Mingying Xu
Cross-Media Scientific Research Achievements Retrieval Based on Deep Language Model
Mar 29, 2022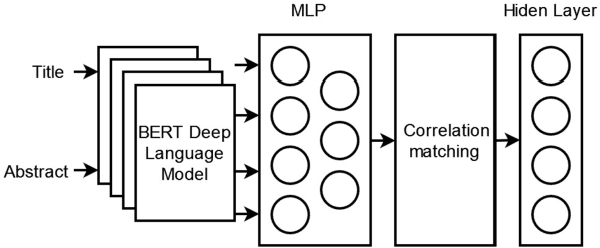

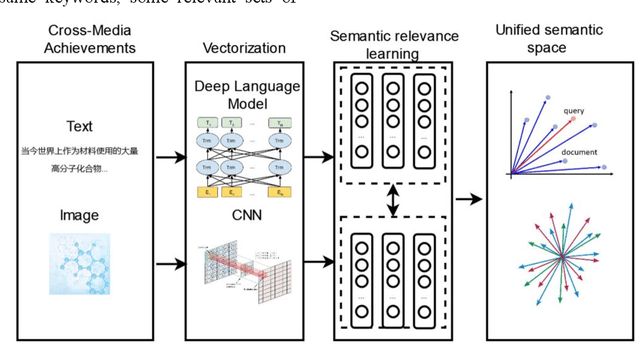
Abstract:Science and technology big data contain a lot of cross-media information.There are images and texts in the scientific paper.The s ingle modal search method cannot well meet the needs of scientific researchers.This paper proposes a cross-media scientific research achievements retrieval method based on deep language model (CARDL).It achieves a unified cross-media semantic representation by learning the semantic association between different modal data, and is applied to the generation of text semantic vector of scientific research achievements, and then cross-media retrieval is realized through semantic similarity matching between different modal data.Experimental results show that the proposed CARDL method achieves better cross-modal retrieval performance than existing methods. Key words science and technology big data ; cross-media retrieval; cross-media semantic association learning; deep language model; semantic similarity
Scientific and Technological Information Oriented Semantics-adversarial and Media-adversarial Cross-media Retrieval
Mar 16, 2022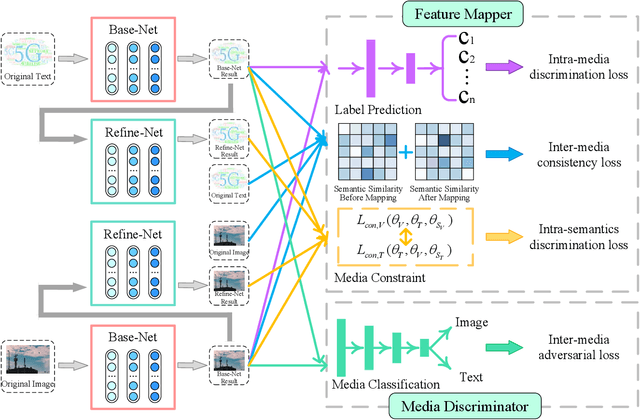
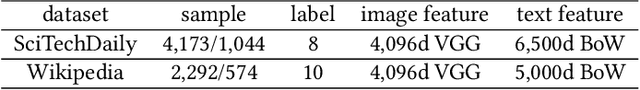
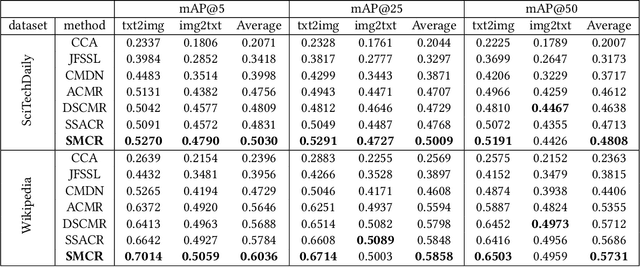
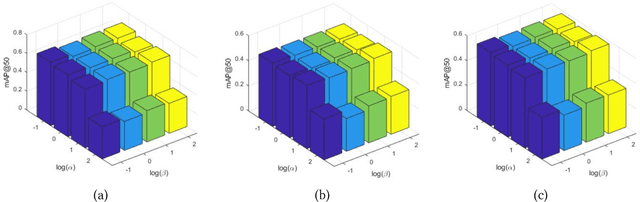
Abstract:Cross-media retrieval of scientific and technological information is one of the important tasks in the cross-media study. Cross-media scientific and technological information retrieval obtain target information from massive multi-source and heterogeneous scientific and technological resources, which helps to design applications that meet users' needs, including scientific and technological information recommendation, personalized scientific and technological information retrieval, etc. The core of cross-media retrieval is to learn a common subspace, so that data from different media can be directly compared with each other after being mapped into this subspace. In subspace learning, existing methods often focus on modeling the discrimination of intra-media data and the invariance of inter-media data after mapping; however, they ignore the semantic consistency of inter-media data before and after mapping and media discrimination of intra-semantics data, which limit the result of cross-media retrieval. In light of this, we propose a scientific and technological information oriented Semantics-adversarial and Media-adversarial Cross-media Retrieval method (SMCR) to find an effective common subspace. Specifically, SMCR minimizes the loss of inter-media semantic consistency in addition to modeling intra-media semantic discrimination, to preserve semantic similarity before and after mapping. Furthermore, SMCR constructs a basic feature mapping network and a refined feature mapping network to jointly minimize the media discriminative loss within semantics, so as to enhance the feature mapping network's ability to confuse the media discriminant network. Experimental results on two datasets demonstrate that the proposed SMCR outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cross-media retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge