Matteo Cartiglia
SPAIC: A sub-$μ$W/Channel, 16-Channel General-Purpose Event-Based Analog Front-End with Dual-Mode Encoders
Aug 31, 2023



Abstract:Low-power event-based analog front-ends (AFE) are a crucial component required to build efficient end-to-end neuromorphic processing systems for edge computing. Although several neuromorphic chips have been developed for implementing spiking neural networks (SNNs) and solving a wide range of sensory processing tasks, there are only a few general-purpose analog front-end devices that can be used to convert analog sensory signals into spikes and interfaced to neuromorphic processors. In this work, we present a novel, highly configurable analog front-end chip, denoted as SPAIC (signal-to-spike converter for analog AI computation), that offers a general-purpose dual-mode analog signal-to-spike encoding with delta modulation and pulse frequency modulation, with tunable frequency bands. The ASIC is designed in a 180 nm process. It supports and encodes a wide variety of signals spanning 4 orders of magnitude in frequency, and provides an event-based output that is compatible with existing neuromorphic processors. We validated the ASIC for its functions and present initial silicon measurement results characterizing the basic building blocks of the chip.
Neuromorphic analog circuits for robust on-chip always-on learning in spiking neural networks
Jul 12, 2023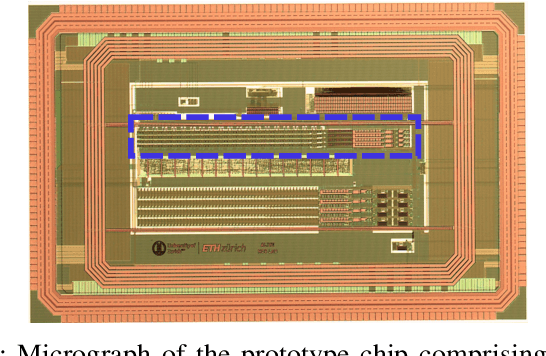
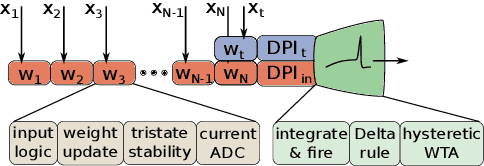
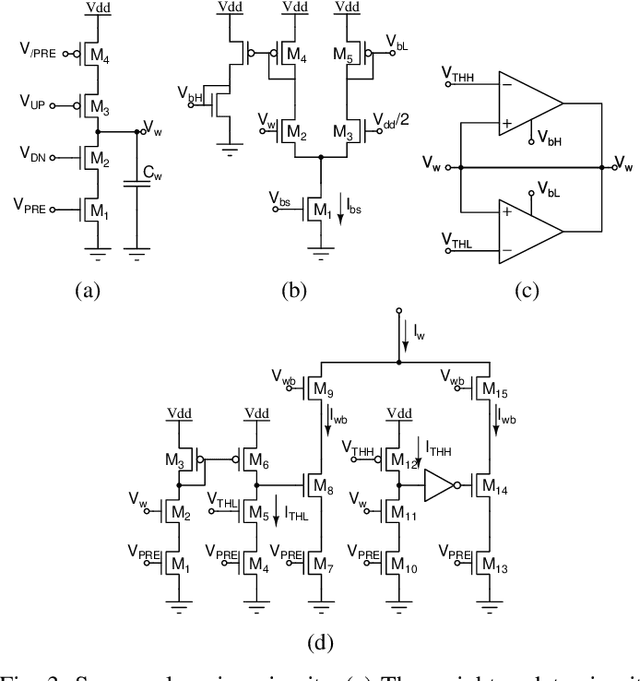
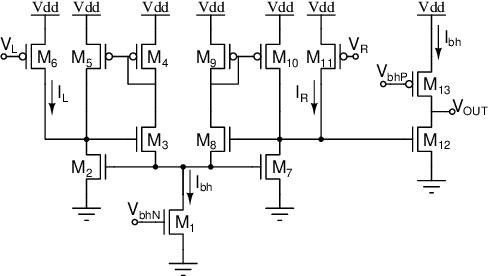
Abstract:Mixed-signal neuromorphic systems represent a promising solution for solving extreme-edge computing tasks without relying on external computing resources. Their spiking neural network circuits are optimized for processing sensory data on-line in continuous-time. However, their low precision and high variability can severely limit their performance. To address this issue and improve their robustness to inhomogeneities and noise in both their internal state variables and external input signals, we designed on-chip learning circuits with short-term analog dynamics and long-term tristate discretization mechanisms. An additional hysteretic stop-learning mechanism is included to improve stability and automatically disable weight updates when necessary, to enable continuous always-on learning. We designed a spiking neural network with these learning circuits in a prototype chip using a 180 nm CMOS technology. Simulation and silicon measurement results from the prototype chip are presented. These circuits enable the construction of large-scale spiking neural networks with online learning capabilities for real-world edge computing tasks.
Spike-based local synaptic plasticity: A survey of computational models and neuromorphic circuits
Sep 30, 2022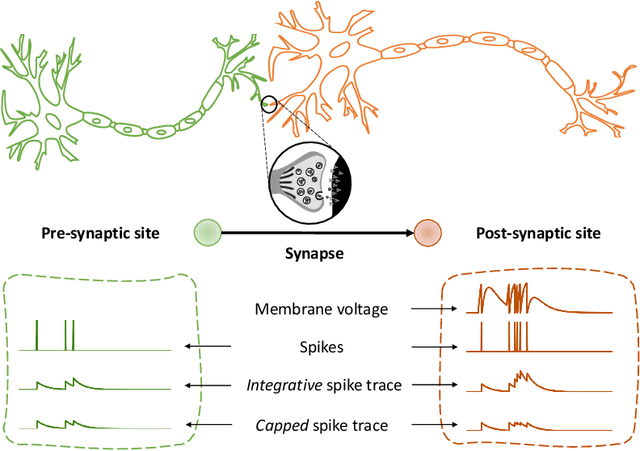



Abstract:Understanding how biological neural networks carry out learning using spike-based local plasticity mechanisms can lead to the development of powerful, energy-efficient, and adaptive neuromorphic processing systems. A large number of spike-based learning models have recently been proposed following different approaches. However, it is difficult to assess if and how they could be mapped onto neuromorphic hardware, and to compare their features and ease of implementation. To this end, in this survey, we provide a comprehensive overview of representative brain-inspired synaptic plasticity models and mixed-signal \acs{CMOS} neuromorphic circuits within a unified framework. We review historical, bottom-up, and top-down approaches to modeling synaptic plasticity, and we identify computational primitives that can support low-latency and low-power hardware implementations of spike-based learning rules. We provide a common definition of a locality principle based on pre- and post-synaptic neuron information, which we propose as a fundamental requirement for physical implementations of synaptic plasticity. Based on this principle, we compare the properties of these models within the same framework, and describe the mixed-signal electronic circuits that implement their computing primitives, pointing out how these building blocks enable efficient on-chip and online learning in neuromorphic processing systems.
Online Detection of Vibration Anomalies Using Balanced Spiking Neural Networks
Jun 01, 2021


Abstract:Vibration patterns yield valuable information about the health state of a running machine, which is commonly exploited in predictive maintenance tasks for large industrial systems. However, the overhead, in terms of size, complexity and power budget, required by classical methods to exploit this information is often prohibitive for smaller-scale applications such as autonomous cars, drones or robotics. Here we propose a neuromorphic approach to perform vibration analysis using spiking neural networks that can be applied to a wide range of scenarios. We present a spike-based end-to-end pipeline able to detect system anomalies from vibration data, using building blocks that are compatible with analog-digital neuromorphic circuits. This pipeline operates in an online unsupervised fashion, and relies on a cochlea model, on feedback adaptation and on a balanced spiking neural network. We show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance or better against two publicly available data sets. Further, we demonstrate a working proof-of-concept implemented on an asynchronous neuromorphic processor device. This work represents a significant step towards the design and implementation of autonomous low-power edge-computing devices for online vibration monitoring.
An error-propagation spiking neural network compatible with neuromorphic processors
Apr 12, 2021



Abstract:Spiking neural networks have shown great promise for the design of low-power sensory-processing and edge-computing hardware platforms. However, implementing on-chip learning algorithms on such architectures is still an open challenge, especially for multi-layer networks that rely on the back-propagation algorithm. In this paper, we present a spike-based learning method that approximates back-propagation using local weight update mechanisms and which is compatible with mixed-signal analog/digital neuromorphic circuits. We introduce a network architecture that enables synaptic weight update mechanisms to back-propagate error signals across layers and present a network that can be trained to distinguish between two spike-based patterns that have identical mean firing rates, but different spike-timings. This work represents a first step towards the design of ultra-low power mixed-signal neuromorphic processing systems with on-chip learning circuits that can be trained to recognize different spatio-temporal patterns of spiking activity (e.g. produced by event-based vision or auditory sensors).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge