Sari Sadiya
Efficient Unsupervised Shortcut Learning Detection and Mitigation in Transformers
Jan 01, 2025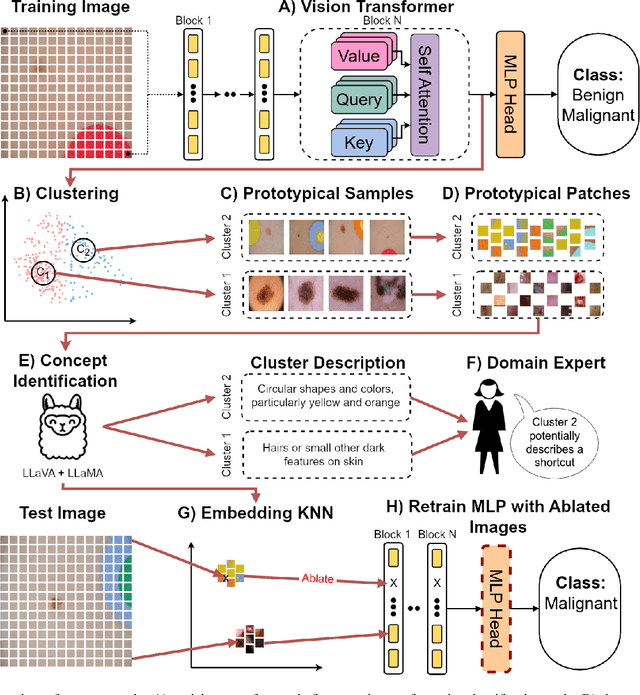
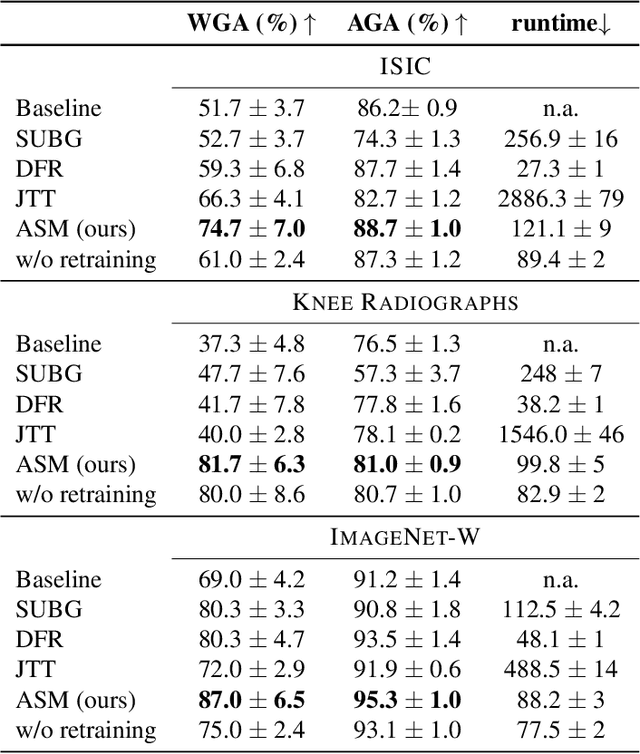

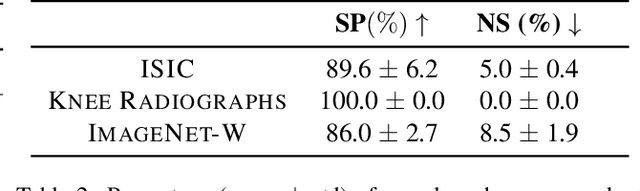
Abstract:Shortcut learning, i.e., a model's reliance on undesired features not directly relevant to the task, is a major challenge that severely limits the applications of machine learning algorithms, particularly when deploying them to assist in making sensitive decisions, such as in medical diagnostics. In this work, we leverage recent advancements in machine learning to create an unsupervised framework that is capable of both detecting and mitigating shortcut learning in transformers. We validate our method on multiple datasets. Results demonstrate that our framework significantly improves both worst-group accuracy (samples misclassified due to shortcuts) and average accuracy, while minimizing human annotation effort. Moreover, we demonstrate that the detected shortcuts are meaningful and informative to human experts, and that our framework is computationally efficient, allowing it to be run on consumer hardware.
Limited but consistent gains in adversarial robustness by co-training object recognition models with human EEG
Sep 05, 2024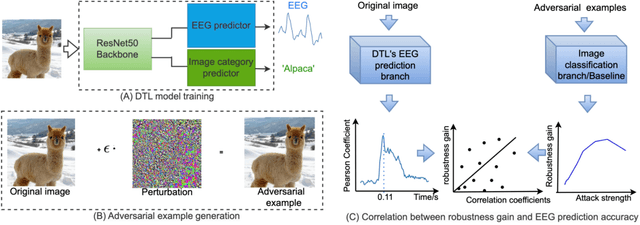
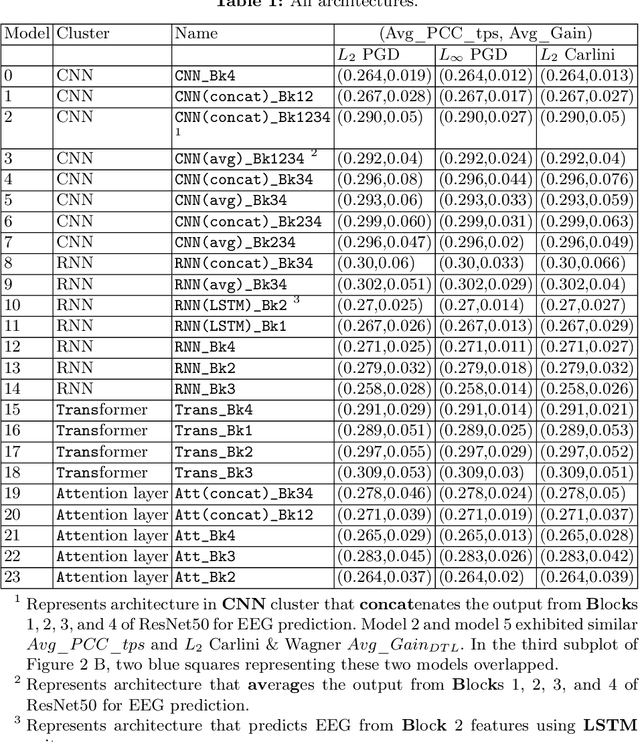
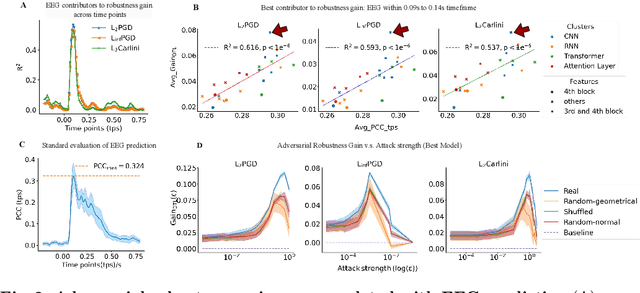
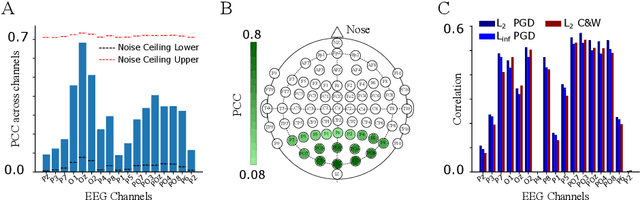
Abstract:In contrast to human vision, artificial neural networks (ANNs) remain relatively susceptible to adversarial attacks. To address this vulnerability, efforts have been made to transfer inductive bias from human brains to ANNs, often by training the ANN representations to match their biological counterparts. Previous works relied on brain data acquired in rodents or primates using invasive techniques, from specific regions of the brain, under non-natural conditions (anesthetized animals), and with stimulus datasets lacking diversity and naturalness. In this work, we explored whether aligning model representations to human EEG responses to a rich set of real-world images increases robustness to ANNs. Specifically, we trained ResNet50-backbone models on a dual task of classification and EEG prediction; and evaluated their EEG prediction accuracy and robustness to adversarial attacks. We observed significant correlation between the networks' EEG prediction accuracy, often highest around 100 ms post stimulus onset, and their gains in adversarial robustness. Although effect size was limited, effects were consistent across different random initializations and robust for architectural variants. We further teased apart the data from individual EEG channels and observed strongest contribution from electrodes in the parieto-occipital regions. The demonstrated utility of human EEG for such tasks opens up avenues for future efforts that scale to larger datasets under diverse stimuli conditions with the promise of stronger effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge