Masaya Kinoshita
Real-time Multi-Plane Segmentation Based on GPU Accelerated High-Resolution 3D Voxel Mapping for Legged Robot Locomotion
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a real-time multi-plane segmentation method based on GPU-accelerated high-resolution 3D voxel mapping for legged robot locomotion. Existing online planar mapping approaches struggle to balance accuracy and computational efficiency: direct depth image segmentation from specific sensors suffers from poor temporal integration, height map-based methods cannot represent complex 3D structures like overhangs, and voxel-based plane segmentation remains unexplored for real-time applications. To address these limitations, we develop a novel framework that integrates vertex-based connected component labeling with random sample consensus based plane detection and convex hull, leveraging GPU parallel computing to rapidly extract planar regions from point clouds accumulated in high-resolution 3D voxel maps. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves fast and accurate 3D multi-plane segmentation at over 30 Hz update rate even at a resolution of 0.01 m, enabling the detected planes to be utilized in real time for locomotion tasks. Furthermore, we validate the effectiveness of our approach through experiments in both simulated environments and physical legged robot platforms, confirming robust locomotion performance when considering 3D planar structures.
Learning Bipedal Locomotion on Gear-Driven Humanoid Robot Using Foot-Mounted IMUs
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:Sim-to-real reinforcement learning (RL) for humanoid robots with high-gear ratio actuators remains challenging due to complex actuator dynamics and the absence of torque sensors. To address this, we propose a novel RL framework leveraging foot-mounted inertial measurement units (IMUs). Instead of pursuing detailed actuator modeling and system identification, we utilize foot-mounted IMU measurements to enhance rapid stabilization capabilities over challenging terrains. Additionally, we propose symmetric data augmentation dedicated to the proposed observation space and random network distillation to enhance bipedal locomotion learning over rough terrain. We validate our approach through hardware experiments on a miniature-sized humanoid EVAL-03 over a variety of environments. The experimental results demonstrate that our method improves rapid stabilization capabilities over non-rigid surfaces and sudden environmental transitions.
Constraints as Rewards: Reinforcement Learning for Robots without Reward Functions
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning has become an essential algorithm for generating complex robotic behaviors. However, to learn such behaviors, it is necessary to design a reward function that describes the task, which often consists of multiple objectives that needs to be balanced. This tuning process is known as reward engineering and typically involves extensive trial-and-error. In this paper, to avoid this trial-and-error process, we propose the concept of Constraints as Rewards (CaR). CaR formulates the task objective using multiple constraint functions instead of a reward function and solves a reinforcement learning problem with constraints using the Lagrangian-method. By adopting this approach, different objectives are automatically balanced, because Lagrange multipliers serves as the weights among the objectives. In addition, we will demonstrate that constraints, expressed as inequalities, provide an intuitive interpretation of the optimization target designed for the task. We apply the proposed method to the standing-up motion generation task of a six-wheeled-telescopic-legged robot and demonstrate that the proposed method successfully acquires the target behavior, even though it is challenging to learn with manually designed reward functions.
Development of a Compact Robust Passive Transformable Omni-Ball for Enhanced Step-Climbing and Vibration Reduction
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces the Passive Transformable Omni-Ball (PTOB), an advanced omnidirectional wheel engineered to enhance step-climbing performance, incorporate built-in actuators, diminish vibrations, and fortify structural integrity. By modifying the omni-ball's structure from two to three segments, we have achieved improved in-wheel actuation and a reduction in vibrational feedback. Additionally, we have implemented a sliding mechanism in the follower wheels to boost the wheel's step-climbing abilities. A prototype with a 127 mm diameter PTOB was constructed, which confirmed its functionality for omnidirectional movement and internal actuation. Compared to a traditional omni-wheel, the PTOB demonstrated a comparable level of vibration while offering superior capabilities. Extensive testing in varied settings showed that the PTOB can adeptly handle step obstacles up to 45 mm, equivalent to 35 $\%$ of the wheel's diameter, in both the forward and lateral directions. The PTOB showcased robust construction and proved to be versatile in navigating through environments with diverse obstacles.
Extrinsic Calibration of Multiple LiDARs for a Mobile Robot based on Floor Plane And Object Segmentation
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:Mobile robots equipped with multiple light detection and ranging (LiDARs) and capable of recognizing their surroundings are increasing due to the minitualization and cost reduction of LiDAR. This paper proposes a target-less extrinsic calibration method of multiple LiDARs with non-overlapping field of view (FoV). The proposed method uses accumulated point clouds of floor plane and objects while in motion. It enables accurate calibration with challenging configuration of LiDARs that directed towards the floor plane, caused by biased feature values. Additionally, the method includes a noise removal module that considers the scanning pattern to address bleeding points, which are noises of significant source of error in point cloud alignment using high-density LiDARs. Evaluations through simulation demonstrate that the proposed method achieved higher accuracy extrinsic calibration with two and four LiDARs than conventional methods, regardless type of objects. Furthermore, the experiments using a real mobile robot has shown that our proposed noise removal module can eliminate noise more precisely than conventional methods, and the estimated extrinsic parameters have successfully created consistent 3D maps.
Versatile Telescopic-Wheeled-Legged Locomotion of Tachyon 3 via Full-Centroidal Nonlinear Model Predictive Control
Dec 14, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) toward versatile motion generation for the telescopic-wheeled-legged robot Tachyon 3, the unique hardware structure of which poses challenges in control and motion planning. We apply the full-centroidal NMPC formulation with dedicated constraints that can capture the accurate kinematics and dynamics of Tachyon 3. We have developed a control pipeline that includes an internal state integrator to apply NMPC to Tachyon 3, the actuators of which employ high-gain position-controllers. We conducted simulation and hardware experiments on the perceptive locomotion of Tachyon 3 over structured terrains and demonstrated that the proposed method can achieve smooth and dynamic motion generation under harsh physical and environmental constraints.
Real-time Perceptive Motion Control using Control Barrier Functions with Analytical Smoothing for Six-Wheeled-Telescopic-Legged Robot Tachyon 3
Oct 18, 2023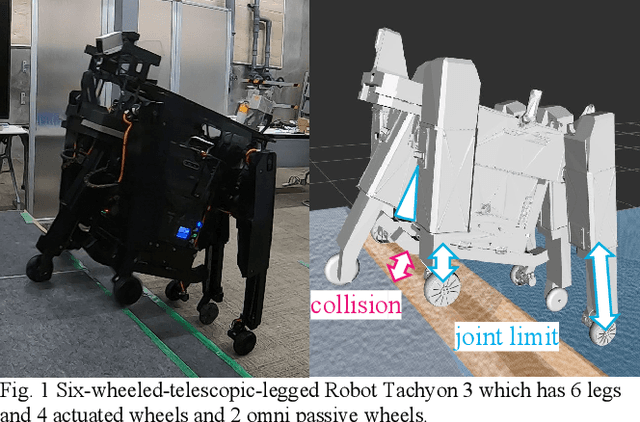
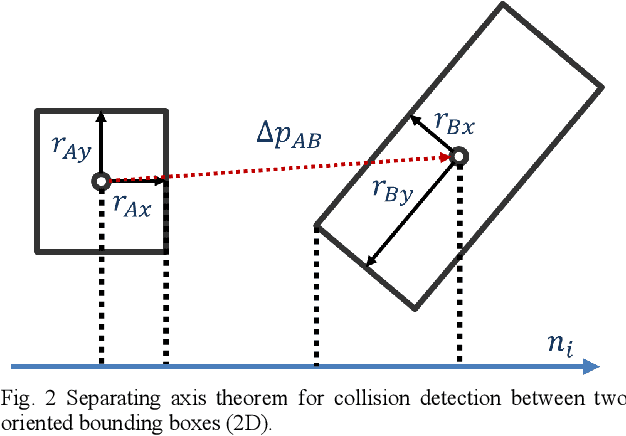
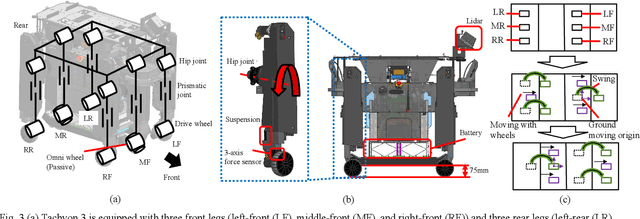
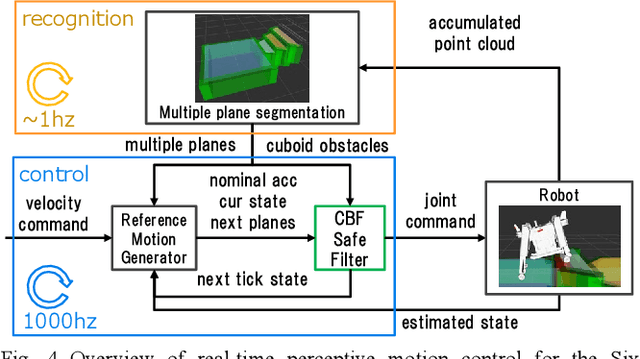
Abstract:To achieve safe legged locomotion, it is important to generate motion in real-time considering various constraints in robots and environments. In this study, we propose a lightweight real-time perspective motion control system for the newly developed six-wheeled-telescopic-legged robot, Tachyon 3. In the proposed method, analytically smoothed constraints including Smooth Separating Axis Theorem (Smooth SAT) as a novel higher order differentiable collision detection for 3D shapes is applied to the Control Barrier Function (CBF). The proposed system integrating the CBF achieves online motion generation in a short control cycle of 1 ms that satisfies joint limitations, environmental collision avoidance and safe convex foothold constraints. The efficiency of Smooth SAT is shown from the collision detection time of 1 us or less and the CBF constraint computation time for Tachyon3 of several us. Furthermore, the effectiveness of the proposed system is verified through the stair-climbing motion, integrating online recognition in a simulation and a real machine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge