Mengmeng Cui
Graph and Skipped Transformer: Exploiting Spatial and Temporal Modeling Capacities for Efficient 3D Human Pose Estimation
Jul 03, 2024Abstract:In recent years, 2D-to-3D pose uplifting in monocular 3D Human Pose Estimation (HPE) has attracted widespread research interest. GNN-based methods and Transformer-based methods have become mainstream architectures due to their advanced spatial and temporal feature learning capacities. However, existing approaches typically construct joint-wise and frame-wise attention alignments in spatial and temporal domains, resulting in dense connections that introduce considerable local redundancy and computational overhead. In this paper, we take a global approach to exploit spatio-temporal information and realise efficient 3D HPE with a concise Graph and Skipped Transformer architecture. Specifically, in Spatial Encoding stage, coarse-grained body parts are deployed to construct Spatial Graph Network with a fully data-driven adaptive topology, ensuring model flexibility and generalizability across various poses. In Temporal Encoding and Decoding stages, a simple yet effective Skipped Transformer is proposed to capture long-range temporal dependencies and implement hierarchical feature aggregation. A straightforward Data Rolling strategy is also developed to introduce dynamic information into 2D pose sequence. Extensive experiments are conducted on Human3.6M, MPI-INF-3DHP and Human-Eva benchmarks. G-SFormer series methods achieve superior performances compared with previous state-of-the-arts with only around ten percent of parameters and significantly reduced computational complexity. Additionally, G-SFormer also exhibits outstanding robustness to inaccuracies in detected 2D poses.
The Short Text Matching Model Enhanced with Knowledge via Contrastive Learning
Apr 08, 2023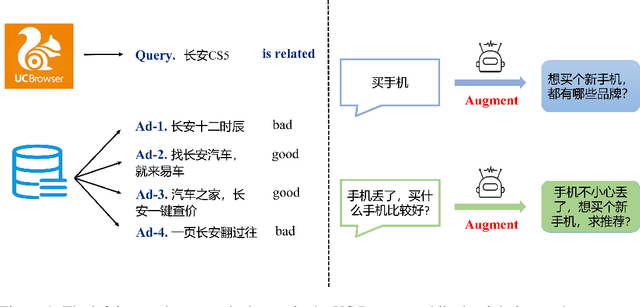
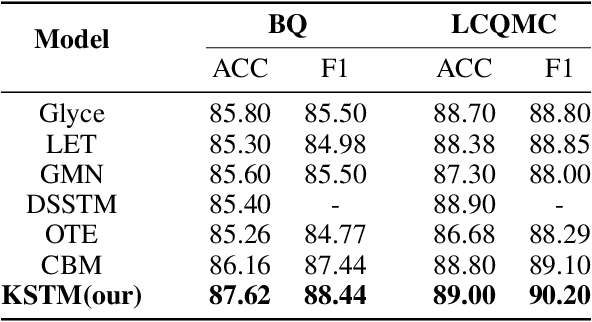
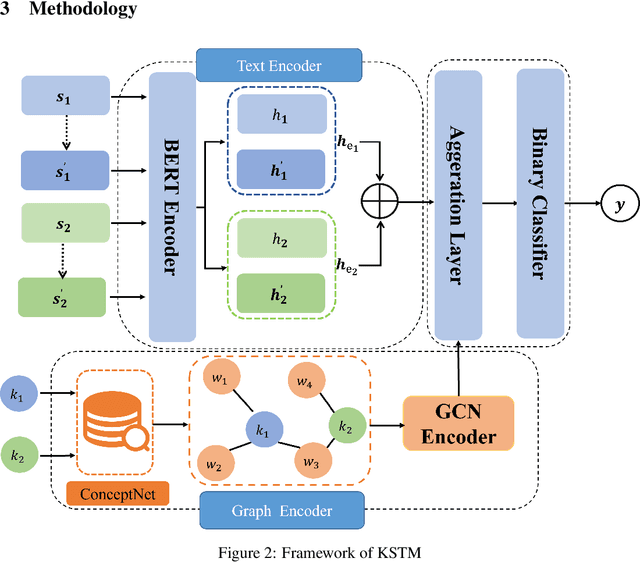
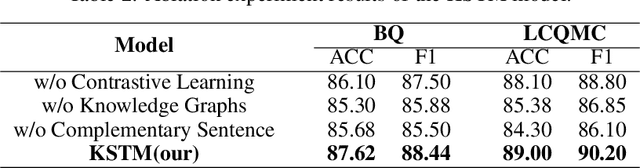
Abstract:In recent years, short Text Matching tasks have been widely applied in the fields ofadvertising search and recommendation. The difficulty lies in the lack of semantic information and word ambiguity caused by the short length of the text. Previous works have introduced complement sentences or knowledge bases to provide additional feature information. However, these methods have not fully interacted between the original sentence and the complement sentence, and have not considered the noise issue that may arise from the introduction of external knowledge bases. Therefore, this paper proposes a short Text Matching model that combines contrastive learning and external knowledge. The model uses a generative model to generate corresponding complement sentences and uses the contrastive learning method to guide the model to obtain more semantically meaningful encoding of the original sentence. In addition, to avoid noise, we use keywords as the main semantics of the original sentence to retrieve corresponding knowledge words in the knowledge base, and construct a knowledge graph. The graph encoding model is used to integrate the knowledge base information into the model. Our designed model achieves state-of-the-art performance on two publicly available Chinese Text Matching datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of our model.
Representation and Correlation Enhanced Encoder-Decoder Framework for Scene Text Recognition
Jun 13, 2021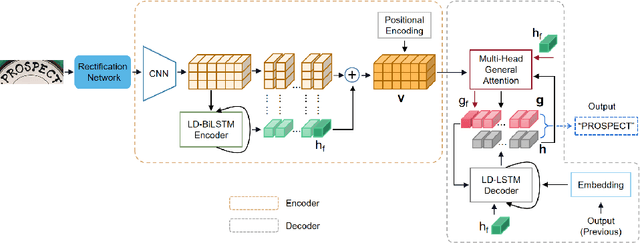
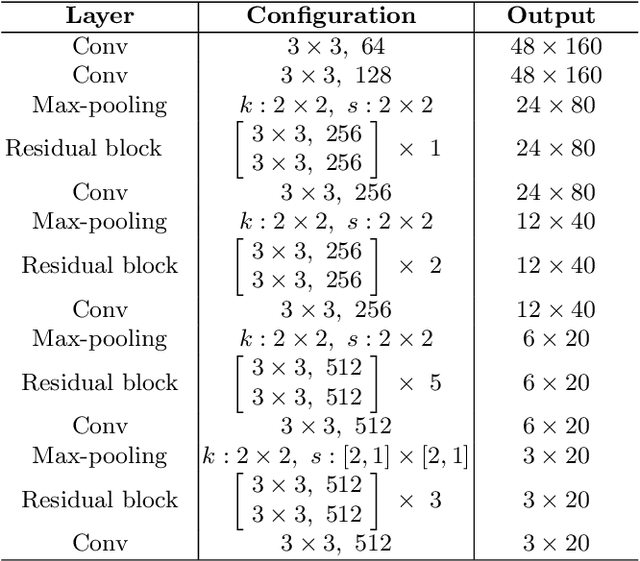

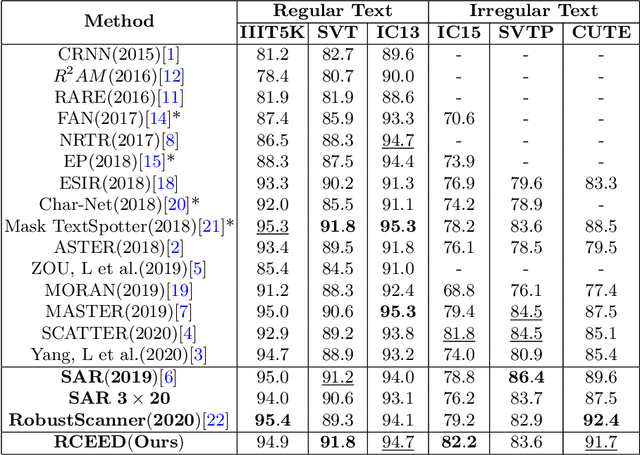
Abstract:Attention-based encoder-decoder framework is widely used in the scene text recognition task. However, for the current state-of-the-art(SOTA) methods, there is room for improvement in terms of the efficient usage of local visual and global context information of the input text image, as well as the robust correlation between the scene processing module(encoder) and the text processing module(decoder). In this paper, we propose a Representation and Correlation Enhanced Encoder-Decoder Framework(RCEED) to address these deficiencies and break performance bottleneck. In the encoder module, local visual feature, global context feature, and position information are aligned and fused to generate a small-size comprehensive feature map. In the decoder module, two methods are utilized to enhance the correlation between scene and text feature space. 1) The decoder initialization is guided by the holistic feature and global glimpse vector exported from the encoder. 2) The feature enriched glimpse vector produced by the Multi-Head General Attention is used to assist the RNN iteration and the character prediction at each time step. Meanwhile, we also design a Layernorm-Dropout LSTM cell to improve model's generalization towards changeable texts. Extensive experiments on the benchmarks demonstrate the advantageous performance of RCEED in scene text recognition tasks, especially the irregular ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge