Michael Voit
DiffAnt: Diffusion Models for Action Anticipation
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:Anticipating future actions is inherently uncertain. Given an observed video segment containing ongoing actions, multiple subsequent actions can plausibly follow. This uncertainty becomes even larger when predicting far into the future. However, the majority of existing action anticipation models adhere to a deterministic approach, neglecting to account for future uncertainties. In this work, we rethink action anticipation from a generative view, employing diffusion models to capture different possible future actions. In this framework, future actions are iteratively generated from standard Gaussian noise in the latent space, conditioned on the observed video, and subsequently transitioned into the action space. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets, i.e., Breakfast, 50Salads, EpicKitchens, and EGTEA Gaze+, are performed and the proposed method achieves superior or comparable results to state-of-the-art methods, showing the effectiveness of a generative approach for action anticipation. Our code and trained models will be published on GitHub.
A Survey on Deep Learning Techniques for Action Anticipation
Sep 29, 2023Abstract:The ability to anticipate possible future human actions is essential for a wide range of applications, including autonomous driving and human-robot interaction. Consequently, numerous methods have been introduced for action anticipation in recent years, with deep learning-based approaches being particularly popular. In this work, we review the recent advances of action anticipation algorithms with a particular focus on daily-living scenarios. Additionally, we classify these methods according to their primary contributions and summarize them in tabular form, allowing readers to grasp the details at a glance. Furthermore, we delve into the common evaluation metrics and datasets used for action anticipation and provide future directions with systematical discussions.
Anticipative Feature Fusion Transformer for Multi-Modal Action Anticipation
Oct 23, 2022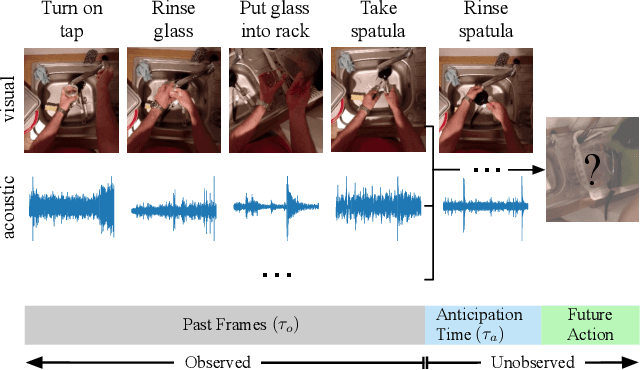
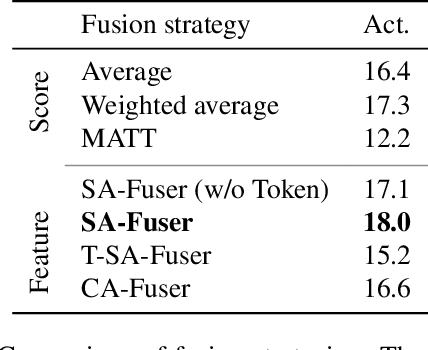
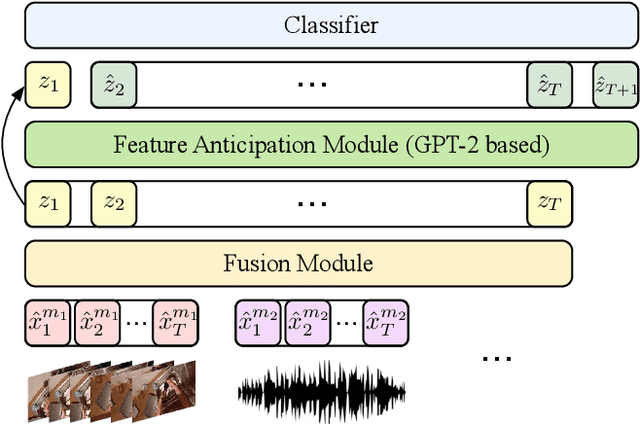
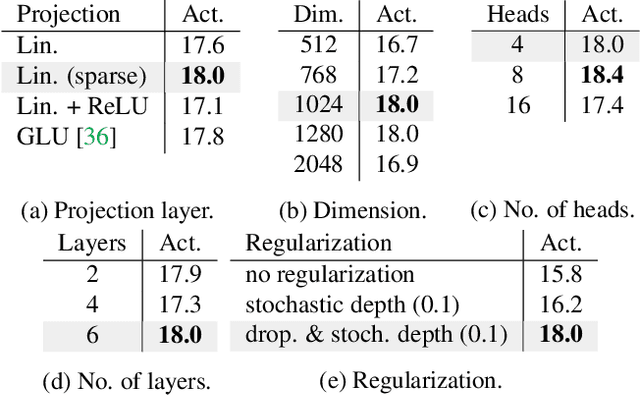
Abstract:Although human action anticipation is a task which is inherently multi-modal, state-of-the-art methods on well known action anticipation datasets leverage this data by applying ensemble methods and averaging scores of unimodal anticipation networks. In this work we introduce transformer based modality fusion techniques, which unify multi-modal data at an early stage. Our Anticipative Feature Fusion Transformer (AFFT) proves to be superior to popular score fusion approaches and presents state-of-the-art results outperforming previous methods on EpicKitchens-100 and EGTEA Gaze+. Our model is easily extensible and allows for adding new modalities without architectural changes. Consequently, we extracted audio features on EpicKitchens-100 which we add to the set of commonly used features in the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge