Michael Bommarito
GPT as Knowledge Worker: A Zero-Shot Evaluation of CPA Capabilities
Jan 11, 2023Abstract:The global economy is increasingly dependent on knowledge workers to meet the needs of public and private organizations. While there is no single definition of knowledge work, organizations and industry groups still attempt to measure individuals' capability to engage in it. The most comprehensive assessment of capability readiness for professional knowledge workers is the Uniform CPA Examination developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). In this paper, we experimentally evaluate OpenAI's `text-davinci-003` and prior versions of GPT on both a sample Regulation (REG) exam and an assessment of over 200 multiple-choice questions based on the AICPA Blueprints for legal, financial, accounting, technology, and ethical tasks. First, we find that `text-davinci-003` achieves a correct rate of 14.4% on a sample REG exam section, significantly underperforming human capabilities on quantitative reasoning in zero-shot prompts. Second, `text-davinci-003` appears to be approaching human-level performance on the Remembering & Understanding and Application skill levels in the Exam absent calculation. For best prompt and parameters, the model answers 57.6% of questions correctly, significantly better than the 25% guessing rate, and its top two answers are correct 82.1% of the time, indicating strong non-entailment. Finally, we find that recent generations of GPT-3 demonstrate material improvements on this assessment, rising from 30% for `text-davinci-001` to 57% for `text-davinci-003`. These findings strongly suggest that large language models have the potential to transform the quality and efficiency of future knowledge work.
LexGLUE: A Benchmark Dataset for Legal Language Understanding in English
Oct 13, 2021
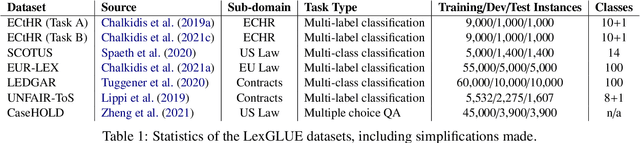
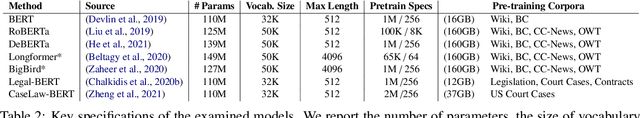
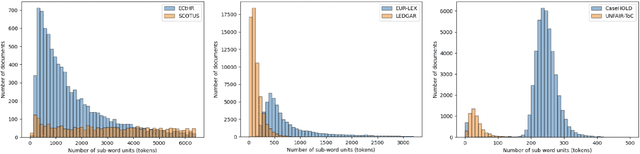
Abstract:Law, interpretations of law, legal arguments, agreements, etc. are typically expressed in writing, leading to the production of vast corpora of legal text. Their analysis, which is at the center of legal practice, becomes increasingly elaborate as these collections grow in size. Natural language understanding (NLU) technologies can be a valuable tool to support legal practitioners in these endeavors. Their usefulness, however, largely depends on whether current state-of-the-art models can generalize across various tasks in the legal domain. To answer this currently open question, we introduce the Legal General Language Understanding Evaluation (LexGLUE) benchmark, a collection of datasets for evaluating model performance across a diverse set of legal NLU tasks in a standardized way. We also provide an evaluation and analysis of several generic and legal-oriented models demonstrating that the latter consistently offer performance improvements across multiple tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge