Matt W. Hoffman
Knowledge Transfer from Teachers to Learners in Growing-Batch Reinforcement Learning
May 09, 2023



Abstract:Standard approaches to sequential decision-making exploit an agent's ability to continually interact with its environment and improve its control policy. However, due to safety, ethical, and practicality constraints, this type of trial-and-error experimentation is often infeasible in many real-world domains such as healthcare and robotics. Instead, control policies in these domains are typically trained offline from previously logged data or in a growing-batch manner. In this setting a fixed policy is deployed to the environment and used to gather an entire batch of new data before being aggregated with past batches and used to update the policy. This improvement cycle can then be repeated multiple times. While a limited number of such cycles is feasible in real-world domains, the quality and diversity of the resulting data are much lower than in the standard continually-interacting approach. However, data collection in these domains is often performed in conjunction with human experts, who are able to label or annotate the collected data. In this paper, we first explore the trade-offs present in this growing-batch setting, and then investigate how information provided by a teacher (i.e., demonstrations, expert actions, and gradient information) can be leveraged at training time to mitigate the sample complexity and coverage requirements for actor-critic methods. We validate our contributions on tasks from the DeepMind Control Suite.
One-Shot High-Fidelity Imitation: Training Large-Scale Deep Nets with RL
Oct 11, 2018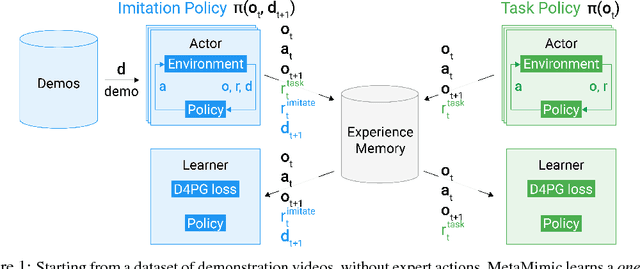
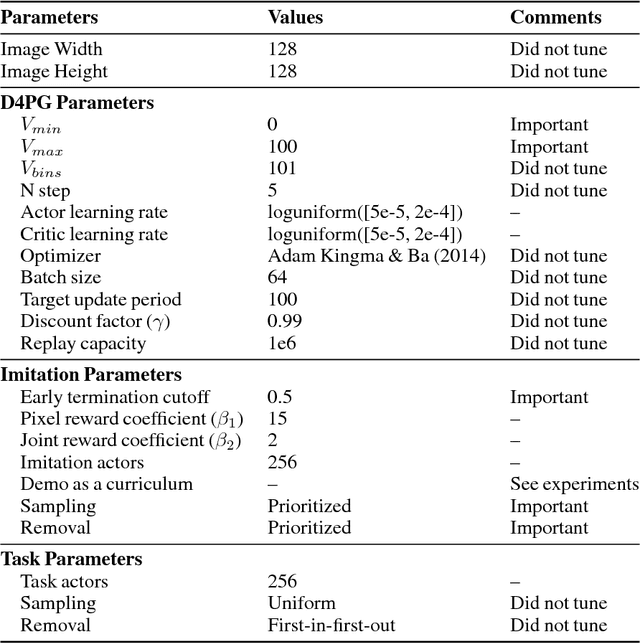
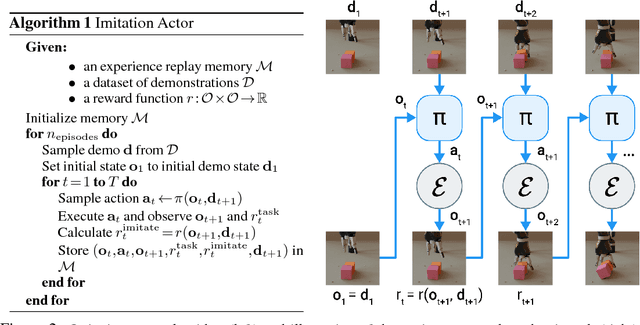
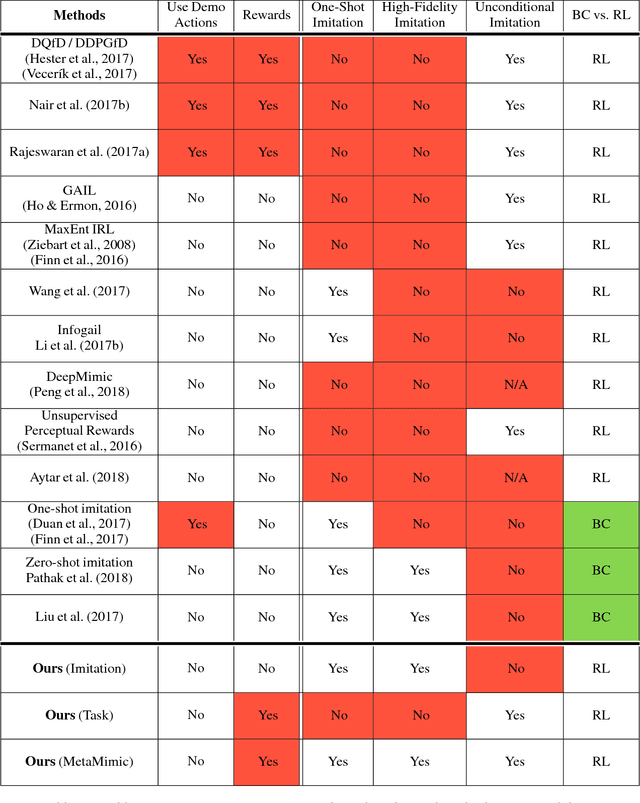
Abstract:Humans are experts at high-fidelity imitation -- closely mimicking a demonstration, often in one attempt. Humans use this ability to quickly solve a task instance, and to bootstrap learning of new tasks. Achieving these abilities in autonomous agents is an open problem. In this paper, we introduce an off-policy RL algorithm (MetaMimic) to narrow this gap. MetaMimic can learn both (i) policies for high-fidelity one-shot imitation of diverse novel skills, and (ii) policies that enable the agent to solve tasks more efficiently than the demonstrators. MetaMimic relies on the principle of storing all experiences in a memory and replaying these to learn massive deep neural network policies by off-policy RL. This paper introduces, to the best of our knowledge, the largest existing neural networks for deep RL and shows that larger networks with normalization are needed to achieve one-shot high-fidelity imitation on a challenging manipulation task. The results also show that both types of policy can be learned from vision, in spite of the task rewards being sparse, and without access to demonstrator actions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge