Melanie Hingle
Counterfactual Modeling with Fine-Tuned LLMs for Health Intervention Design and Sensor Data Augmentation
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Counterfactual explanations (CFEs) provide human-centric interpretability by identifying the minimal, actionable changes required to alter a machine learning model's prediction. Therefore, CFs can be used as (i) interventions for abnormality prevention and (ii) augmented data for training robust models. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of CF generation using large language models (LLMs), including GPT-4 (zero-shot and few-shot) and two open-source models-BioMistral-7B and LLaMA-3.1-8B, in both pretrained and fine-tuned configurations. Using the multimodal AI-READI clinical dataset, we assess CFs across three dimensions: intervention quality, feature diversity, and augmentation effectiveness. Fine-tuned LLMs, particularly LLaMA-3.1-8B, produce CFs with high plausibility (up to 99%), strong validity (up to 0.99), and realistic, behaviorally modifiable feature adjustments. When used for data augmentation under controlled label-scarcity settings, LLM-generated CFs substantially restore classifier performance, yielding an average 20% F1 recovery across three scarcity scenarios. Compared with optimization-based baselines such as DiCE, CFNOW, and NICE, LLMs offer a flexible, model-agnostic approach that generates more clinically actionable and semantically coherent counterfactuals. Overall, this work demonstrates the promise of LLM-driven counterfactuals for both interpretable intervention design and data-efficient model training in sensor-based digital health. Impact: SenseCF fine-tunes an LLM to generate valid, representative counterfactual explanations and supplement minority class in an imbalanced dataset for improving model training and boosting model robustness and predictive performance
Analyzing the Language of Food on Social Media
Sep 11, 2014
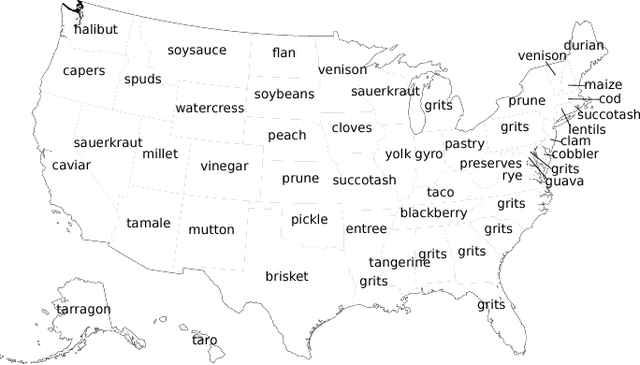

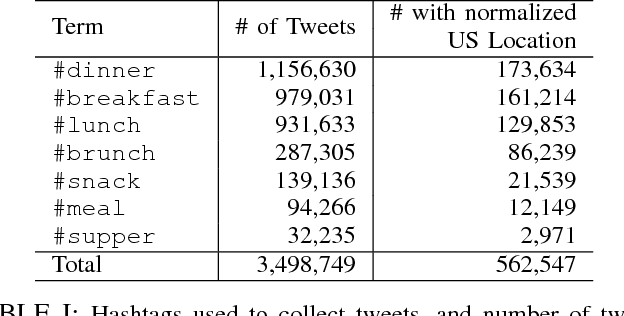
Abstract:We investigate the predictive power behind the language of food on social media. We collect a corpus of over three million food-related posts from Twitter and demonstrate that many latent population characteristics can be directly predicted from this data: overweight rate, diabetes rate, political leaning, and home geographical location of authors. For all tasks, our language-based models significantly outperform the majority-class baselines. Performance is further improved with more complex natural language processing, such as topic modeling. We analyze which textual features have most predictive power for these datasets, providing insight into the connections between the language of food, geographic locale, and community characteristics. Lastly, we design and implement an online system for real-time query and visualization of the dataset. Visualization tools, such as geo-referenced heatmaps, semantics-preserving wordclouds and temporal histograms, allow us to discover more complex, global patterns mirrored in the language of food.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge