Michael Zevin
Advancing Glitch Classification in Gravity Spy: Multi-view Fusion with Attention-based Machine Learning for Advanced LIGO's Fourth Observing Run
Jan 23, 2024Abstract:The first successful detection of gravitational waves by ground-based observatories, such as the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), marked a revolutionary breakthrough in our comprehension of the Universe. However, due to the unprecedented sensitivity required to make such observations, gravitational-wave detectors also capture disruptive noise sources called glitches, potentially masking or appearing as gravitational-wave signals themselves. To address this problem, a community-science project, Gravity Spy, incorporates human insight and machine learning to classify glitches in LIGO data. The machine learning classifier, integrated into the project since 2017, has evolved over time to accommodate increasing numbers of glitch classes. Despite its success, limitations have arisen in the ongoing LIGO fourth observing run (O4) due to its architecture's simplicity, which led to poor generalization and inability to handle multi-time window inputs effectively. We propose an advanced classifier for O4 glitches. Our contributions include evaluating fusion strategies for multi-time window inputs, using label smoothing to counter noisy labels, and enhancing interpretability through attention module-generated weights. This development seeks to enhance glitch classification, aiding in the ongoing exploration of gravitational-wave phenomena.
DIRECT: Deep Discriminative Embedding for Clustering of LIGO Data
May 07, 2018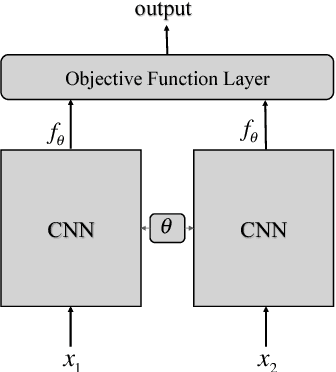
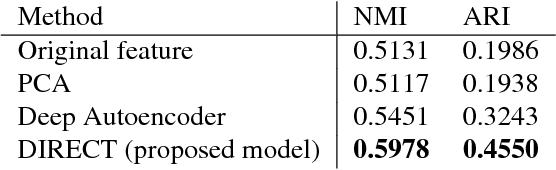
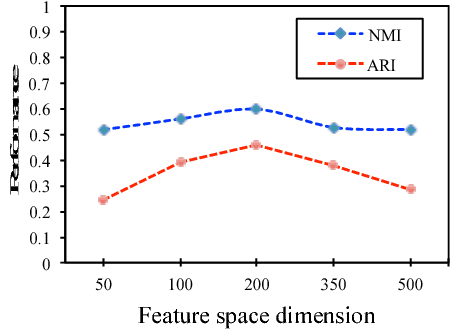
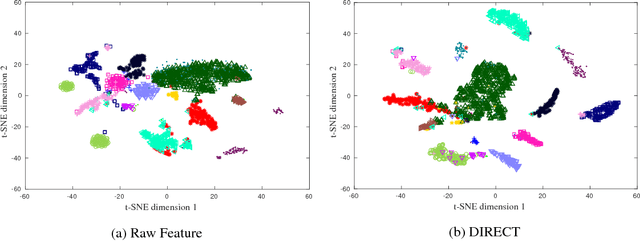
Abstract:In this paper, benefiting from the strong ability of deep neural network in estimating non-linear functions, we propose a discriminative embedding function to be used as a feature extractor for clustering tasks. The trained embedding function transfers knowledge from the domain of a labeled set of morphologically-distinct images, known as classes, to a new domain within which new classes can potentially be isolated and identified. Our target application in this paper is the Gravity Spy Project, which is an effort to characterize transient, non-Gaussian noise present in data from the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory, or LIGO. Accumulating large, labeled sets of noise features and identifying of new classes of noise lead to a better understanding of their origin, which makes their removal from the data and/or detectors possible.
Deep Multi-view Models for Glitch Classification
Apr 28, 2017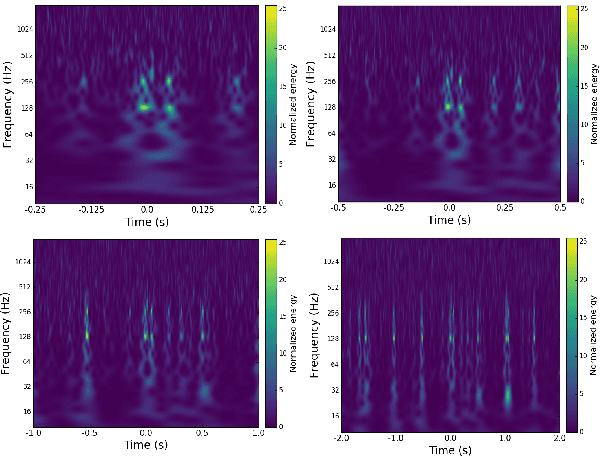
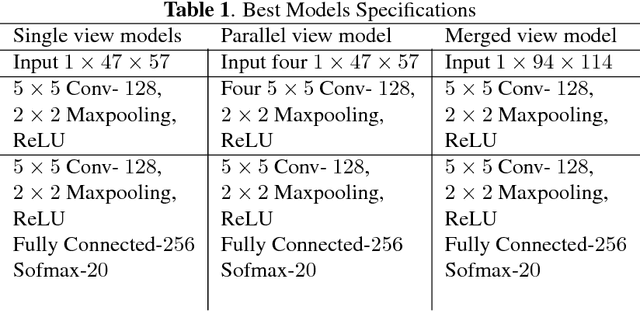
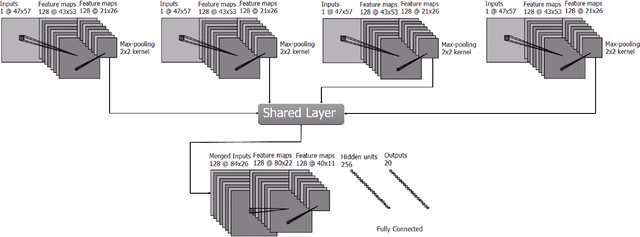
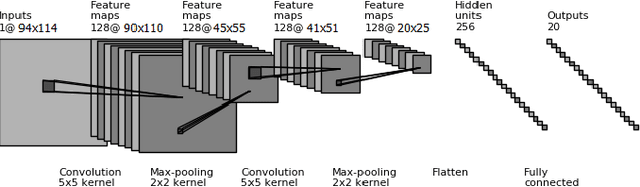
Abstract:Non-cosmic, non-Gaussian disturbances known as "glitches", show up in gravitational-wave data of the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory, or aLIGO. In this paper, we propose a deep multi-view convolutional neural network to classify glitches automatically. The primary purpose of classifying glitches is to understand their characteristics and origin, which facilitates their removal from the data or from the detector entirely. We visualize glitches as spectrograms and leverage the state-of-the-art image classification techniques in our model. The suggested classifier is a multi-view deep neural network that exploits four different views for classification. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model improves the overall accuracy of the classification compared to traditional single view algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge