Antonis Anastasopoulos
The ML-SUPERB 2.0 Challenge: Towards Inclusive ASR Benchmarking for All Language Varieties
Sep 08, 2025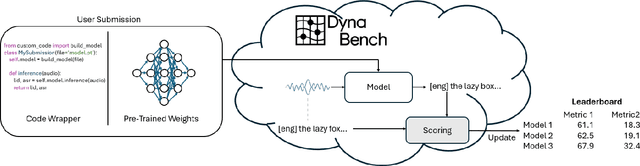
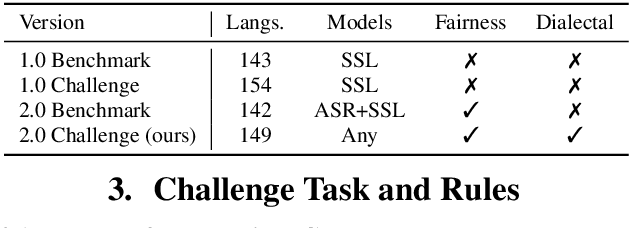
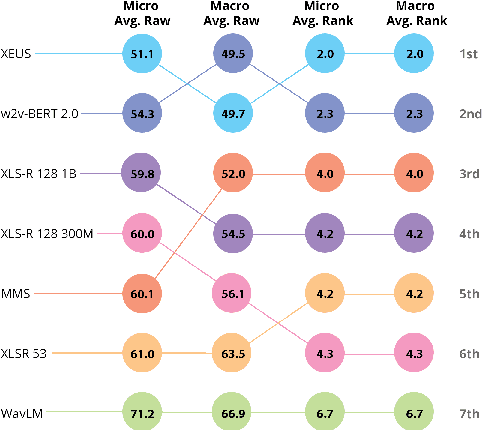
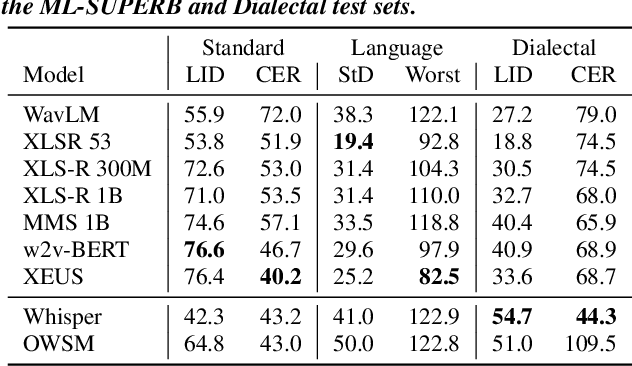
Abstract:Recent improvements in multilingual ASR have not been equally distributed across languages and language varieties. To advance state-of-the-art (SOTA) ASR models, we present the Interspeech 2025 ML-SUPERB 2.0 Challenge. We construct a new test suite that consists of data from 200+ languages, accents, and dialects to evaluate SOTA multilingual speech models. The challenge also introduces an online evaluation server based on DynaBench, allowing for flexibility in model design and architecture for participants. The challenge received 5 submissions from 3 teams, all of which outperformed our baselines. The best-performing submission achieved an absolute improvement in LID accuracy of 23% and a reduction in CER of 18% when compared to the best baseline on a general multilingual test set. On accented and dialectal data, the best submission obtained 30.2% lower CER and 15.7% higher LID accuracy, showing the importance of community challenges in making speech technologies more inclusive.
When Being Unseen from mBERT is just the Beginning: Handling New Languages With Multilingual Language Models
Oct 24, 2020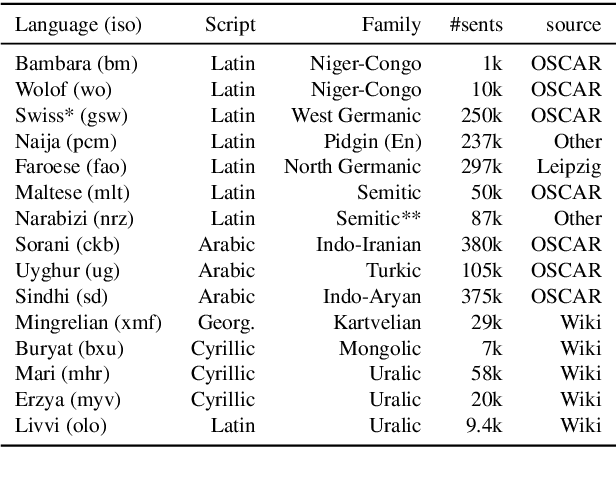
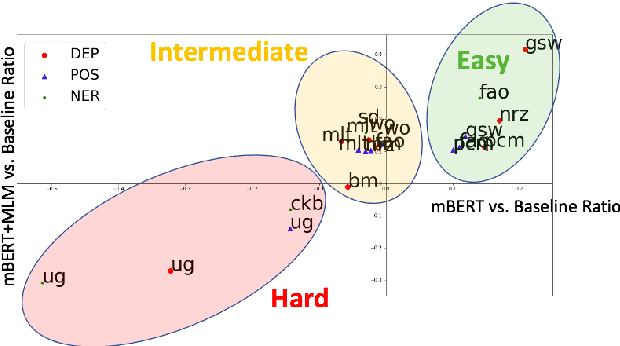
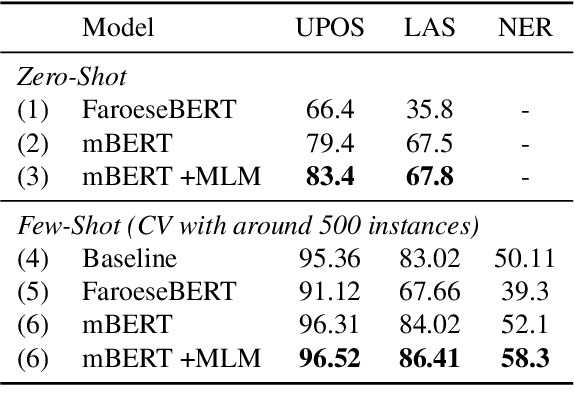
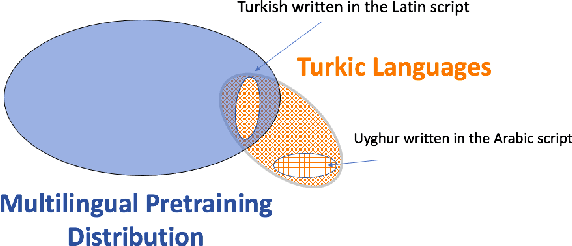
Abstract:Transfer learning based on pretraining language models on a large amount of raw data has become a new norm to reach state-of-the-art performance in NLP. Still, it remains unclear how this approach should be applied for unseen languages that are not covered by any available large-scale multilingual language model and for which only a small amount of raw data is generally available. In this work, by comparing multilingual and monolingual models, we show that such models behave in multiple ways on unseen languages. Some languages greatly benefit from transfer learning and behave similarly to closely related high resource languages whereas others apparently do not. Focusing on the latter, we show that this failure to transfer is largely related to the impact of the script used to write such languages. Transliterating those languages improves very significantly the ability of large-scale multilingual language models on downstream tasks.
Leveraging translations for speech transcription in low-resource settings
Jun 11, 2018



Abstract:Recently proposed data collection frameworks for endangered language documentation aim not only to collect speech in the language of interest, but also to collect translations into a high-resource language that will render the collected resource interpretable. We focus on this scenario and explore whether we can improve transcription quality under these extremely low-resource settings with the assistance of text translations. We present a neural multi-source model and evaluate several variations of it on three low-resource datasets. We find that our multi-source model with shared attention outperforms the baselines, reducing transcription character error rate by up to 12.3%.
Part-of-Speech Tagging on an Endangered Language: a Parallel Griko-Italian Resource
Jun 11, 2018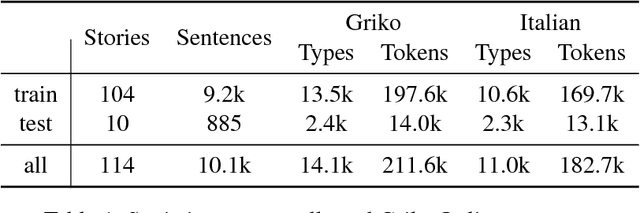

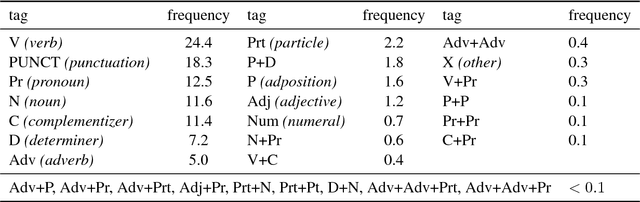

Abstract:Most work on part-of-speech (POS) tagging is focused on high resource languages, or examines low-resource and active learning settings through simulated studies. We evaluate POS tagging techniques on an actual endangered language, Griko. We present a resource that contains 114 narratives in Griko, along with sentence-level translations in Italian, and provides gold annotations for the test set. Based on a previously collected small corpus, we investigate several traditional methods, as well as methods that take advantage of monolingual data or project cross-lingual POS tags. We show that the combination of a semi-supervised method with cross-lingual transfer is more appropriate for this extremely challenging setting, with the best tagger achieving an accuracy of 72.9%. With an applied active learning scheme, which we use to collect sentence-level annotations over the test set, we achieve improvements of more than 21 percentage points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge