Mengxia Wu
LAIP: Learning Local Alignment from Image-Phrase Modeling for Text-based Person Search
Jun 16, 2024Abstract:Text-based person search aims at retrieving images of a particular person based on a given textual description. A common solution for this task is to directly match the entire images and texts, i.e., global alignment, which fails to deal with discerning specific details that discriminate against appearance-similar people. As a result, some works shift their attention towards local alignment. One group matches fine-grained parts using forward attention weights of the transformer yet underutilizes information. Another implicitly conducts local alignment by reconstructing masked parts based on unmasked context yet with a biased masking strategy. All limit performance improvement. This paper proposes the Local Alignment from Image-Phrase modeling (LAIP) framework, with Bidirectional Attention-weighted local alignment (BidirAtt) and Mask Phrase Modeling (MPM) module.BidirAtt goes beyond the typical forward attention by considering the gradient of the transformer as backward attention, utilizing two-sided information for local alignment. MPM focuses on mask reconstruction within the noun phrase rather than the entire text, ensuring an unbiased masking strategy. Extensive experiments conducted on the CUHK-PEDES, ICFG-PEDES, and RSTPReid datasets demonstrate the superiority of the LAIP framework over existing methods.
An Empirical Study of Frame Selection for Text-to-Video Retrieval
Nov 01, 2023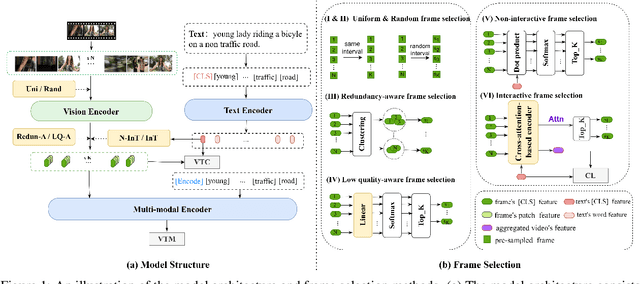
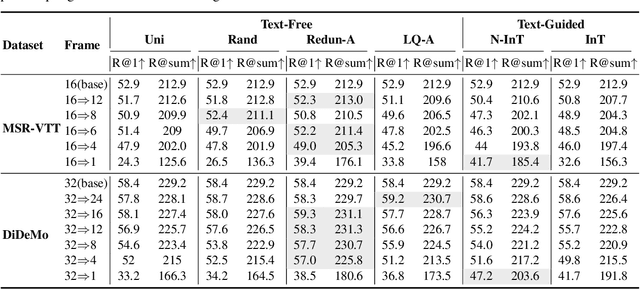
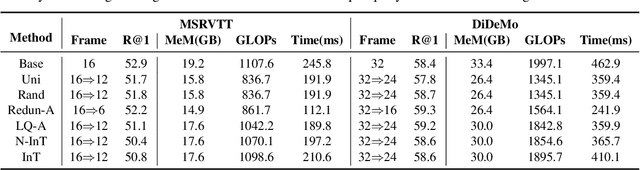

Abstract:Text-to-video retrieval (TVR) aims to find the most relevant video in a large video gallery given a query text. The intricate and abundant context of the video challenges the performance and efficiency of TVR. To handle the serialized video contexts, existing methods typically select a subset of frames within a video to represent the video content for TVR. How to select the most representative frames is a crucial issue, whereby the selected frames are required to not only retain the semantic information of the video but also promote retrieval efficiency by excluding temporally redundant frames. In this paper, we make the first empirical study of frame selection for TVR. We systemically classify existing frame selection methods into text-free and text-guided ones, under which we detailedly analyze six different frame selections in terms of effectiveness and efficiency. Among them, two frame selections are first developed in this paper. According to the comprehensive analysis on multiple TVR benchmarks, we empirically conclude that the TVR with proper frame selections can significantly improve the retrieval efficiency without sacrificing the retrieval performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge