Mingjian Jiang
GeoAda: Efficiently Finetune Geometric Diffusion Models with Equivariant Adapters
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Geometric diffusion models have shown remarkable success in molecular dynamics and structure generation. However, efficiently fine-tuning them for downstream tasks with varying geometric controls remains underexplored. In this work, we propose an SE(3)-equivariant adapter framework ( GeoAda) that enables flexible and parameter-efficient fine-tuning for controlled generative tasks without modifying the original model architecture. GeoAda introduces a structured adapter design: control signals are first encoded through coupling operators, then processed by a trainable copy of selected pretrained model layers, and finally projected back via decoupling operators followed by an equivariant zero-initialized convolution. By fine-tuning only these lightweight adapter modules, GeoAda preserves the model's geometric consistency while mitigating overfitting and catastrophic forgetting. We theoretically prove that the proposed adapters maintain SE(3)-equivariance, ensuring that the geometric inductive biases of the pretrained diffusion model remain intact during adaptation. We demonstrate the wide applicability of GeoAda across diverse geometric control types, including frame control, global control, subgraph control, and a broad range of application domains such as particle dynamics, molecular dynamics, human motion prediction, and molecule generation. Empirical results show that GeoAda achieves state-of-the-art fine-tuning performance while preserving original task accuracy, whereas other baselines experience significant performance degradation due to overfitting and catastrophic forgetting.
Putting It All into Context: Simplifying Agents with LCLMs
May 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in language model (LM) agents have demonstrated significant potential for automating complex real-world tasks. To make progress on these difficult tasks, LM agent architectures have become increasingly complex, often incorporating multi-step retrieval tools, multiple agents, and scaffolding adapted to the underlying LM. In this work, we investigate whether all of this complexity is necessary, or if parts of these scaffolds can be removed on challenging tasks like SWE-bench. We show that in the case of SWE-bench, simply putting the entire environment into the context of a long context language model (LCLM) and properly prompting the model makes it competitive with carefully tuned, complex agent scaffolds. We show that a Gemini-1.5-Pro model without any scaffolding or tools achieves 38% on SWE-Bench-Verified, comparable with approaches using carefully tuned agent scaffolds (32%). While the unscaffolded approach with Gemini-1.5-Pro falls short of the strongest agentic architectures, we demonstrate that the more capable Gemini-2.5-Pro using the same unscaffolded approach directly attains a 50.8% solve rate. Additionally, a two-stage approach combining Gemini-1.5-Pro with Claude-3.7 achieves a competitive 48.6% solve rate.
$f$-PO: Generalizing Preference Optimization with $f$-divergence Minimization
Oct 29, 2024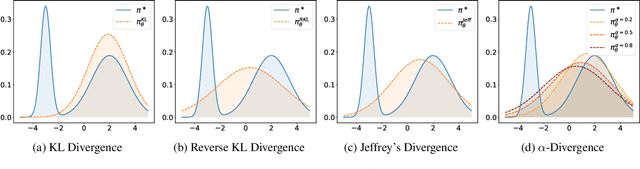
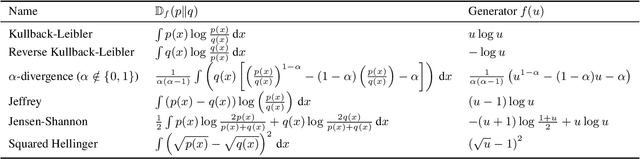
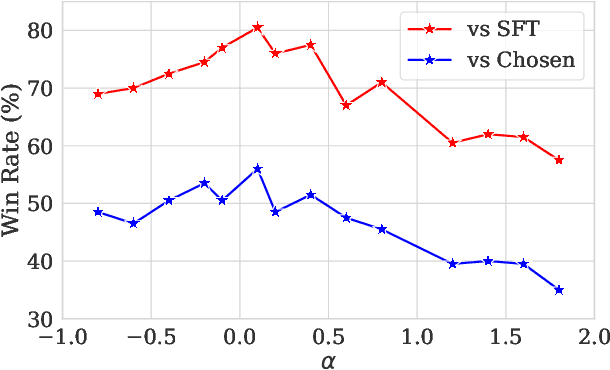

Abstract:Preference optimization has made significant progress recently, with numerous methods developed to align language models with human preferences. This paper introduces $f$-divergence Preference Optimization ($f$-PO), a novel framework that generalizes and extends existing approaches. $f$-PO minimizes $f$-divergences between the optimized policy and the optimal policy, encompassing a broad family of alignment methods using various divergences. Our approach unifies previous algorithms like DPO and EXO, while offering new variants through different choices of $f$-divergences. We provide theoretical analysis of $f$-PO's properties and conduct extensive experiments on state-of-the-art language models using benchmark datasets. Results demonstrate $f$-PO's effectiveness across various tasks, achieving superior performance compared to existing methods on popular benchmarks such as AlpacaEval 2, Arena-Hard, and MT-Bench. Additionally, we present ablation studies exploring the impact of different $f$-divergences, offering insights into the trade-offs between regularization and performance in offline preference optimization. Our work contributes both practical algorithms and theoretical understanding to the field of language model alignment. Code is available at https://github.com/MinkaiXu/fPO.
Graph-based Uncertainty Metrics for Long-form Language Model Outputs
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly improved text generation capabilities, but these systems are still known to hallucinate, and granular uncertainty estimation for long-form LLM generations remains challenging. In this work, we propose Graph Uncertainty -- which represents the relationship between LLM generations and claims within them as a bipartite graph and estimates the claim-level uncertainty with a family of graph centrality metrics. Under this view, existing uncertainty estimation methods based on the concept of self-consistency can be viewed as using degree centrality as an uncertainty measure, and we show that more sophisticated alternatives such as closeness centrality provide consistent gains at claim-level uncertainty estimation. Moreover, we present uncertainty-aware decoding techniques that leverage both the graph structure and uncertainty estimates to improve the factuality of LLM generations by preserving only the most reliable claims. Compared to existing methods, our graph-based uncertainty metrics lead to an average of 6.8% relative gains on AUPRC across various long-form generation settings, and our end-to-end system provides consistent 2-4% gains in factuality over existing decoding techniques while significantly improving the informativeness of generated responses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge