Martina G. Vilas
The Computational Complexity of Circuit Discovery for Inner Interpretability
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Many proposed applications of neural networks in machine learning, cognitive/brain science, and society hinge on the feasibility of inner interpretability via circuit discovery. This calls for empirical and theoretical explorations of viable algorithmic options. Despite advances in the design and testing of heuristics, there are concerns about their scalability and faithfulness at a time when we lack understanding of the complexity properties of the problems they are deployed to solve. To address this, we study circuit discovery with classical and parameterized computational complexity theory: (1) we describe a conceptual scaffolding to reason about circuit finding queries in terms of affordances for description, explanation, prediction and control; (2) we formalize a comprehensive set of queries that capture mechanistic explanation, and propose a formal framework for their analysis; (3) we use it to settle the complexity of many query variants and relaxations of practical interest on multi-layer perceptrons (part of, e.g., transformers). Our findings reveal a challenging complexity landscape. Many queries are intractable (NP-hard, $\Sigma^p_2$-hard), remain fixed-parameter intractable (W[1]-hard) when constraining model/circuit features (e.g., depth), and are inapproximable under additive, multiplicative, and probabilistic approximation schemes. To navigate this landscape, we prove there exist transformations to tackle some of these hard problems (NP- vs. $\Sigma^p_2$-complete) with better-understood heuristics, and prove the tractability (PTIME) or fixed-parameter tractability (FPT) of more modest queries which retain useful affordances. This framework allows us to understand the scope and limits of interpretability queries, explore viable options, and compare their resource demands among existing and future architectures.
Limited but consistent gains in adversarial robustness by co-training object recognition models with human EEG
Sep 05, 2024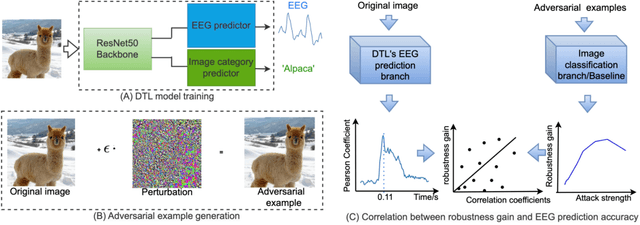
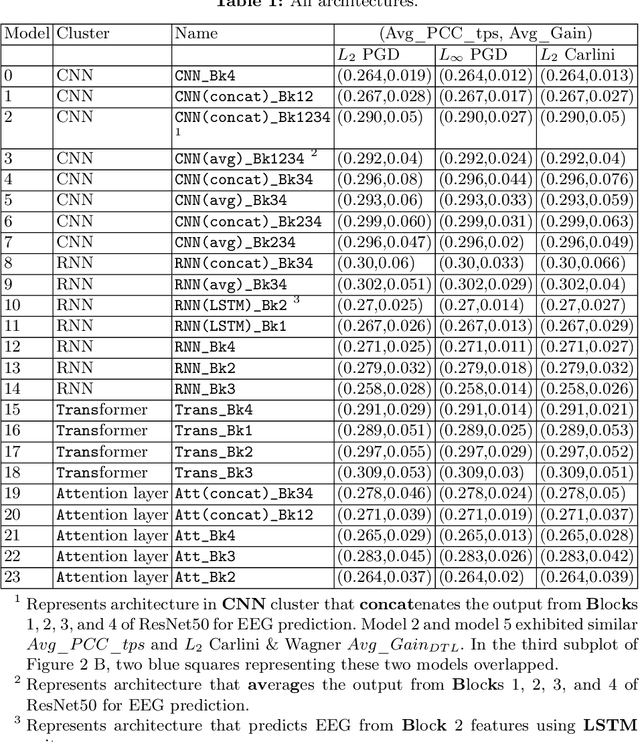
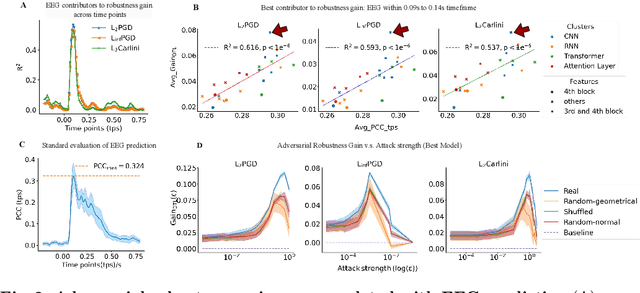
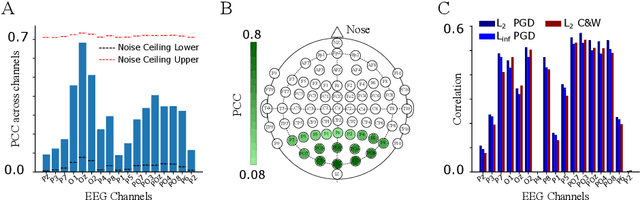
Abstract:In contrast to human vision, artificial neural networks (ANNs) remain relatively susceptible to adversarial attacks. To address this vulnerability, efforts have been made to transfer inductive bias from human brains to ANNs, often by training the ANN representations to match their biological counterparts. Previous works relied on brain data acquired in rodents or primates using invasive techniques, from specific regions of the brain, under non-natural conditions (anesthetized animals), and with stimulus datasets lacking diversity and naturalness. In this work, we explored whether aligning model representations to human EEG responses to a rich set of real-world images increases robustness to ANNs. Specifically, we trained ResNet50-backbone models on a dual task of classification and EEG prediction; and evaluated their EEG prediction accuracy and robustness to adversarial attacks. We observed significant correlation between the networks' EEG prediction accuracy, often highest around 100 ms post stimulus onset, and their gains in adversarial robustness. Although effect size was limited, effects were consistent across different random initializations and robust for architectural variants. We further teased apart the data from individual EEG channels and observed strongest contribution from electrodes in the parieto-occipital regions. The demonstrated utility of human EEG for such tasks opens up avenues for future efforts that scale to larger datasets under diverse stimuli conditions with the promise of stronger effects.
Position Paper: An Inner Interpretability Framework for AI Inspired by Lessons from Cognitive Neuroscience
Jun 03, 2024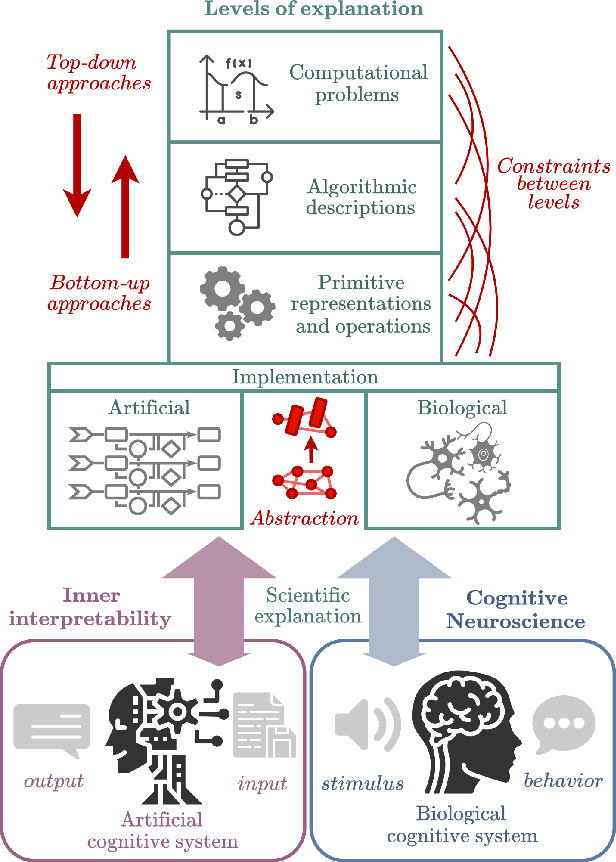
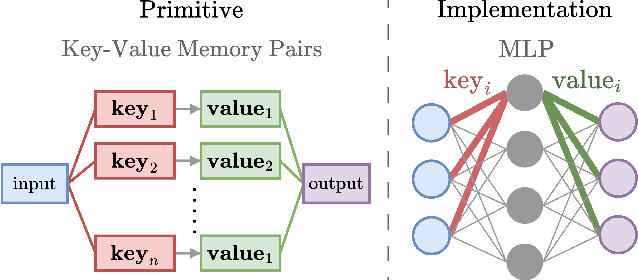
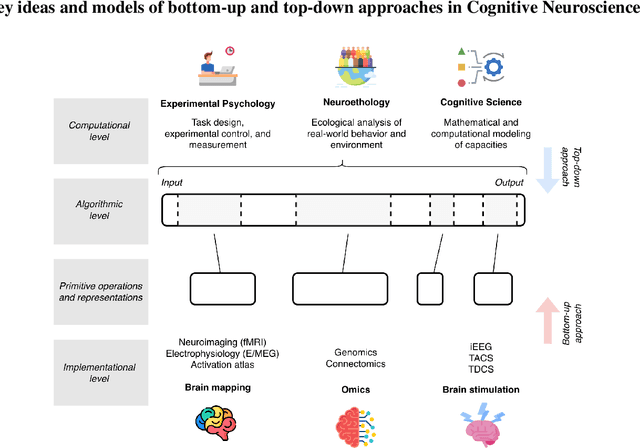
Abstract:Inner Interpretability is a promising emerging field tasked with uncovering the inner mechanisms of AI systems, though how to develop these mechanistic theories is still much debated. Moreover, recent critiques raise issues that question its usefulness to advance the broader goals of AI. However, it has been overlooked that these issues resemble those that have been grappled with in another field: Cognitive Neuroscience. Here we draw the relevant connections and highlight lessons that can be transferred productively between fields. Based on these, we propose a general conceptual framework and give concrete methodological strategies for building mechanistic explanations in AI inner interpretability research. With this conceptual framework, Inner Interpretability can fend off critiques and position itself on a productive path to explain AI systems.
Analyzing Vision Transformers for Image Classification in Class Embedding Space
Oct 29, 2023



Abstract:Despite the growing use of transformer models in computer vision, a mechanistic understanding of these networks is still needed. This work introduces a method to reverse-engineer Vision Transformers trained to solve image classification tasks. Inspired by previous research in NLP, we demonstrate how the inner representations at any level of the hierarchy can be projected onto the learned class embedding space to uncover how these networks build categorical representations for their predictions. We use our framework to show how image tokens develop class-specific representations that depend on attention mechanisms and contextual information, and give insights on how self-attention and MLP layers differentially contribute to this categorical composition. We additionally demonstrate that this method (1) can be used to determine the parts of an image that would be important for detecting the class of interest, and (2) exhibits significant advantages over traditional linear probing approaches. Taken together, our results position our proposed framework as a powerful tool for mechanistic interpretability and explainability research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge