Mengde Li
Bridging Speech, Emotion, and Motion: a VLM-based Multimodal Edge-deployable Framework for Humanoid Robots
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Effective human-robot interaction requires emotionally rich multimodal expressions, yet most humanoid robots lack coordinated speech, facial expressions, and gestures. Meanwhile, real-world deployment demands on-device solutions that can operate autonomously without continuous cloud connectivity. To bridging \underline{\textit{S}}peech, \underline{\textit{E}}motion, and \underline{\textit{M}}otion, we present \textit{SeM$^2$}, a Vision Language Model-based framework that orchestrates emotionally coherent multimodal interactions through three key components: a multimodal perception module capturing user contextual cues, a Chain-of-Thought reasoning for response planning, and a novel Semantic-Sequence Aligning Mechanism (SSAM) that ensures precise temporal coordination between verbal content and physical expressions. We implement both cloud-based and \underline{\textit{e}}dge-deployed versions (\textit{SeM$^2_e$}), with the latter knowledge distilled to operate efficiently on edge hardware while maintaining 95\% of the relative performance. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms unimodal baselines in naturalness, emotional clarity, and modal coherence, advancing socially expressive humanoid robotics for diverse real-world environments.
When Attention Betrays: Erasing Backdoor Attacks in Robotic Policies by Reconstructing Visual Tokens
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Downstream fine-tuning of vision-language-action (VLA) models enhances robotics, yet exposes the pipeline to backdoor risks. Attackers can pretrain VLAs on poisoned data to implant backdoors that remain stealthy but can trigger harmful behavior during inference. However, existing defenses either lack mechanistic insight into multimodal backdoors or impose prohibitive computational costs via full-model retraining. To this end, we uncover a deep-layer attention grabbing mechanism: backdoors redirect late-stage attention and form compact embedding clusters near the clean manifold. Leveraging this insight, we introduce Bera, a test-time backdoor erasure framework that detects tokens with anomalous attention via latent-space localization, masks suspicious regions using deep-layer cues, and reconstructs a trigger-free image to break the trigger-unsafe-action mapping while restoring correct behavior. Unlike prior defenses, Bera requires neither retraining of VLAs nor any changes to the training pipeline. Extensive experiments across multiple embodied platforms and tasks show that Bera effectively maintains nominal performance, significantly reduces attack success rates, and consistently restores benign behavior from backdoored outputs, thereby offering a robust and practical defense mechanism for securing robotic systems.
RGMP: Recurrent Geometric-prior Multimodal Policy for Generalizable Humanoid Robot Manipulation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots exhibit significant potential in executing diverse human-level skills. However, current research predominantly relies on data-driven approaches that necessitate extensive training datasets to achieve robust multimodal decision-making capabilities and generalizable visuomotor control. These methods raise concerns due to the neglect of geometric reasoning in unseen scenarios and the inefficient modeling of robot-target relationships within the training data, resulting in significant waste of training resources. To address these limitations, we present the Recurrent Geometric-prior Multimodal Policy (RGMP), an end-to-end framework that unifies geometric-semantic skill reasoning with data-efficient visuomotor control. For perception capabilities, we propose the Geometric-prior Skill Selector, which infuses geometric inductive biases into a vision language model, producing adaptive skill sequences for unseen scenes with minimal spatial common sense tuning. To achieve data-efficient robotic motion synthesis, we introduce the Adaptive Recursive Gaussian Network, which parameterizes robot-object interactions as a compact hierarchy of Gaussian processes that recursively encode multi-scale spatial relationships, yielding dexterous, data-efficient motion synthesis even from sparse demonstrations. Evaluated on both our humanoid robot and desktop dual-arm robot, the RGMP framework achieves 87% task success in generalization tests and exhibits 5x greater data efficiency than the state-of-the-art model. This performance underscores its superior cross-domain generalization, enabled by geometric-semantic reasoning and recursive-Gaussion adaptation.
Learning Robust Grasping Strategy Through Tactile Sensing and Adaption Skill
Nov 13, 2024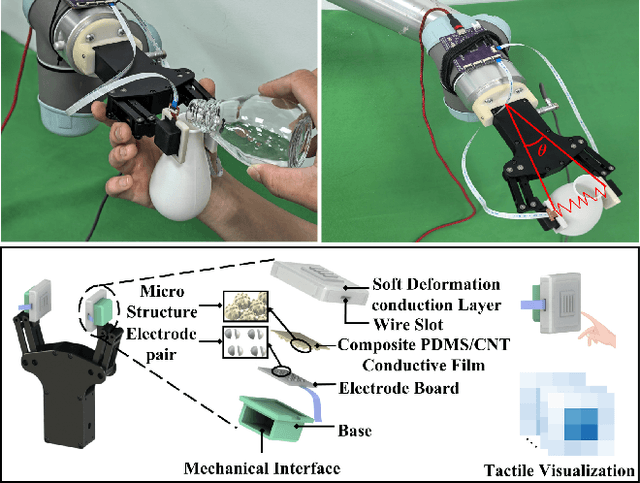
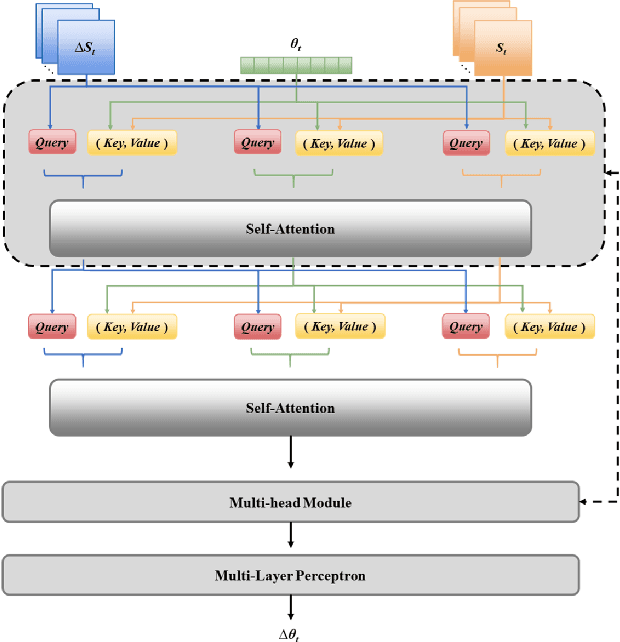
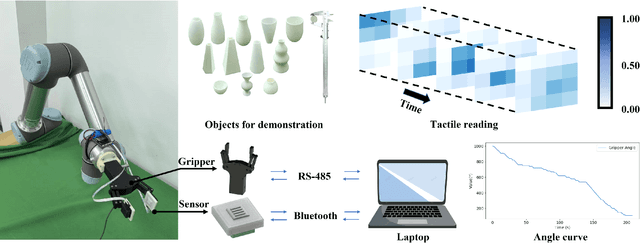
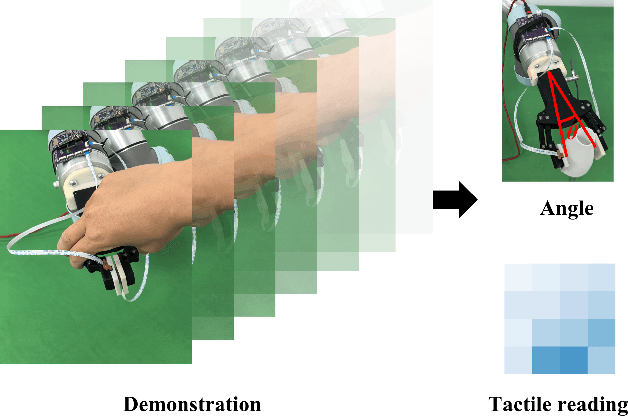
Abstract:Robust grasping represents an essential task in robotics, necessitating tactile feedback and reactive grasping adjustments for robust grasping of objects. Previous research has extensively combined tactile sensing with grasping, primarily relying on rule-based approaches, frequently neglecting post-grasping difficulties such as external disruptions or inherent uncertainties of the object's physics and geometry. To address these limitations, this paper introduces an human-demonstration-based adaptive grasping policy base on tactile, which aims to achieve robust gripping while resisting disturbances to maintain grasp stability. Our trained model generalizes to daily objects with seven different sizes, shapes, and textures. Experimental results demonstrate that our method performs well in dynamic and force interaction tasks and exhibits excellent generalization ability.
Fast calibration for ultrasound imaging guidance based on depth camera
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:During the process of robot-assisted ultrasound(US) puncture, it is important to estimate the location of the puncture from the 2D US images. To this end, the calibration of the US image becomes an important issue. In this paper, we proposed a depth camera-based US calibration method, where an easy-to-deploy device is designed for the calibration. With this device, the coordinates of the puncture needle tip are collected respectively in US image and in the depth camera, upon which a correspondence matrix is built for calibration. Finally, a number of experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of our calibration method.
A novel tactile palm for robotic object manipulation
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Tactile sensing is of great importance during human hand usage such as object exploration, grasping and manipulation. Different types of tactile sensors have been designed during the past decades, which are mainly focused on either the fingertips for grasping or the upper-body for human-robot interaction. In this paper, a novel soft tactile sensor has been designed to mimic the functionality of human palm that can estimate the contact state of different objects. The tactile palm mainly consists of three parts including an electrode array, a soft cover skin and the conductive sponge. The design principle are described in details, with a number of experiments showcasing the effectiveness of the proposed design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge