DIRECT: Deep Discriminative Embedding for Clustering of LIGO Data
Paper and Code
May 07, 2018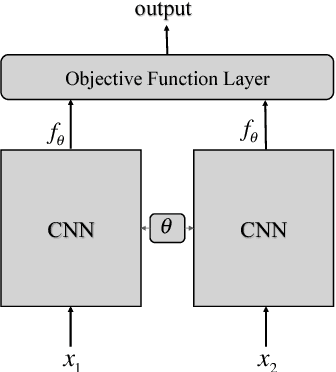
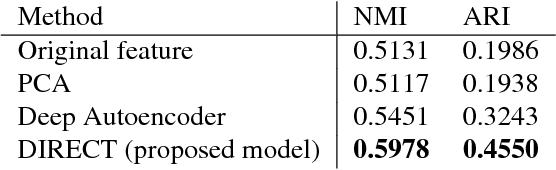
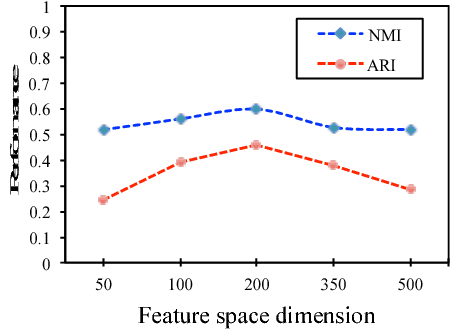
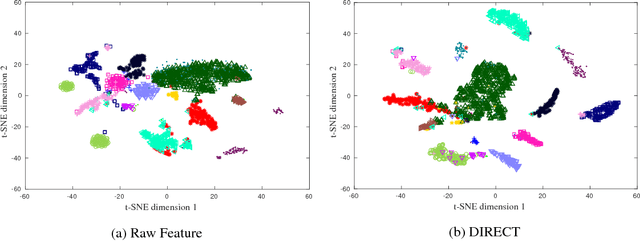
In this paper, benefiting from the strong ability of deep neural network in estimating non-linear functions, we propose a discriminative embedding function to be used as a feature extractor for clustering tasks. The trained embedding function transfers knowledge from the domain of a labeled set of morphologically-distinct images, known as classes, to a new domain within which new classes can potentially be isolated and identified. Our target application in this paper is the Gravity Spy Project, which is an effort to characterize transient, non-Gaussian noise present in data from the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory, or LIGO. Accumulating large, labeled sets of noise features and identifying of new classes of noise lead to a better understanding of their origin, which makes their removal from the data and/or detectors possible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge