Marloes Arts
Internal-Coordinate Density Modelling of Protein Structure: Covariance Matters
Feb 27, 2023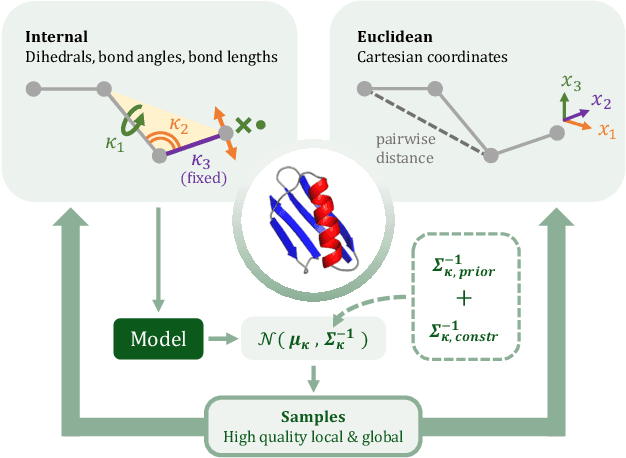
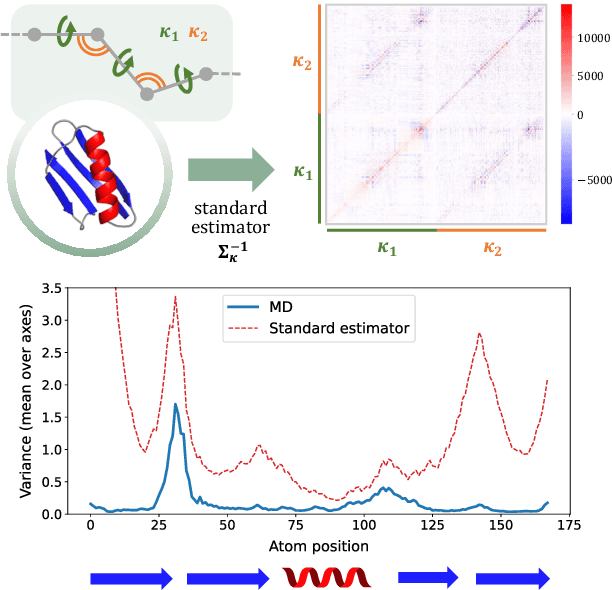
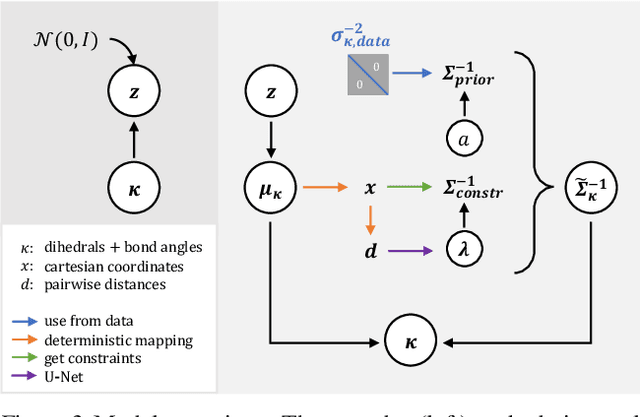
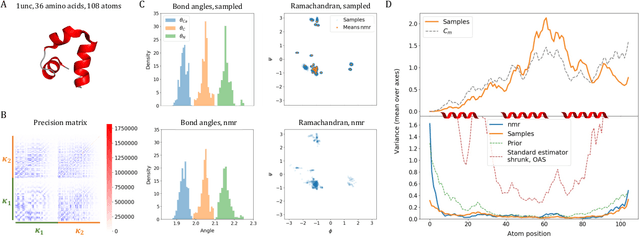
Abstract:After the recent ground-breaking advances in protein structure prediction, one of the remaining challenges in protein machine learning is to reliably predict distributions of structural states. Parametric models of small-scale fluctuations are difficult to fit due to complex covariance structures between degrees of freedom in the protein chain, often causing models to either violate local or global structural constraints. In this paper, we present a new strategy for modelling protein densities in internal coordinates, which uses constraints in 3D space to induce covariance structure between the internal degrees of freedom. We illustrate the potential of the procedure by constructing a variational autoencoder with full covariance output induced by the constraints implied by the conditional mean in 3D, and demonstrate that our approach makes it possible to scale density models of internal coordinates to full-size proteins.
Two for One: Diffusion Models and Force Fields for Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics
Feb 01, 2023Abstract:Coarse-grained (CG) molecular dynamics enables the study of biological processes at temporal and spatial scales that would be intractable at an atomistic resolution. However, accurately learning a CG force field remains a challenge. In this work, we leverage connections between score-based generative models, force fields and molecular dynamics to learn a CG force field without requiring any force inputs during training. Specifically, we train a diffusion generative model on protein structures from molecular dynamics simulations, and we show that its score function approximates a force field that can directly be used to simulate CG molecular dynamics. While having a vastly simplified training setup compared to previous work, we demonstrate that our approach leads to improved performance across several small- to medium-sized protein simulations, reproducing the CG equilibrium distribution, and preserving dynamics of all-atom simulations such as protein folding events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge