Marika Lekakou
A small Griko-Italian speech translation corpus
Jul 27, 2018



Abstract:This paper presents an extension to a very low-resource parallel corpus collected in an endangered language, Griko, making it useful for computational research. The corpus consists of 330 utterances (about 20 minutes of speech) which have been transcribed and translated in Italian, with annotations for word-level speech-to-transcription and speech-to-translation alignments. The corpus also includes morphosyntactic tags and word-level glosses. Applying an automatic unit discovery method, pseudo-phones were also generated. We detail how the corpus was collected, cleaned and processed, and we illustrate its use on zero-resource tasks by presenting some baseline results for the task of speech-to-translation alignment and unsupervised word discovery. The dataset is available online, aiming to encourage replicability and diversity in computational language documentation experiments.
Part-of-Speech Tagging on an Endangered Language: a Parallel Griko-Italian Resource
Jun 11, 2018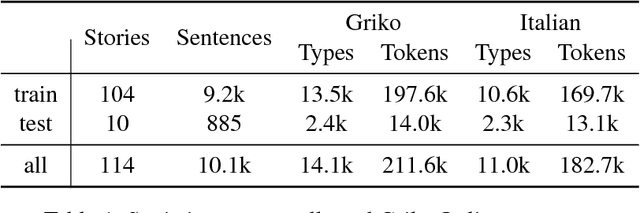

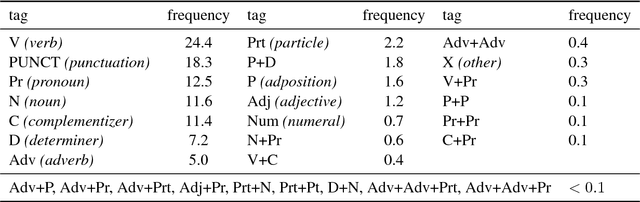

Abstract:Most work on part-of-speech (POS) tagging is focused on high resource languages, or examines low-resource and active learning settings through simulated studies. We evaluate POS tagging techniques on an actual endangered language, Griko. We present a resource that contains 114 narratives in Griko, along with sentence-level translations in Italian, and provides gold annotations for the test set. Based on a previously collected small corpus, we investigate several traditional methods, as well as methods that take advantage of monolingual data or project cross-lingual POS tags. We show that the combination of a semi-supervised method with cross-lingual transfer is more appropriate for this extremely challenging setting, with the best tagger achieving an accuracy of 72.9%. With an applied active learning scheme, which we use to collect sentence-level annotations over the test set, we achieve improvements of more than 21 percentage points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge