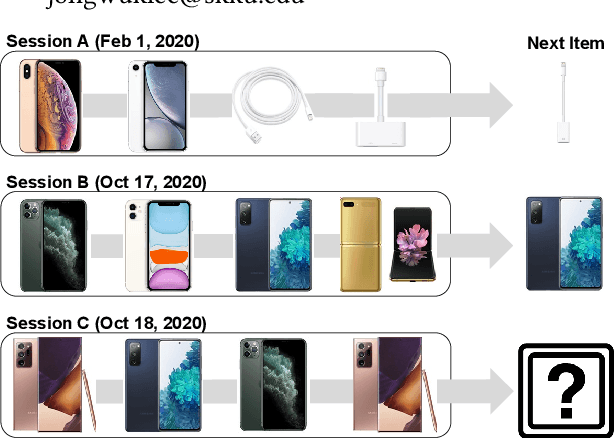
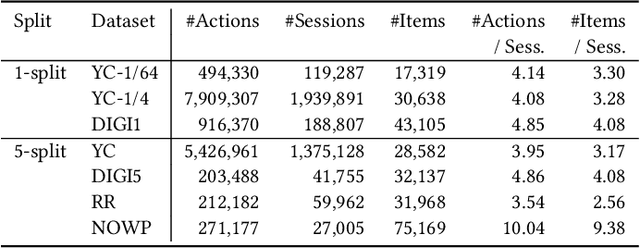
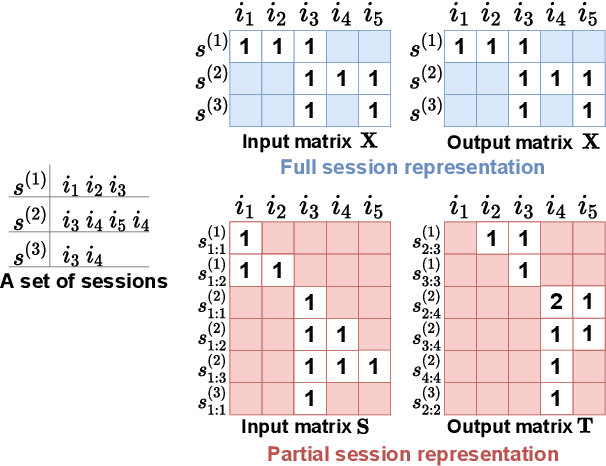
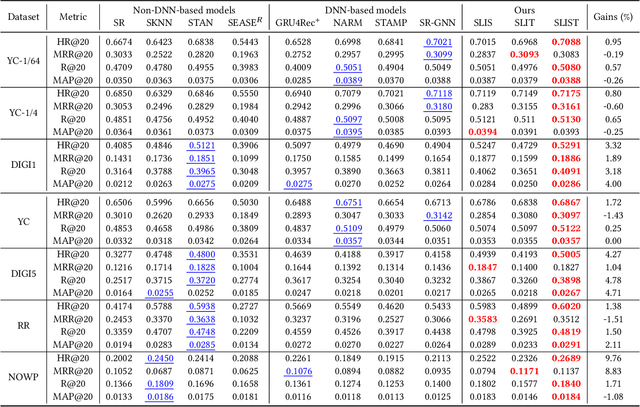
Abstract:Session-based recommendation aims at predicting the next item given a sequence of previous items consumed in the session, e.g., on e-commerce or multimedia streaming services. Specifically, session data exhibits some unique characteristics, i.e., session consistency and sequential dependency over items within the session, repeated item consumption, and session timeliness. In this paper, we propose simple-yet-effective linear models for considering the holistic aspects of the sessions. The comprehensive nature of our models helps improve the quality of session-based recommendation. More importantly, it provides a generalized framework for reflecting different perspectives of session data. Furthermore, since our models can be solved by closed-form solutions, they are highly scalable. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed linear models show competitive or state-of-the-art performance in various metrics on several real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge