Mikhail Bragin
An Optimization Method-Assisted Ensemble Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithm to Solve Unit Commitment Problems
Jun 09, 2022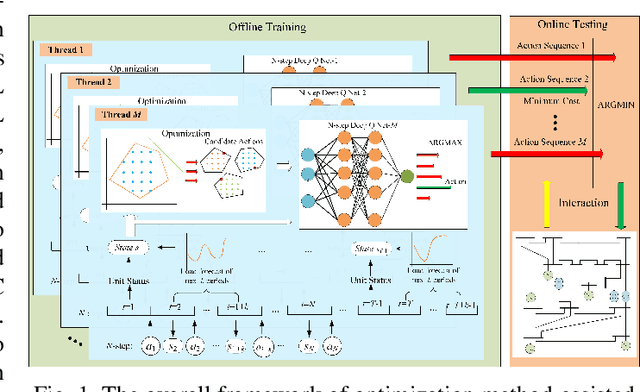
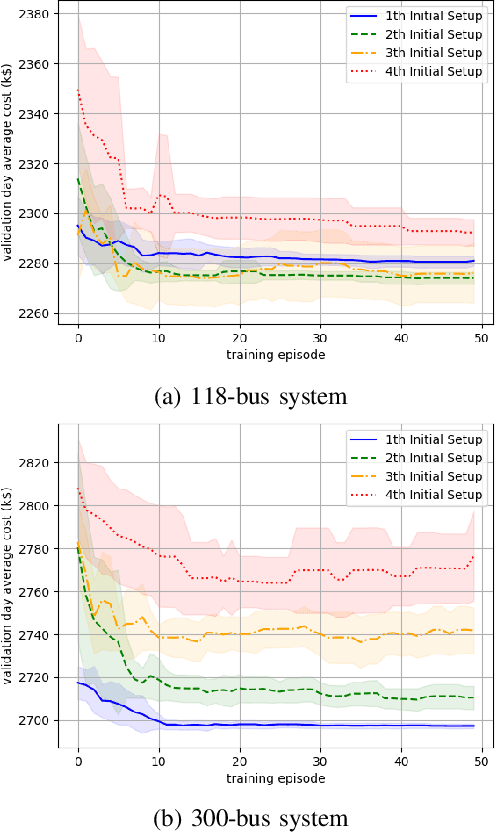

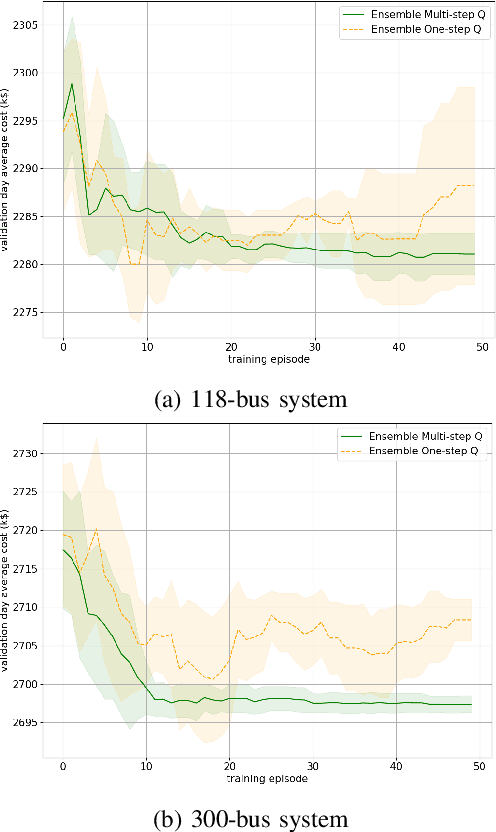
Abstract:Unit commitment (UC) is a fundamental problem in the day-ahead electricity market, and it is critical to solve UC problems efficiently. Mathematical optimization techniques like dynamic programming, Lagrangian relaxation, and mixed-integer quadratic programming (MIQP) are commonly adopted for UC problems. However, the calculation time of these methods increases at an exponential rate with the amount of generators and energy resources, which is still the main bottleneck in industry. Recent advances in artificial intelligence have demonstrated the capability of reinforcement learning (RL) to solve UC problems. Unfortunately, the existing research on solving UC problems with RL suffers from the curse of dimensionality when the size of UC problems grows. To deal with these problems, we propose an optimization method-assisted ensemble deep reinforcement learning algorithm, where UC problems are formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) and solved by multi-step deep Q-learning in an ensemble framework. The proposed algorithm establishes a candidate action set by solving tailored optimization problems to ensure a relatively high performance and the satisfaction of operational constraints. Numerical studies on IEEE 118 and 300-bus systems show that our algorithm outperforms the baseline RL algorithm and MIQP. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm shows strong generalization capacity under unforeseen operational conditions.
A Surrogate Lagrangian Relaxation-based Model Compression for Deep Neural Networks
Dec 18, 2020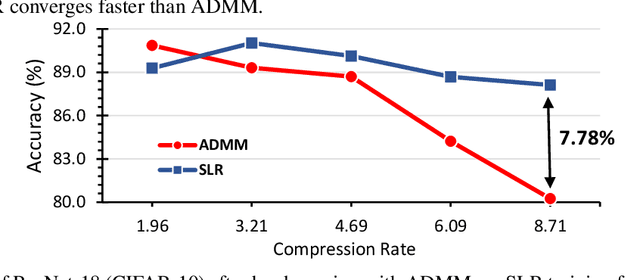
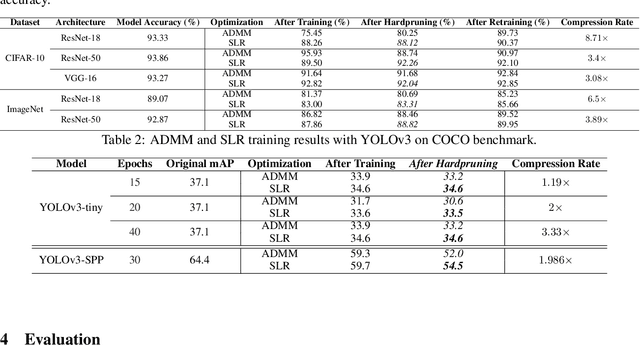
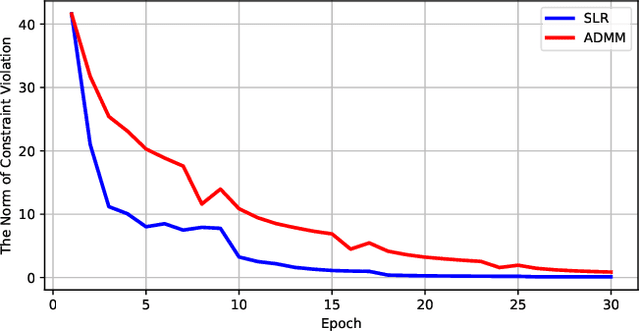
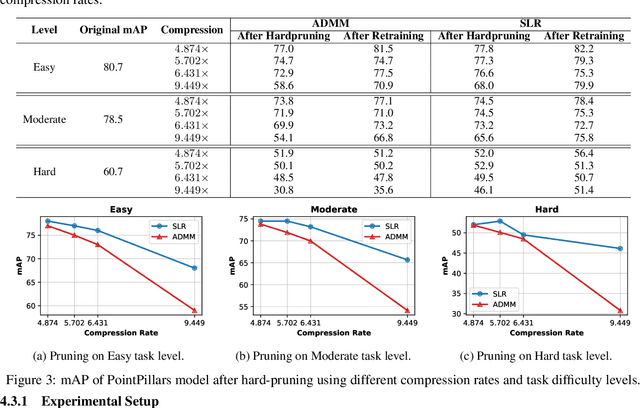
Abstract:Network pruning is a widely used technique to reduce computation cost and model size for deep neural networks. However, the typical three-stage pipeline, i.e., training, pruning and retraining (fine-tuning) significantly increases the overall training trails. For instance, the retraining process could take up to 80 epochs for ResNet-18 on ImageNet, that is 70% of the original model training trails. In this paper, we develop a systematic weight-pruning optimization approach based on Surrogate Lagrangian relaxation (SLR), which is tailored to overcome difficulties caused by the discrete nature of the weight-pruning problem while ensuring fast convergence. We decompose the weight-pruning problem into subproblems, which are coordinated by updating Lagrangian multipliers. Convergence is then accelerated by using quadratic penalty terms. We evaluate the proposed method on image classification tasks, i.e., ResNet-18, ResNet-50 and VGG-16 using ImageNet and CIFAR-10, as well as object detection tasks, i.e., YOLOv3 and YOLOv3-tiny using COCO 2014, PointPillars using KITTI 2017, and Ultra-Fast-Lane-Detection using TuSimple lane detection dataset. Numerical testing results demonstrate that with the adoption of the Surrogate Lagrangian Relaxation method, our SLR-based weight-pruning optimization approach achieves a high model accuracy even at the hard-pruning stage without retraining for many epochs, such as on PointPillars object detection model on KITTI dataset where we achieve 9.44x compression rate by only retraining for 3 epochs with less than 1% accuracy loss. As the compression rate increases, SLR starts to perform better than ADMM and the accuracy gap between them increases. SLR achieves 15.2% better accuracy than ADMM on PointPillars after pruning under 9.49x compression. Given a limited budget of retraining epochs, our approach quickly recovers the model accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge