Miao Fang
Asynchronous and Segmented Bidirectional Encoding for NMT
Feb 19, 2024Abstract:With the rapid advancement of Neural Machine Translation (NMT), enhancing translation efficiency and quality has become a focal point of research. Despite the commendable performance of general models such as the Transformer in various aspects, they still fall short in processing long sentences and fully leveraging bidirectional contextual information. This paper introduces an improved model based on the Transformer, implementing an asynchronous and segmented bidirectional decoding strategy aimed at elevating translation efficiency and accuracy. Compared to traditional unidirectional translations from left-to-right or right-to-left, our method demonstrates heightened efficiency and improved translation quality, particularly in handling long sentences. Experimental results on the IWSLT2017 dataset confirm the effectiveness of our approach in accelerating translation and increasing accuracy, especially surpassing traditional unidirectional strategies in long sentence translation. Furthermore, this study analyzes the impact of sentence length on decoding outcomes and explores the model's performance in various scenarios. The findings of this research not only provide an effective encoding strategy for the NMT field but also pave new avenues and directions for future studies.
Efficient Reinforcemen Learning via Decoupling Exploration and Utilization
Jan 17, 2024Abstract:Deep neural network(DNN) generalization is limited by the over-reliance of current offline reinforcement learning techniques on conservative processing of existing datasets. This method frequently results in algorithms that settle for suboptimal solutions that only adjust to a certain dataset. Similarly, in online reinforcement learning, the previously imposed punitive pessimism also deprives the model of its exploratory potential. Our research proposes a novel framework, Optimistic and Pessimistic Actor Reinforcement Learning (OPARL). OPARL employs a unique dual-actor approach: an optimistic actor dedicated to exploration and a pessimistic actor focused on utilization, thereby effectively differentiating between exploration and utilization strategies. This unique combination in reinforcement learning methods fosters a more balanced and efficient approach. It enables the optimization of policies that focus on actions yielding high rewards through pessimistic utilization strategies, while also ensuring extensive state coverage via optimistic exploration. Experiments and theoretical study demonstrates OPARL improves agents' capacities for application and exploration. In the most tasks of DMControl benchmark and Mujoco environment, OPARL performed better than state-of-the-art methods. Our code has released on https://github.com/yydsok/OPARL
Enhancing Personalized Dialogue Generation with Contrastive Latent Variables: Combining Sparse and Dense Persona
May 19, 2023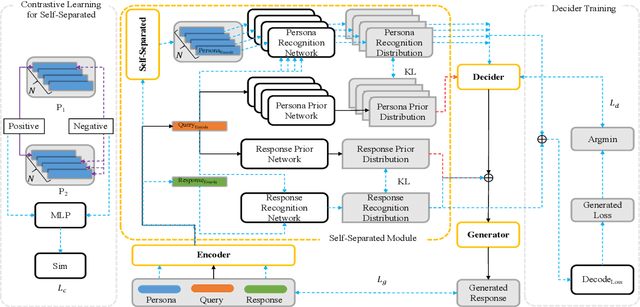
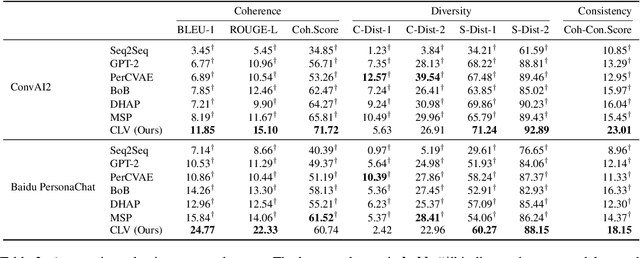
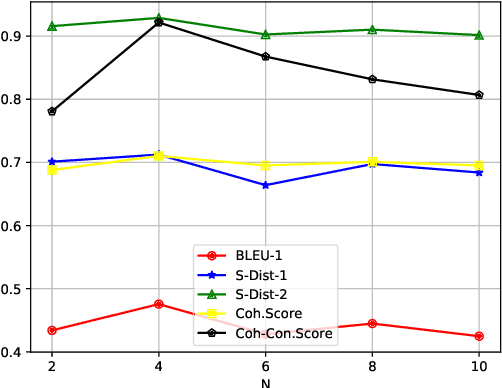
Abstract:The personalized dialogue explores the consistent relationship between dialogue generation and personality. Existing personalized dialogue agents model persona profiles from three resources: sparse or dense persona descriptions and dialogue histories. However, sparse structured persona attributes are explicit but uninformative, dense persona texts contain rich persona descriptions with much noise, and dialogue history query is both noisy and uninformative for persona modeling. In this work, we combine the advantages of the three resources to obtain a richer and more accurate persona. We design a Contrastive Latent Variable-based model (CLV) that clusters the dense persona descriptions into sparse categories, which are combined with the history query to generate personalized responses. Experimental results on Chinese and English datasets demonstrate our model's superiority in personalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge