Mayur Patidar
DBRouting: Routing End User Queries to Databases for Answerability
Jan 27, 2025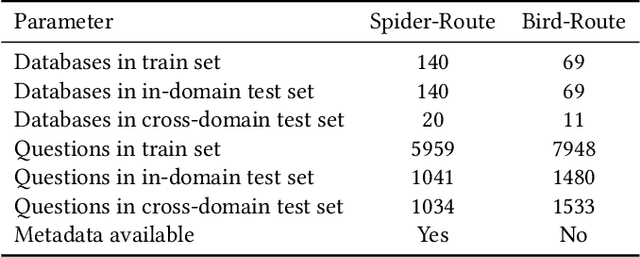
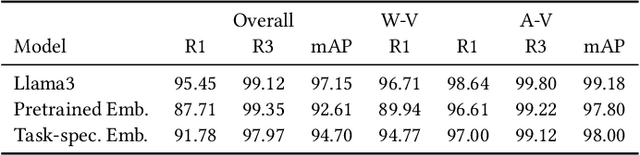
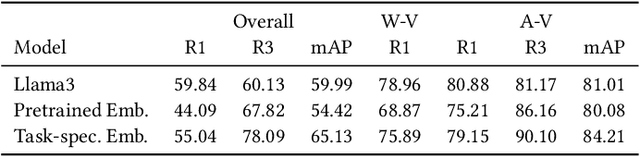
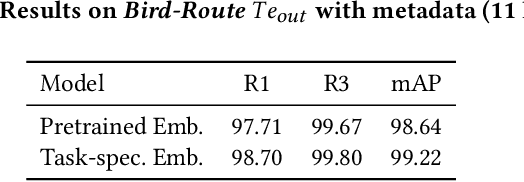
Abstract:Enterprise level data is often distributed across multiple sources and identifying the correct set-of data-sources with relevant information for a knowledge request is a fundamental challenge. In this work, we define the novel task of routing an end-user query to the appropriate data-source, where the data-sources are databases. We synthesize datasets by extending existing datasets designed for NL-to-SQL semantic parsing. We create baselines on these datasets by using open-source LLMs, using both pre-trained and task specific embeddings fine-tuned using the training data. With these baselines we demonstrate that open-source LLMs perform better than embedding based approach, but suffer from token length limitations. Embedding based approaches benefit from task specific fine-tuning, more so when there is availability of data in terms of database specific questions for training. We further find that the task becomes more difficult (i) with an increase in the number of data-sources, (ii) having data-sources closer in terms of their domains,(iii) having databases without external domain knowledge required to interpret its entities and (iv) with ambiguous and complex queries requiring more fine-grained understanding of the data-sources or logical reasoning for routing to an appropriate source. This calls for the need for developing more sophisticated solutions to better address the task.
Translating Across Cultures: LLMs for Intralingual Cultural Adaptation
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:LLMs are increasingly being deployed for multilingual applications and have demonstrated impressive translation capabilities between several low and high resource languages. An aspect of translation that often gets overlooked is that of cultural adaptation, or modifying source culture references to suit the target culture. Cultural adaptation has applications across several creative industries and requires intimate knowledge of source and target cultures during translation. While specialized translation models still outperform LLMs on the machine translation task when viewed from the lens of correctness, they are not sensitive to cultural differences often requiring manual correction. LLMs on the other hand have a rich reservoir of cultural knowledge embedded within its parameters that can be potentially exploited for such applications. In this paper we define the task of cultural adaptation and create an evaluation framework to benchmark different models for this task. We evaluate the performance of modern LLMs for cultural adaptation and analyze their cross cultural knowledge while connecting related concepts across different cultures. We also analyze possible issues with automatic adaptation including cultural biases and stereotypes. We hope that this task will offer more insight into the cultural understanding of LLMs and their creativity in cross-cultural scenarios.
Combining Transfer Learning with In-context Learning using Blackbox LLMs for Zero-shot Knowledge Base Question Answering
Nov 15, 2023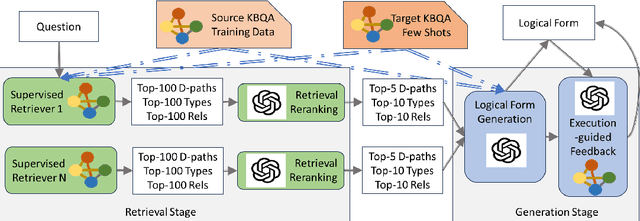
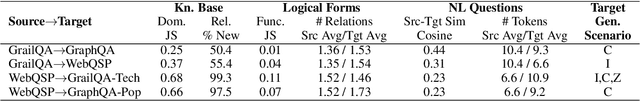
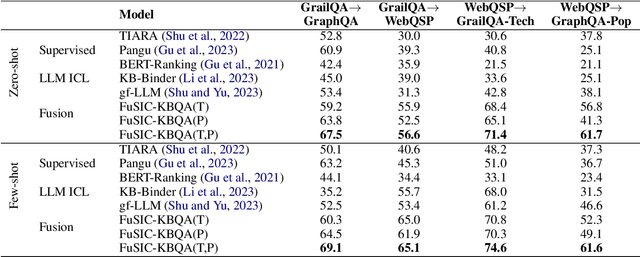
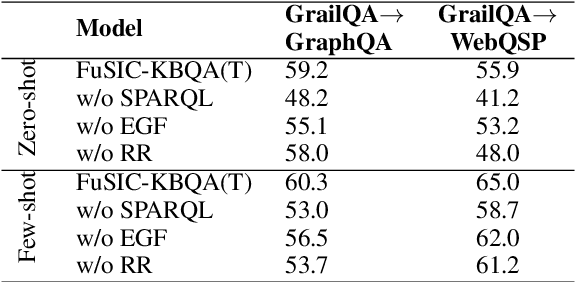
Abstract:We address the zero-shot transfer learning setting for the knowledge base question answering (KBQA) problem, where a large volume of labeled training data is available for the source domain, but no such labeled examples are available for the target domain. Transfer learning for KBQA makes use of large volumes of unlabeled data in the target in addition to the labeled data in the source. More recently, few-shot in-context learning using Black-box Large Language Models (BLLMs) has been adapted for KBQA without considering any source domain data. In this work, we show how to meaningfully combine these two paradigms for KBQA so that their benefits add up. Specifically, we preserve the two stage retrieve-then-generate pipeline of supervised KBQA and introduce interaction between in-context learning using BLLMs and transfer learning from the source for both stages. In addition, we propose execution-guided self-refinement using BLLMs, decoupled from the transfer setting. With the help of experiments using benchmark datasets GrailQA as the source and WebQSP as the target, we show that the proposed combination brings significant improvements to both stages and also outperforms by a large margin state-of-the-art supervised KBQA models trained on the source. We also show that in the in-domain setting, the proposed BLLM augmentation significantly outperforms state-of-the-art supervised models, when the volume of labeled data is limited, and also outperforms these marginally even when using the entire large training dataset.
Do I have the Knowledge to Answer? Investigating Answerability of Knowledge Base Questions
Dec 20, 2022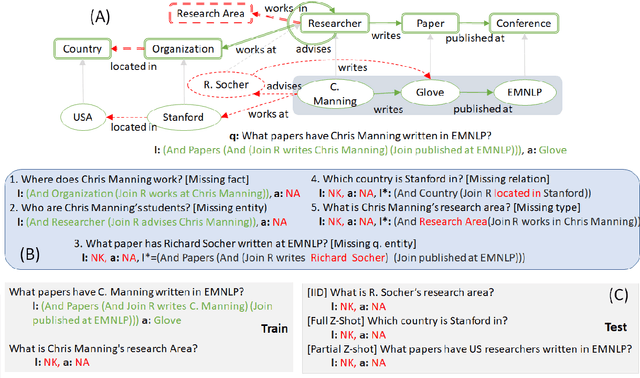

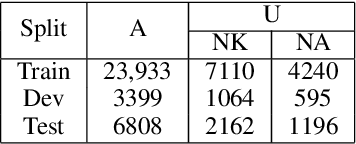
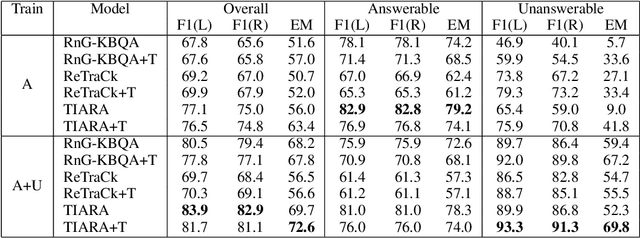
Abstract:When answering natural language questions over knowledge bases (KBs), incompleteness in the KB can naturally lead to many questions being unanswerable. While answerability has been explored in other QA settings, it has not been studied for QA over knowledge bases (KBQA). We first identify various forms of KB incompleteness that can result in a question being unanswerable. We then propose GrailQAbility, a new benchmark dataset, which systematically modifies GrailQA (a popular KBQA dataset) to represent all these incompleteness issues. Testing two state-of-the-art KBQA models (trained on original GrailQA as well as our GrailQAbility), we find that both models struggle to detect unanswerable questions, or sometimes detect them for the wrong reasons. Consequently, both models suffer significant loss in performance, underscoring the need for further research in making KBQA systems robust to unanswerability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge